Node organizing method and resource discovery method in wireless P2P network
A peer-to-peer network and discovery method technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as poor performance and inability to complete simultaneous optimization of peer-to-peer networks, and achieve the effects of reducing the average number of hops, saving maintenance costs, and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
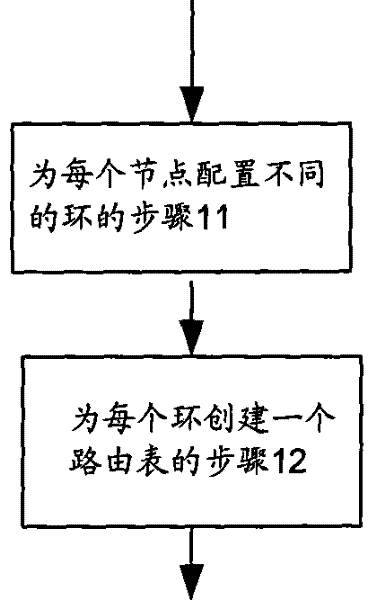
[0034] like figure 1 As shown, a method for organizing nodes in a wireless peer-to-peer network includes:
[0035] Step 11 of configuring different rings for each node: each node is included in at least one ring whose index value is the hash value of the node’s IP address, that is, each node belongs to multiple rings, but each ring does not necessarily contain All nodes in the network;
[0036] Step 12 of creating a routing table for each ring: Each node creates a routing table for each ring including its own node, and each routing table stores the IP addresses of nodes other than its own node in the ring and the IP addresses of each node hash value.
[0037] like Figure 6 As shown, let the hash space be {0, 1, ..., 2 m -1}, where m is an even number, and the index values of all node IP address hash values from small to large are used to configure all corresponding nodes into a row and column of 2 m / 2 ×2 m / 2 The square matrix, that is, the nodes in each row and colu...
Embodiment 2
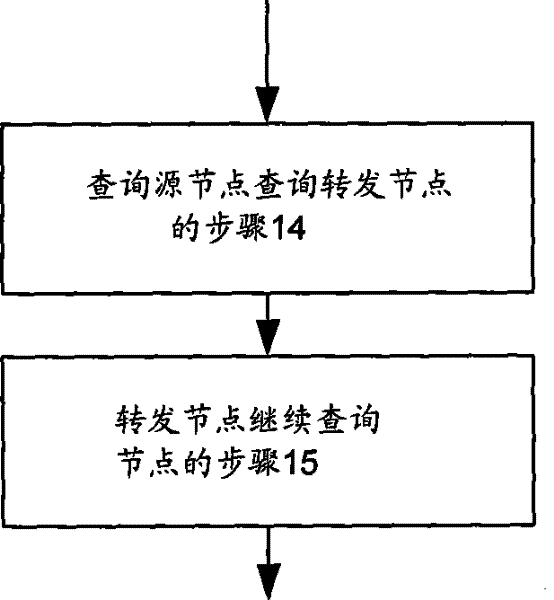
[0044] like figure 2 , Figure 6-10 As shown, a method for discovering resources in a wireless peer-to-peer network, which is based on the peer-to-peer network with node multi-ring configuration described in the first embodiment above, includes:
[0045] Step 14 of querying the source node and querying the forwarding node: the querying source node performs hash transformation on the resource keyword to be searched, and then queries the first forwarding node that is closest to the resource hash value in each routing table it has, that is, the first forwarding node that is the closest to the resource hash value. The node with the shortest path length between the destination nodes of the resource, where the path length between nodes can be obtained by comparing the hash value of the node IP address;
[0046] Step 15 where the forwarding node continues to query nodes: the first forwarding node continues to query the second forwarding node that is closest to the hash value of the...
Embodiment 3
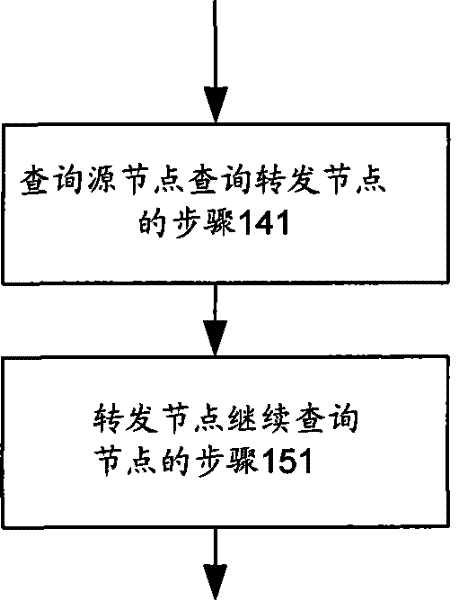
[0050] like image 3 As shown, a method for discovering resources in a wireless peer-to-peer network, when all the nodes are on the peer-to-peer network, it is based on the order of the IP address hash values of all nodes from small to large as described in the first embodiment above: The index value configures all corresponding nodes as a row and column of 2 m / 2 ×2 m / 2 matrix of peer-to-peer networks to choose n 1,1 arrive The straight-line path query node matrix main diagonal nodes as an example, including:
[0051] Step 141 of querying the source node to query the forwarding node: as Figure 6-10 As shown, set the query source node as node n in the first row and column 1,1 , the destination node corresponding to the resource keyword hash value is n d_1,d_2 When , query the source node n 1,1 Query each routing table it has according to the hash value of the resource keyword, and select the row and column numbers that are all smaller than the destination node n d_1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com