Flameproof union fabric for chair upholstery
一种交织织物、阻燃性的技术,应用在阻燃性交织织物领域,能够解决不能充分确保阻燃性等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
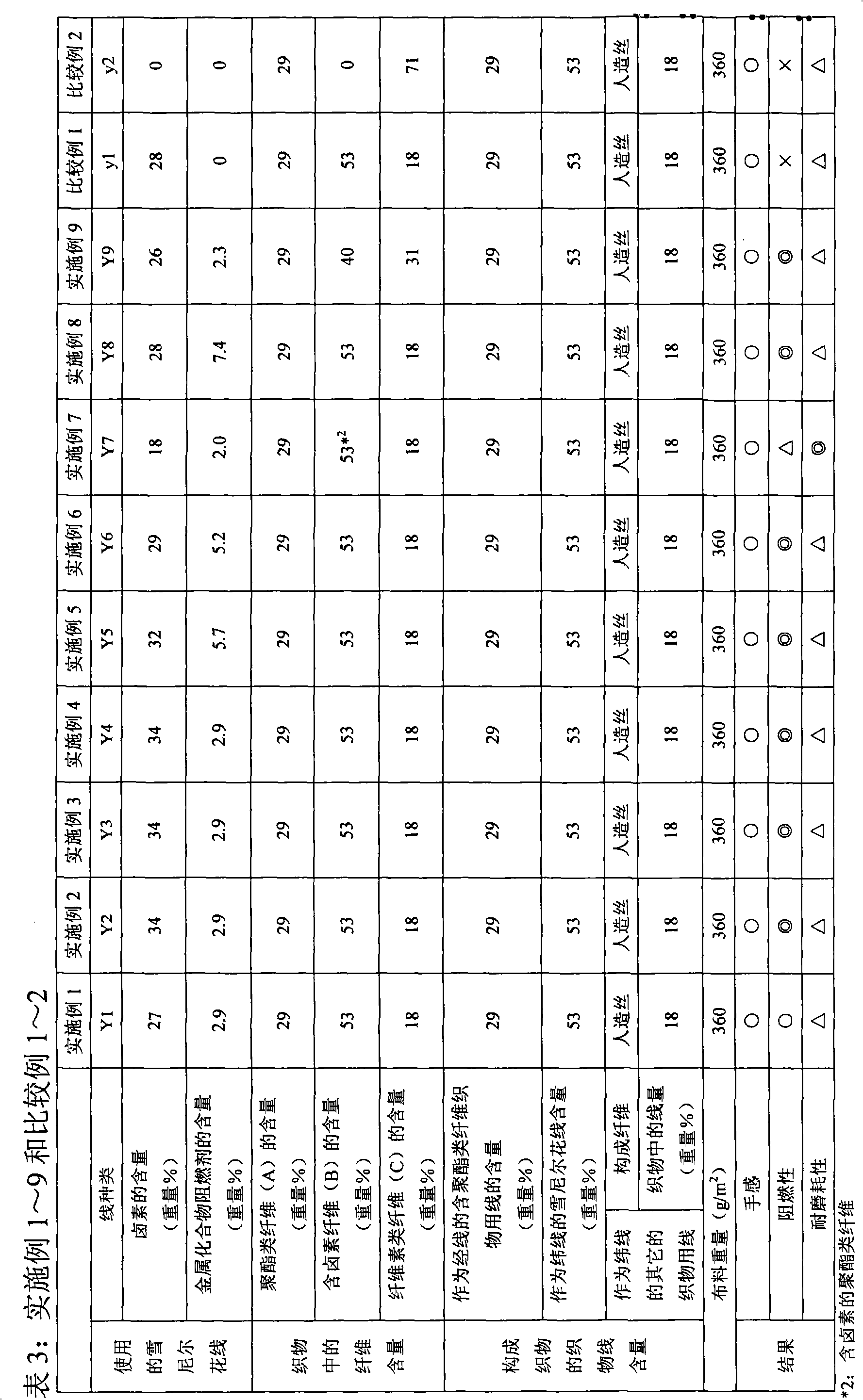
Embodiment 1~9 and comparative example 1~2
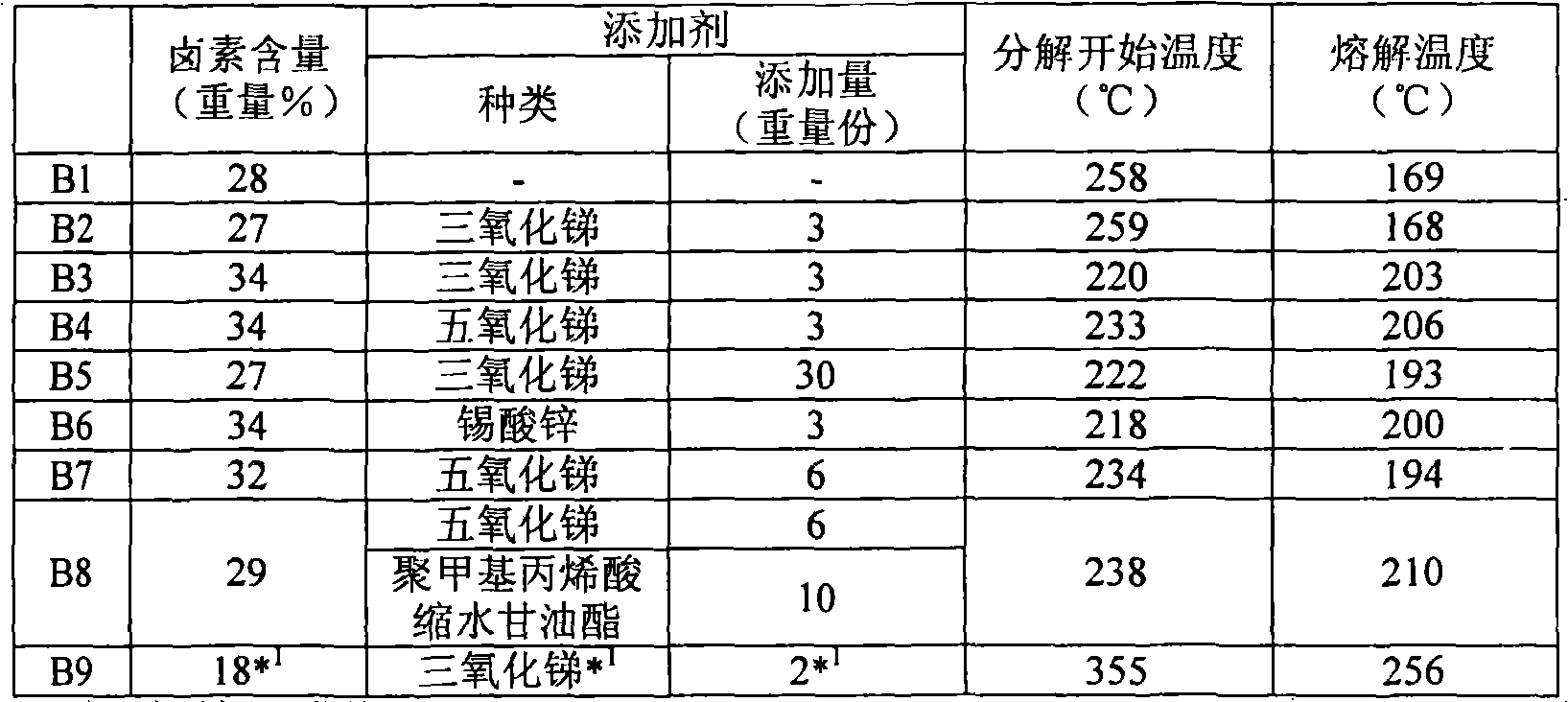
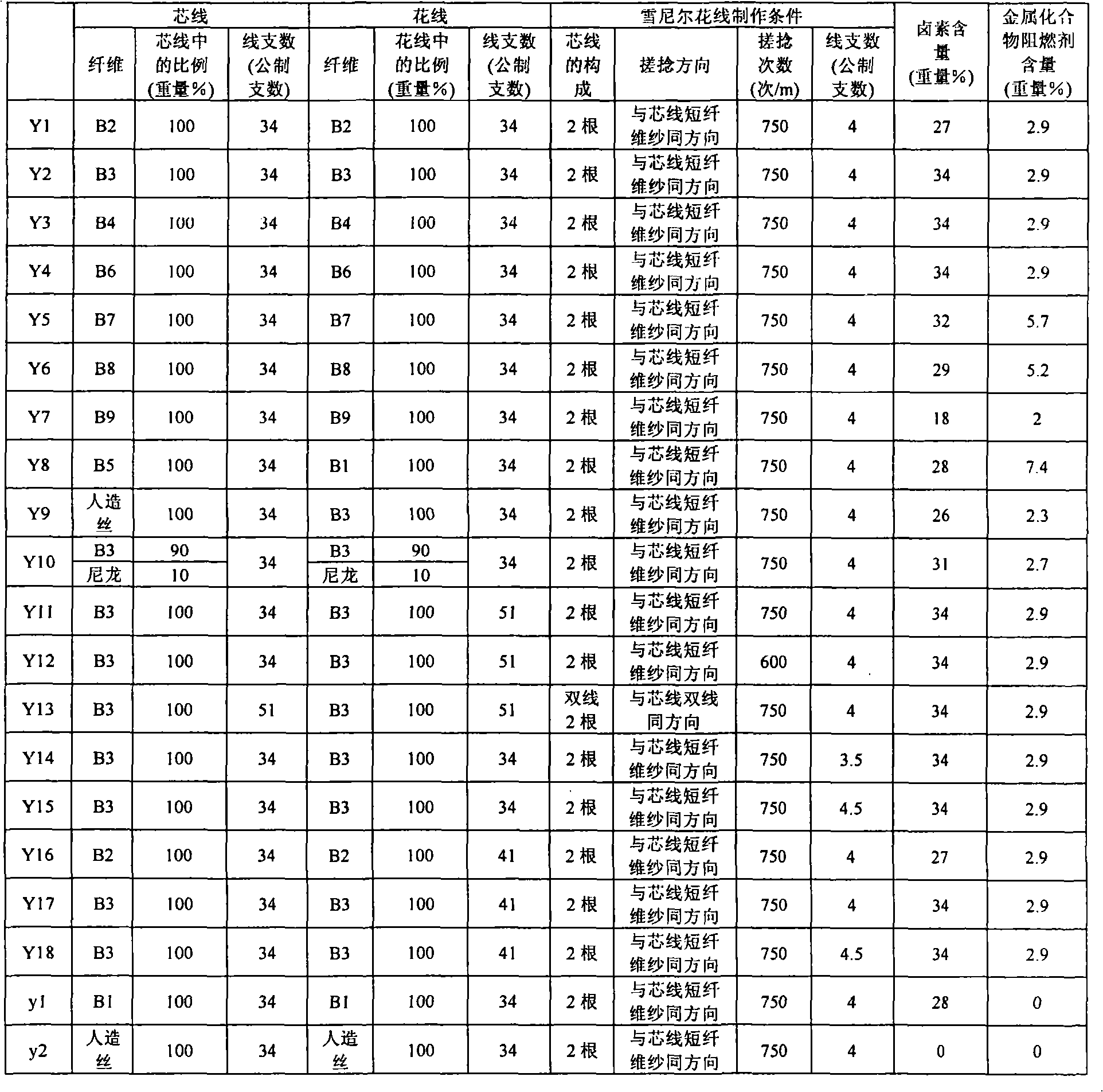
[0103] Use polyester wool type yarn (ウリリー) 60 metric count yarns as warps, so that it is 59 yarns / cm in the fabric. In addition, alternately use flame-retardant chenille yarns shown in Table 3 or non Flame-retardant chenille yarn and rayon 12 metric count staple fiber yarn are used as weft yarns to form a total of 14 yarns / cm in the fabric, and the above-mentioned chenille yarn is floated on the surface to make 5 pieces of satin weave fabrics . Afterwards, evaluation was performed with the side where the chenille threads floated on the surface as the surface side (or evaluation side), and the results are shown in Table 3.
[0104]
[0105] As shown in Table 3, the flame retardancy of the fabrics of Comparative Examples 1 and 2 was insufficient. The reason is that the amount of metal compound flame retardant in Comparative Example 1 is insufficient, and the content of halogen and metal compound flame retardant in Comparative Example 2 is insufficient.
Embodiment 10 and comparative example 6
[0113] The back side of the fabric made in embodiment 2 is coated with water-based acrylic latex, so that its dry weight is 20g / m 2 , and the dried product was referred to as Example 10. In addition, in the water-based acrylic latex solution, 75 parts by weight of antimony trioxide and 25 parts by weight of decabromodiphenyl ether were added relative to the solid content in the solution, and coated on the back of the fabric made in Comparative Example 5, Make it dry weight 40g / m 2 , and this product was referred to as Comparative Example 6. Table 5 shows their evaluation results. The numerical values of "fiber content in the fabric" and "fabric thread amount constituting the fabric" shown in Table 5 are relative to the total weight of the fabric including the coating weight of the above-mentioned water-based acrylic latex coated on the back of the fabric and dried. The numerical value of the weight.
[0114] Table 5: Embodiment 10, Comparative Example 6
[0115] ...
Embodiment 11~12
[0119] The number of wefts in Example 2 was changed to produce fabrics shown in Table 6. In Example 11, the flame-retardant chenille yarn shown in Table 6 and rayon 12 metric count staple fiber yarns are alternately used as wefts to form a total of 12 threads / cm. The flame-retardant chenille yarn shown in 6 and 12 metric count staple fiber yarns of rayon were used as weft yarns to form a total of 16 yarns / cm, and 5 pieces of satin weave fabrics were each produced. Table 6 shows their evaluation results.
[0120] Table 6: Examples 11-12
[0121]
[0122] As shown in Table 6, when the number of wefts of the fabric is changed to change the weight of the fabric, the wear resistance of the fabric changes, but the flame retardancy has no effect.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com