Temperature compensation rod and method for manufacturing multiplexing and de-multiplexing non-heat array wave guide grating
A technology of temperature compensation and waveguide grating, which is applied in the direction of wavelength division multiplexing system and optical waveguide coupling, can solve the problems of high device cost, inability to realize multiplexing and demultiplexing functions at the same time, large size, etc., and achieve good repeatability , low cost, small size effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
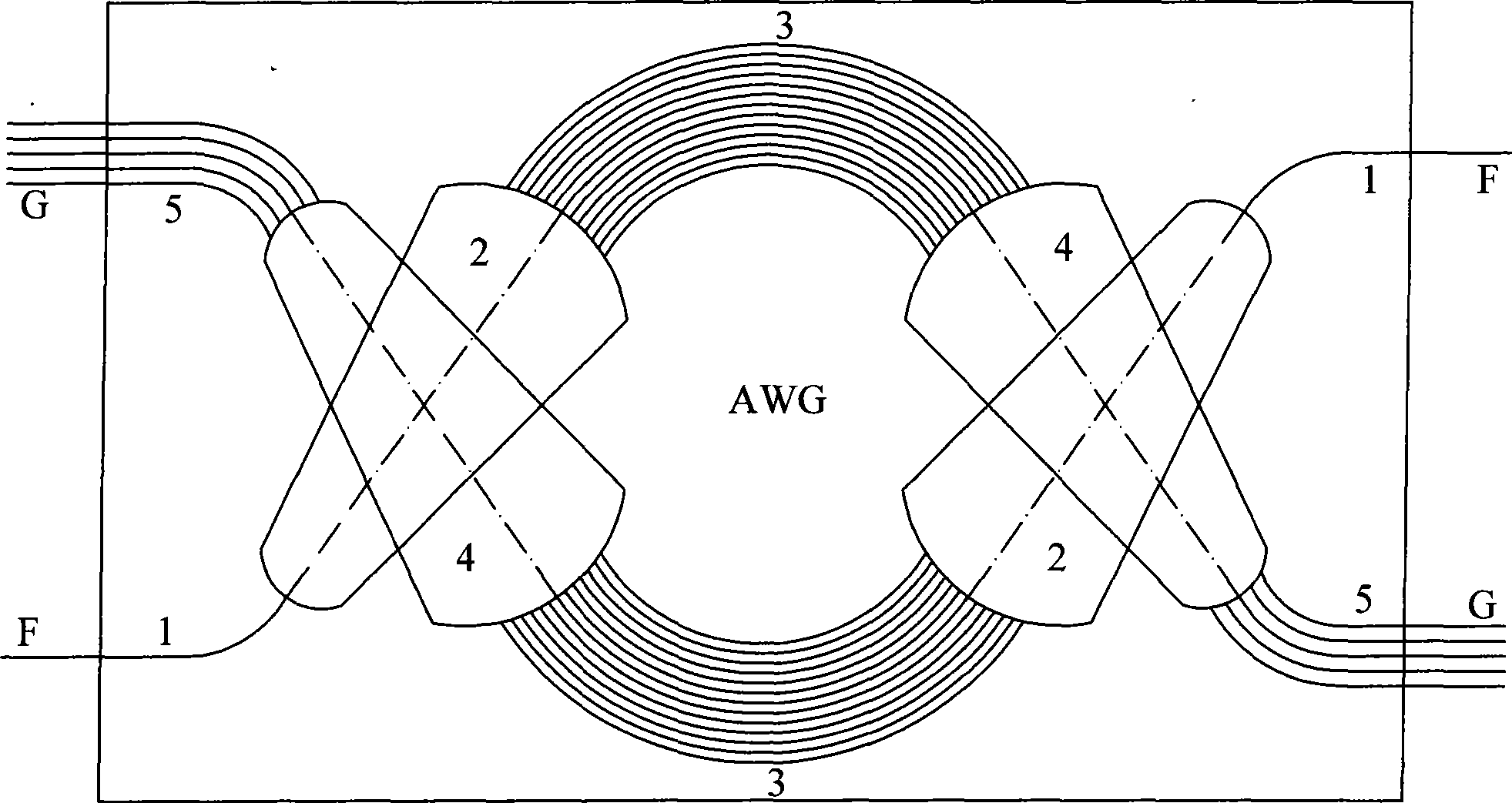
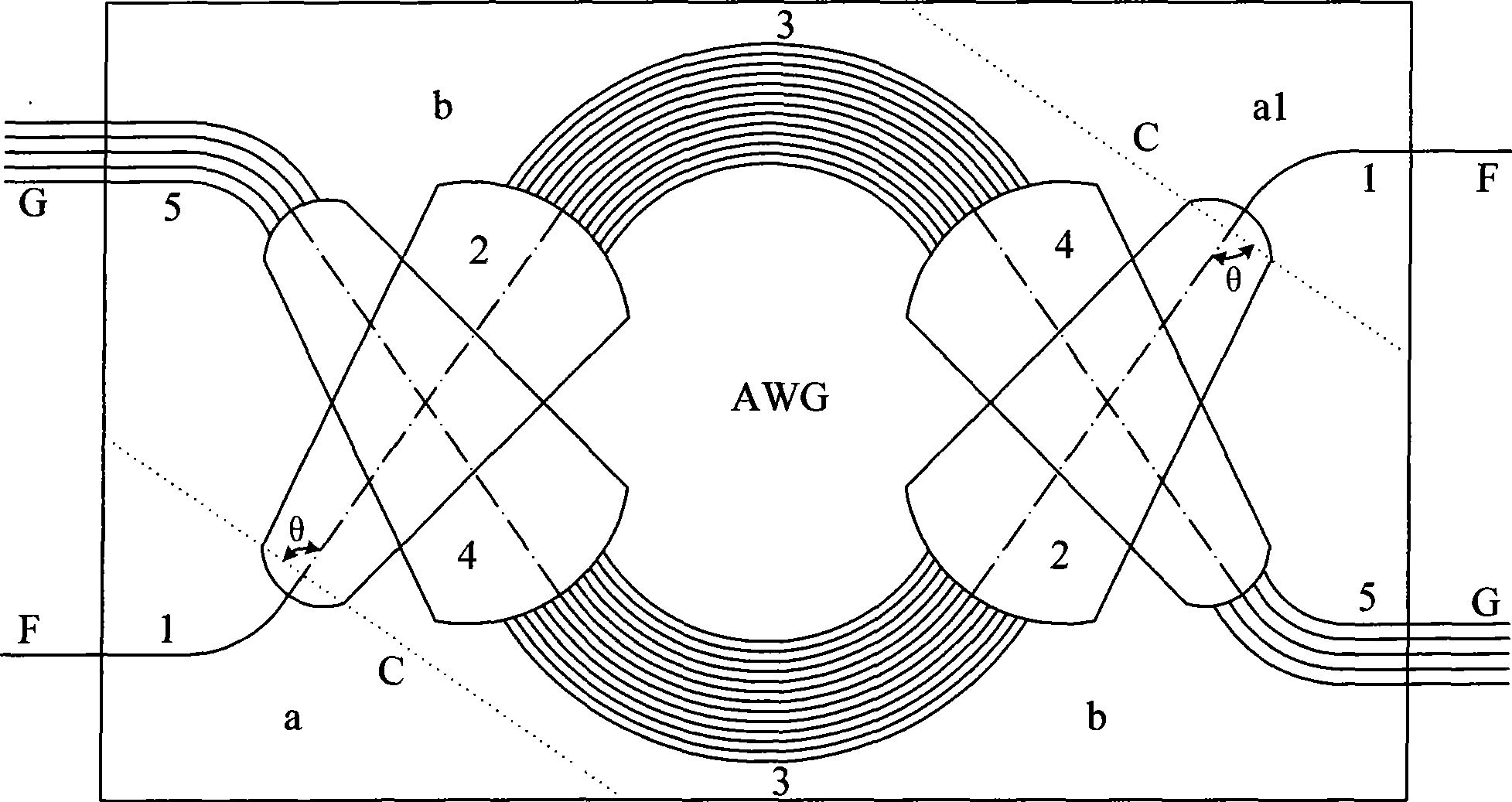
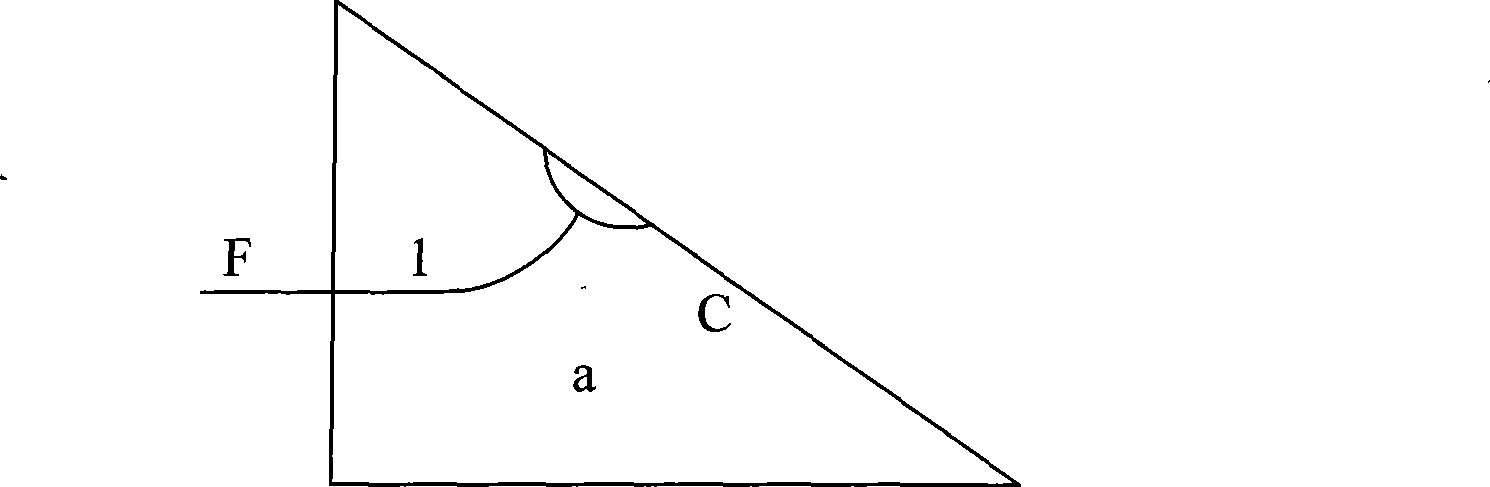
[0033] The temperature compensating rod and the method for manufacturing multiplexing and demultiplexing athermal arrayed waveguide gratings of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the drawings of the embodiments.
[0034] Such as Figure 7 , Figure 8 As shown, the temperature compensation rod of the present invention includes a rod body 8 and "I"-shaped structures 7 respectively formed at both ends of the rod body 8, wherein the upper end structure 7.2. There is a gap between 1 and the rod body 8, and the lower end structure 7.2.2 is integrally formed with the rod body 8; the upper structure 7.1.1 of the "I"-shaped structure 7 on the other side of the rod body 8 is integrated with the rod body Formed, and a gap is formed between the lower end structure 7.1.2 and the rod body 8. The middle parts 7.1 and 7.2 of the "I" shape have the characteristics of thin, long and high in size, so that they can produce elastic deformation in the thickn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com