Bio-medical amorphous titanium alloy and method for producing same
A biomedical and titanium alloy technology, applied in the field of titanium alloys, can solve problems such as cytotoxicity, neurotoxicity, and senile dementia, and achieve excellent corrosion resistance and reduce hazards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Biomedical amorphous alloy T17
[0051] The first step, titanium alloy raw material preparation
[0052] According to the atomic percentage, Ti is 79%, Zr is 7% and Si is 14%, and chemically pure grade Ti, Zr and Si are used as titanium alloy raw materials;
[0053] The second step, the preparation of titanium alloy ingot
[0054] Put the titanium alloy raw material prepared in the first step into the water-cooled copper crucible of a non-consumable vacuum electric arc furnace containing tungsten electrodes, and adjust the position of the tungsten electrode so that the distance between the front end of the tungsten electrode and the titanium alloy raw material particles in the water-cooled copper crucible is 0.5mm, close the furnace door and vent valve of the electric arc furnace, and evacuate to a temperature higher than 2×10 -2 Pa, and then filled with argon until the pressure of the furnace cavity is 0.06Pa, the electric arc furnace is started, and the arc current ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Biomedical amorphous alloy T17
[0059] The first step, titanium alloy raw material preparation
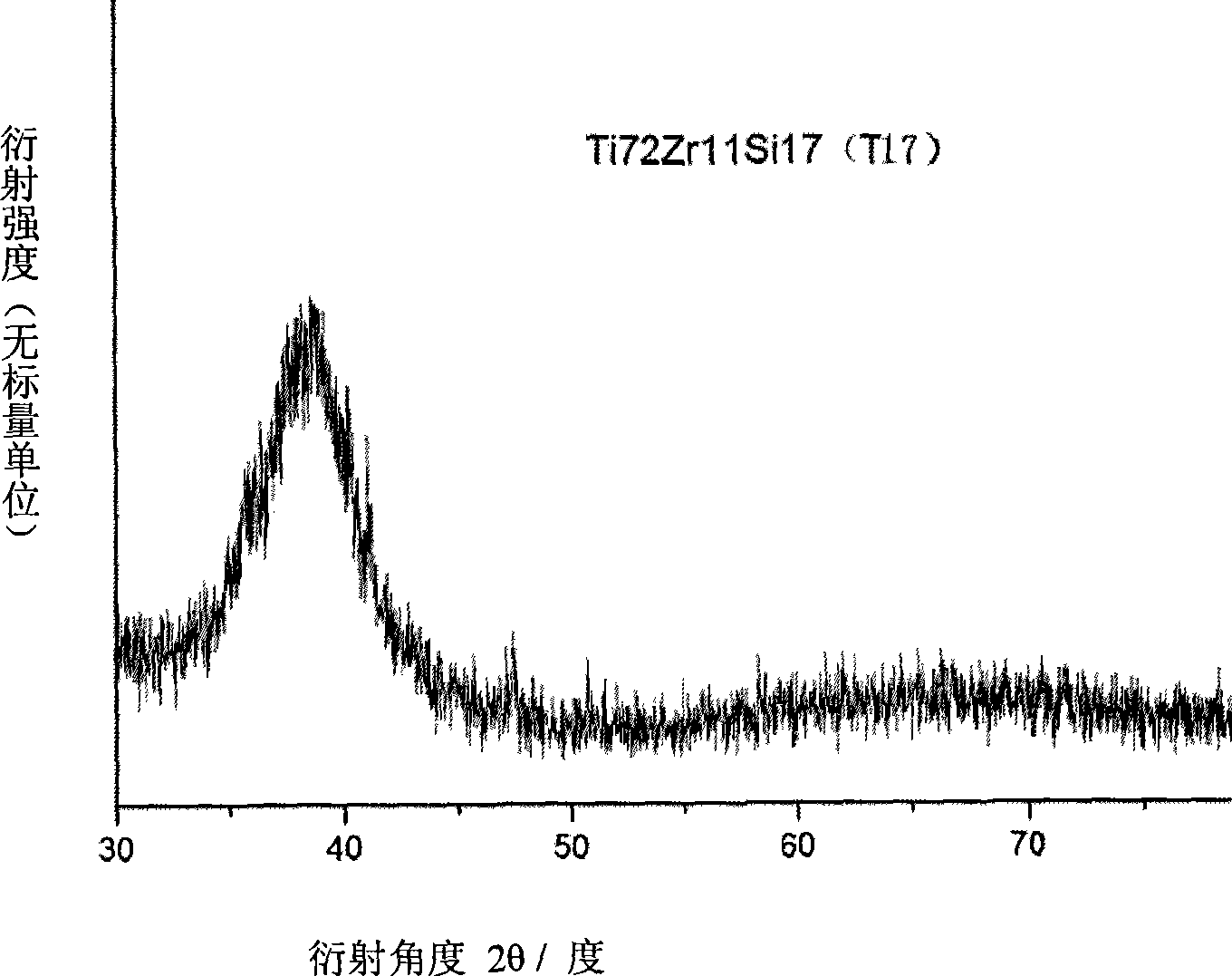
[0060]According to the atomic percentage, Ti is 72%, Zr is 11% and Si is 17%, and chemically pure grade Ti, Zr and Si are used as titanium alloy raw materials;
[0061] The second step, the preparation of titanium alloy ingot
[0062] Put the titanium alloy raw material prepared in the first step into the water-cooled copper crucible of a non-consumable vacuum electric arc furnace containing tungsten electrodes, and adjust the position of the tungsten electrode so that the distance between the front end of the tungsten electrode and the titanium alloy raw material particles in the water-cooled copper crucible is 1.0mm, close the furnace door and vent valve of the electric arc furnace, and evacuate to a temperature higher than 2×10 -2 Pa, and then filled with argon until the pressure of the furnace cavity is 0.07Pa, the electric arc furnace is started, and the arc current ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Biomedical amorphous alloy T17
[0067] The first step, titanium alloy raw material preparation
[0068] According to the atomic percentage, Ti is 65%, Zr is 15% and Si is 20%, and chemically pure grade Ti, Zr and Si are used as titanium alloy raw materials.
[0069] The second step, the preparation of titanium alloy ingot
[0070] Put the titanium alloy raw material prepared in the first step into the water-cooled copper crucible of a non-consumable vacuum electric arc furnace containing tungsten electrodes, and adjust the position of the tungsten electrode so that the distance between the front end of the tungsten electrode and the titanium alloy raw material particles in the water-cooled copper crucible is 1.5mm, close the furnace door and vent valve of the electric arc furnace, and evacuate to higher than 2×10 -2 Pa, and then filled with argon until the pressure of the furnace chamber is 0.08Pa, the electric arc furnace is started, and the arc current is gradually...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com