Treatment of tendinopathy by inhibition of molecules that contribute to cartilage formation
A tendon and cartilage technology, applied in the field of tendinopathy treatment, can solve the problems of expensive surgery, deep infection, scarring and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
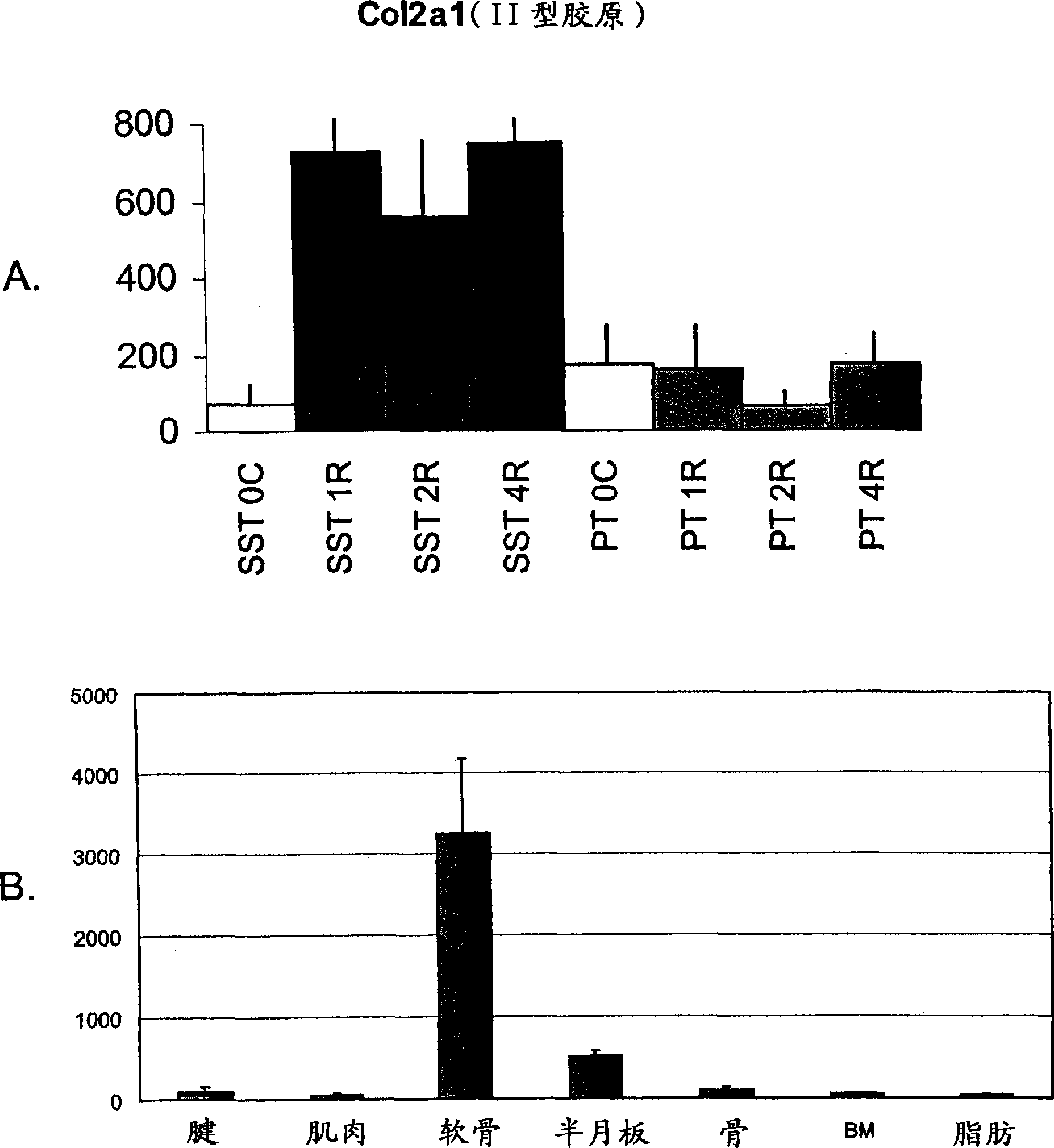
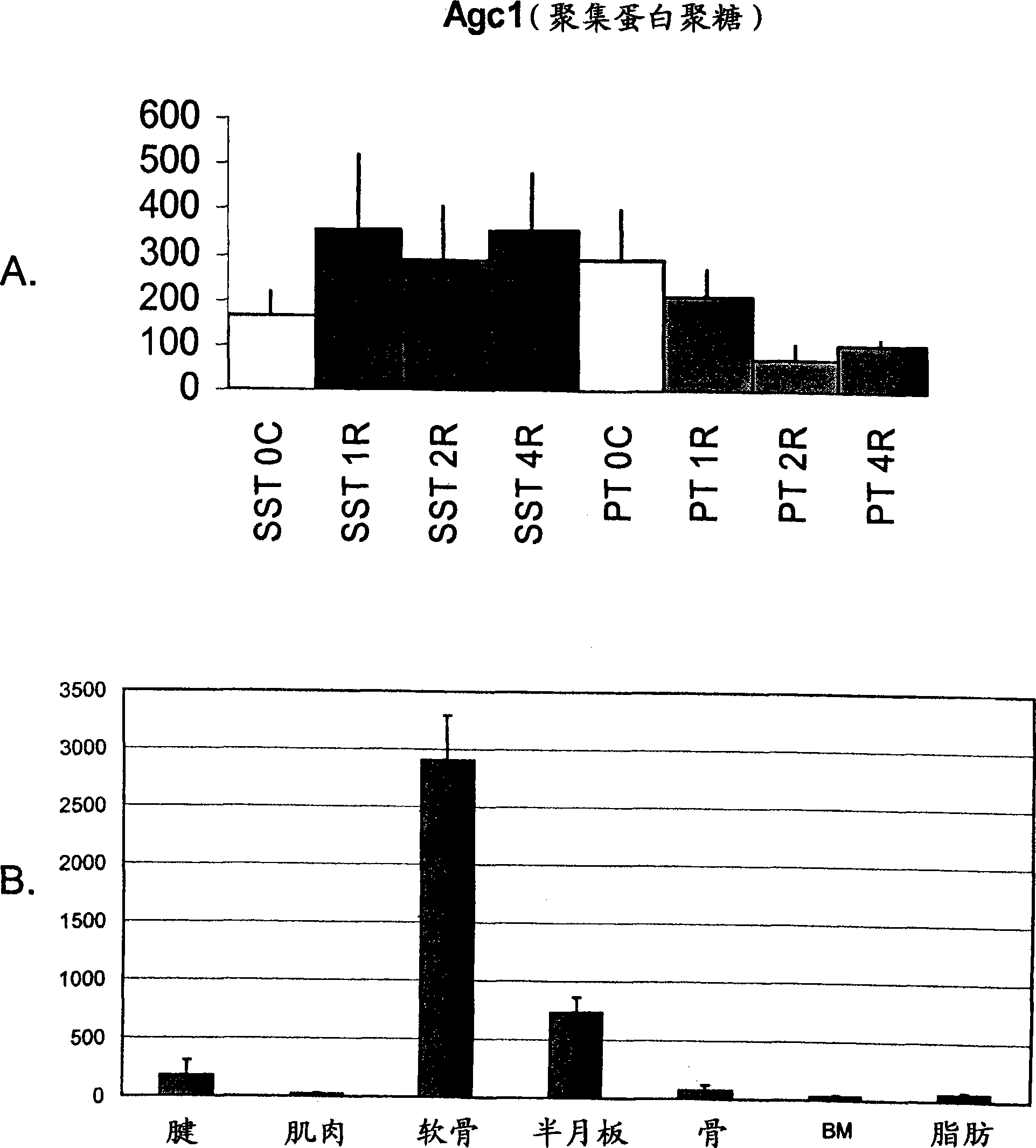
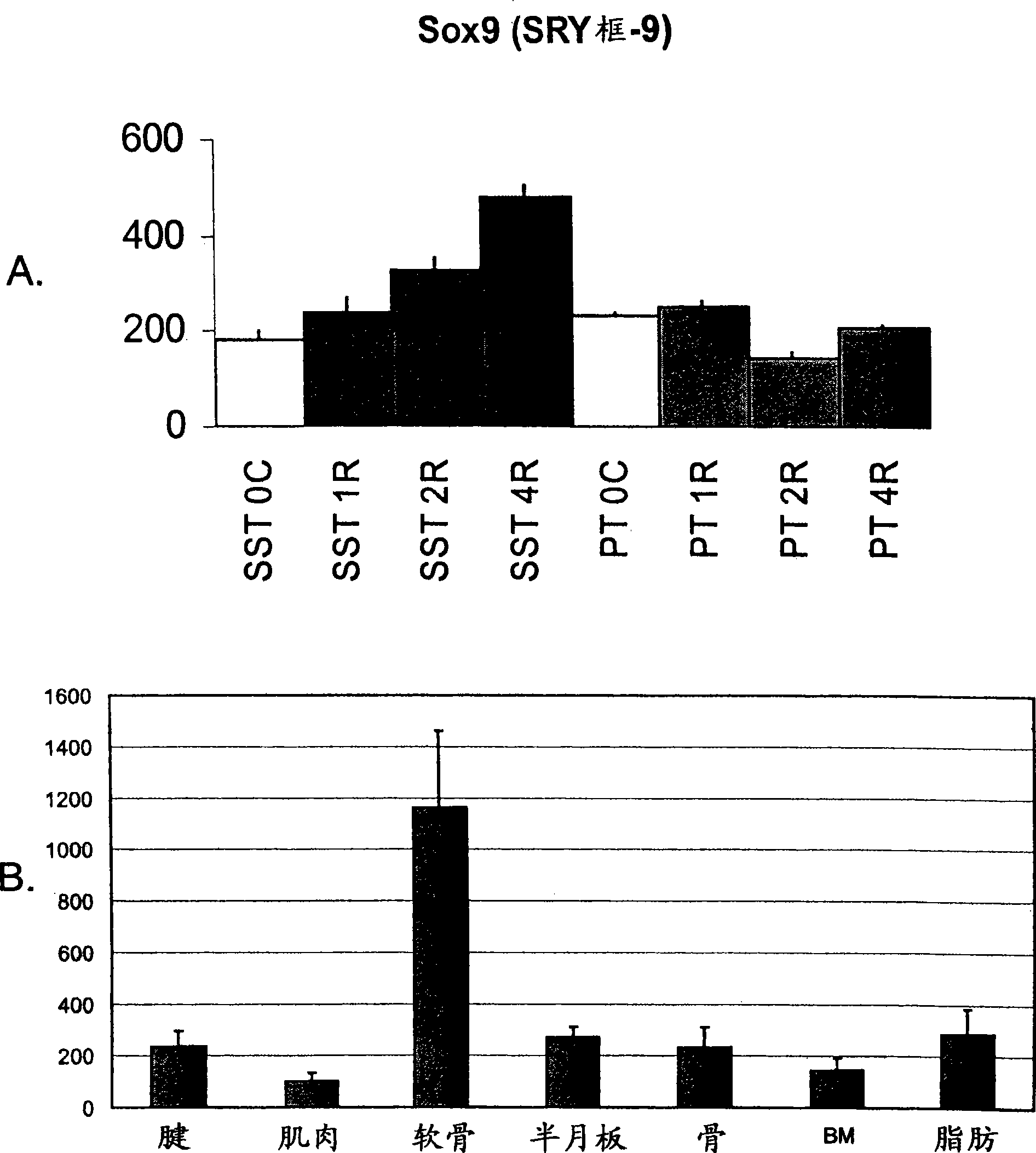
[0163] Example 1: Rat supraspinatus tendon expresses cartilage markers due to overuse
[0164] The response of the rat supraspinatus tendon to overuse was investigated at the molecular level using transcriptional profiling. A rat model of tendon overuse has been described previously. Soslowsky et al., J Shoulder Elbow Surg 9:79-84 (2000). It has been shown that inflammatory and angiogenic markers are altered in this model (Perry et al., J Shoulder Elbow Surg 14:79S-83S (2005)), but a broader approach is taken to understand the events surrounding overuse injury.
[0165] Twenty-four male Sprague-Dawley rats (400-450 g) were subjected to a supraspinatus tendon (SST) overuse protocol for 1 week (n=8), 2 weeks (n=8) and 4 weeks (n=8). The protocol consisted of running downhill at 17 m / min (10% incline) for 1 hour per day, 5 days per week. An additional 6 rats were used as controls for cage activity (time 0). At each time point, two additional non-running rats were used as age-...
Embodiment 2
[0168] Embodiment 2: Preparation of siRNA inhibitor
[0169] The siRNA is selected by entering the nucleotide sequence of CS-GalNAcT-1, GalNT-1 or Hs3st1 into a commercial website (e.g. sirnawizard.com or Ambion siRNA TargetFinder) to design specific siRNA. Sequence selection guidance is included with these tools.
[0170] The efficacy of siRNA was measured by transfecting it into C-20 / A4 and / or C-28 / I2 chondrocytes and monitoring the expression of CS-GalNAcT-1 and / or GalNT-1 by real-time RT-PCR. Appropriate scrambled siRNAs with the same nucleotide composition were used as experimental controls.
Embodiment 3
[0171] Example 3: In vitro test system for inhibitors of proteoglycan synthesis
[0172] If siRNAs were able to reduce the expression of CS-GalNAcT-1, GalNT-1 or Hs3st1 in C-20 / A4 and / or C-28 / I2 chondrocytes, they were tested for their ability to reduce proteoglycan GAG side chain production. C-20 / A4 and / or C-28 / I2 chondrocytes were treated with BMP-2 protein or BMP-2-expressing adenovirus to stimulate extracellular matrix and GAG synthesis. siRNA or, alternatively, a small molecule, inhibitor of GAG synthesis, is added to the culture and the effect of the inhibitor is assessed by comparing the incorporation of 35S into proteoglycans in the presence or absence of the inhibitor. Alternatively, the effect of inhibitors is assessed by comparing the levels of GAGs in the presence or absence of inhibitors using the DMMB assay, as described in Arai et al., Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 12:599-613 (2004).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com