Double-stranded small molecule interfering nucleic acid and combination thereof for inhibiting and killing drug-resistant bacteria
A technology of small molecule interference and double-stranded molecules, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problem of insufficient proof that siRNA can effectively inhibit and kill MRSA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Design of Target Sites
[0044] The present invention adopts all or most of the following principles to select target sequences and design siNA:
[0045] 1. Select a sequence with a length of 18-25bp;
[0046] 2. Calculate the GC content, and select a sequence with a GC content of about 40-55%;
[0047] 3. In more than 90% of Staphylococcus aureus strains, most of the bases of the target sequence of the same gene are conserved; ), DDBJ (Japanese DNA Database) downloaded all the target gene sequences of Staphylococcus aureus, and after homology comparison, the sequence region conserved in more than 90% of the strains was selected as the target sequence.
[0048] 4. The region where the target sequence is located in the target gene of the Staphylococcus aureus strain will not make the siNA molecule inaccessible due to the formation of secondary structures; Cut the mRNA in the middle; if there is a secondary structure in this sequence region and it is difficu...
Embodiment 2
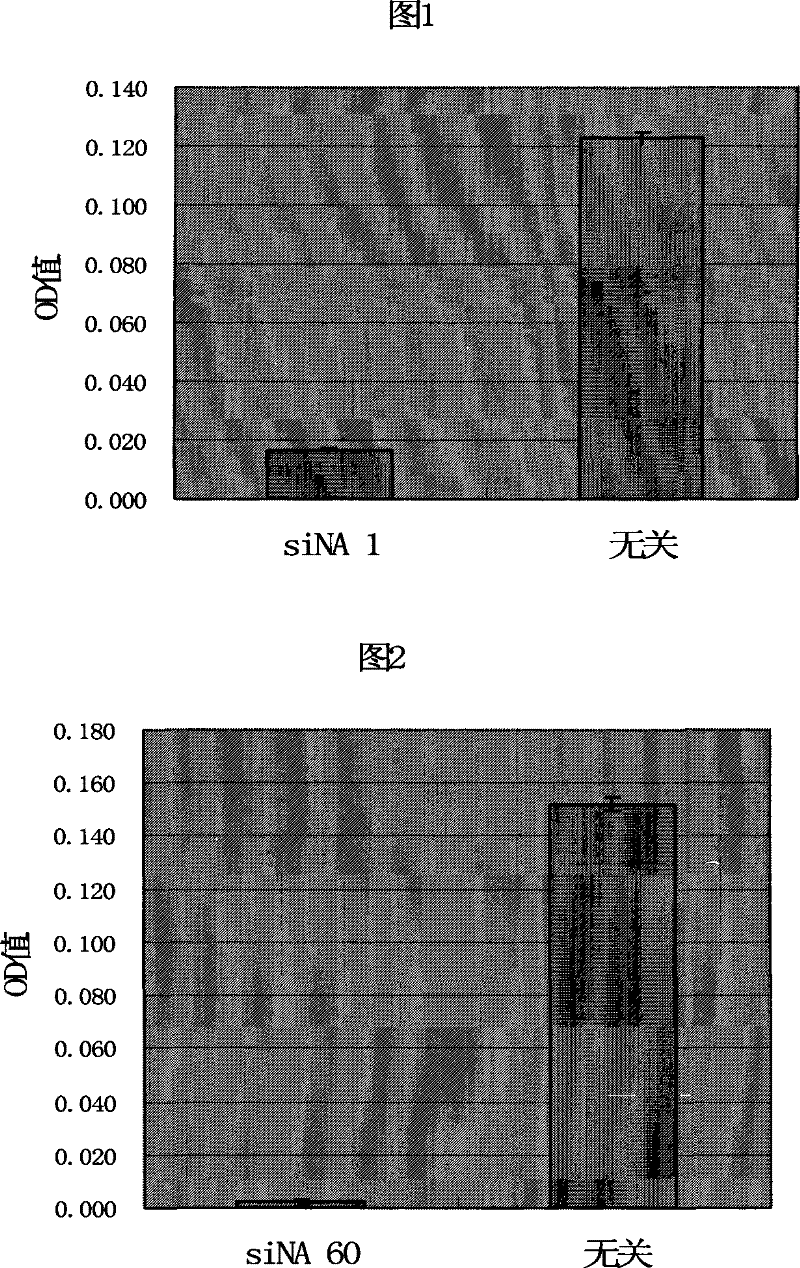
[0051] Example 2: Determination of the antibacterial or bactericidal effectiveness of siNA designed for the dnaA gene
[0052] 1. Synthesis of siNA: According to the target sequence SEQ ID NO.1 in Attached Table 1, one-to-one corresponding sense strand and antisense strand sequences were obtained, and siNA1 with the following structure was synthesized:
[0053] 5’ C U U G G U A G A G A G C A A U U C A dT dT 3’
[0054] | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
[0055] 3’ dT dT G A A C C A T C T C T C G T T A A G T 5’
[0056] The irrelevant siNA is:
[0057] 5’ G A C C C G C A U U G A G C A U C A A dT dT 3’
[0058] | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
[0059] 3’ dT dT C T G G G C G T A A C T C G T A G T T 5’
[0060] 2. Inoculate the MRSA Tanyan'e strain (isolated and identified by the Department of Microbiology, Sun Yat-sen Medical College, Sun Yat-sen University, and stored in the Guangzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention; The minimu...
Embodiment 3
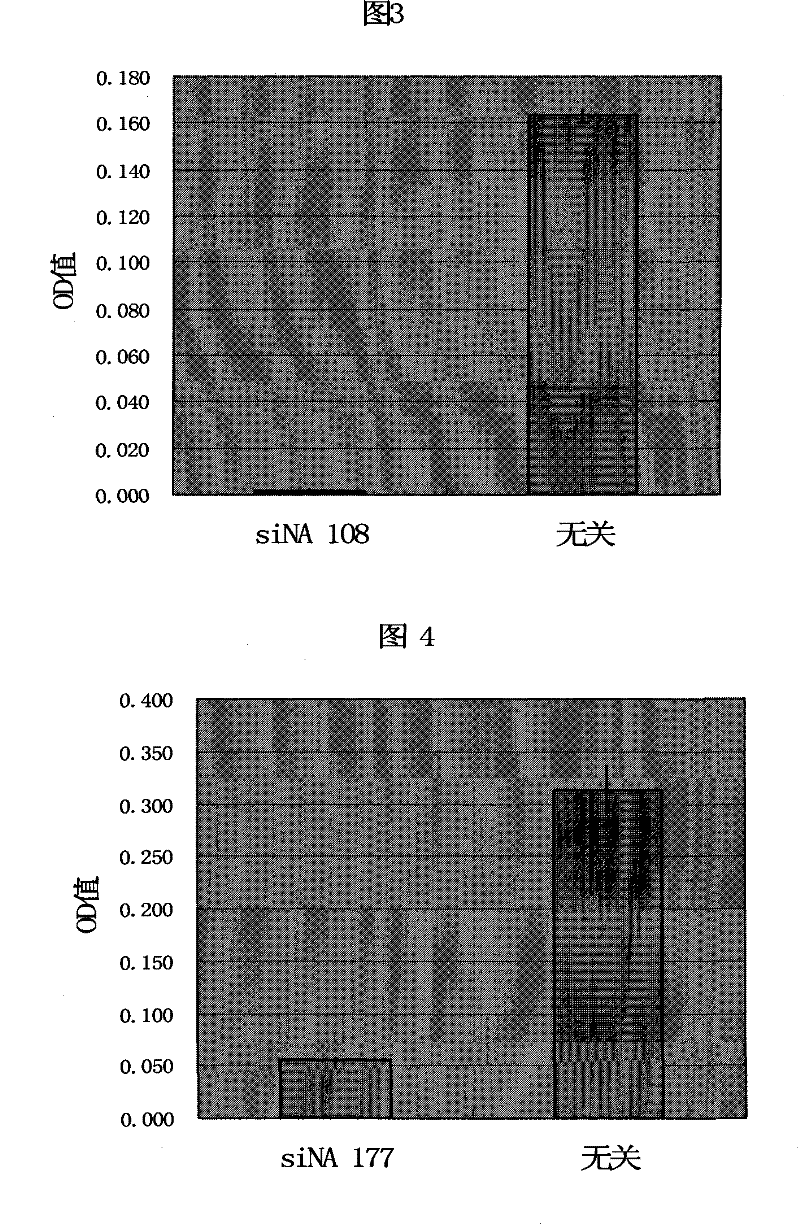
[0065] Example 3: Determination of the antibacterial or bactericidal effectiveness of siNA designed for the ftsZ gene
[0066] 1. Synthesis of siNA: According to the target sequence SEQ ID NO.60 in Attached Table 1, one-to-one corresponding sense strand and antisense strand sequences are obtained, and siNA with the following structure is synthesized:
[0067] siNA60:
[0068] 5’ G U U A C G C C A A G G U G U A C A A dT dT 3’
[0069] | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
[0070] 3’ dT dT C A A T G C G G T T C C A C A T G T T 5’
[0071] The irrelevant siNA is:
[0072] 5’ G A C C C G C A U U G A G C A U C A A dT dT 3’
[0073] | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
[0074] 3’ dT dT C T G G G C G T A A C T C G T A G T T 5’
[0075] 2. Inoculate the MRSA standard strain ATCC25923 (purchased from ATCC in the United States; the minimum inhibitory concentration of oxacillin is 1.2 μg / ml) in the nutrient broth medium;
[0076]3. In 2 glass tubes, ta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com