Discrete velocity layer-striding power distribution method suitable for distributed antenna system
A distributed antenna and allocation method technology, applied in diversity/multi-antenna systems, power management, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of poor fairness of depth-first algorithm, lack of consideration of queue information, poor throughput performance of breadth-first algorithm system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
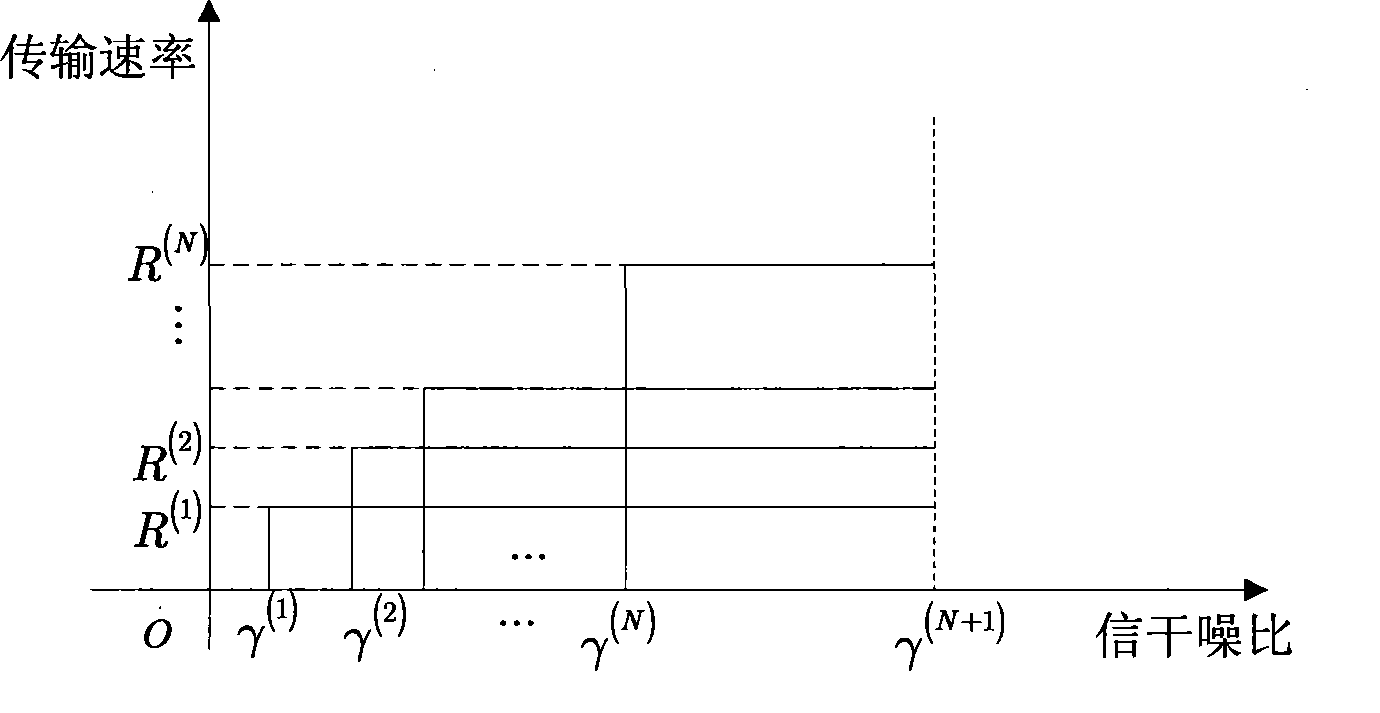
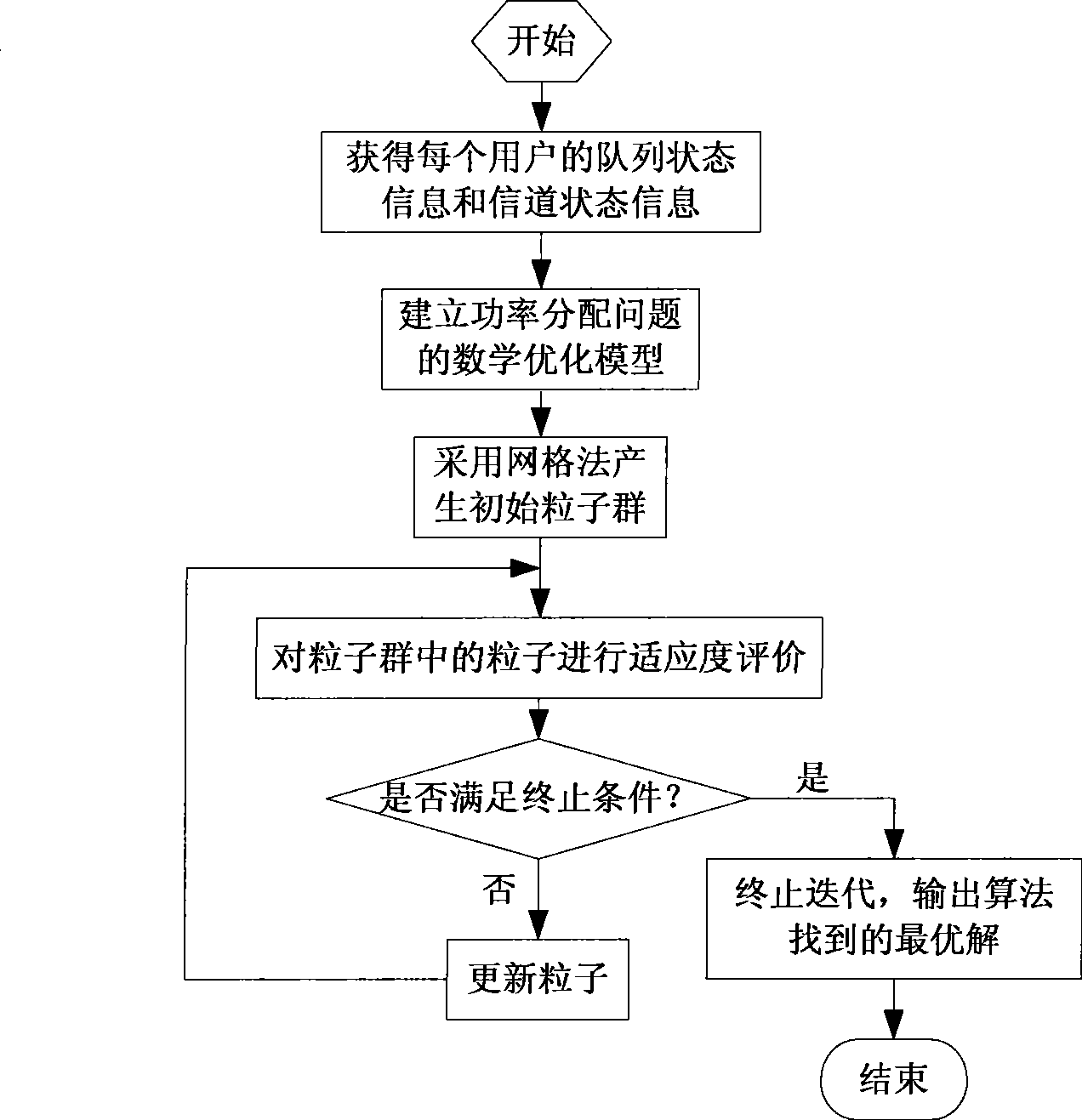
[0026] The present invention proposes a discrete-rate cross-layer power distribution method suitable for distributed antenna systems. The specific implementation steps of the method are:
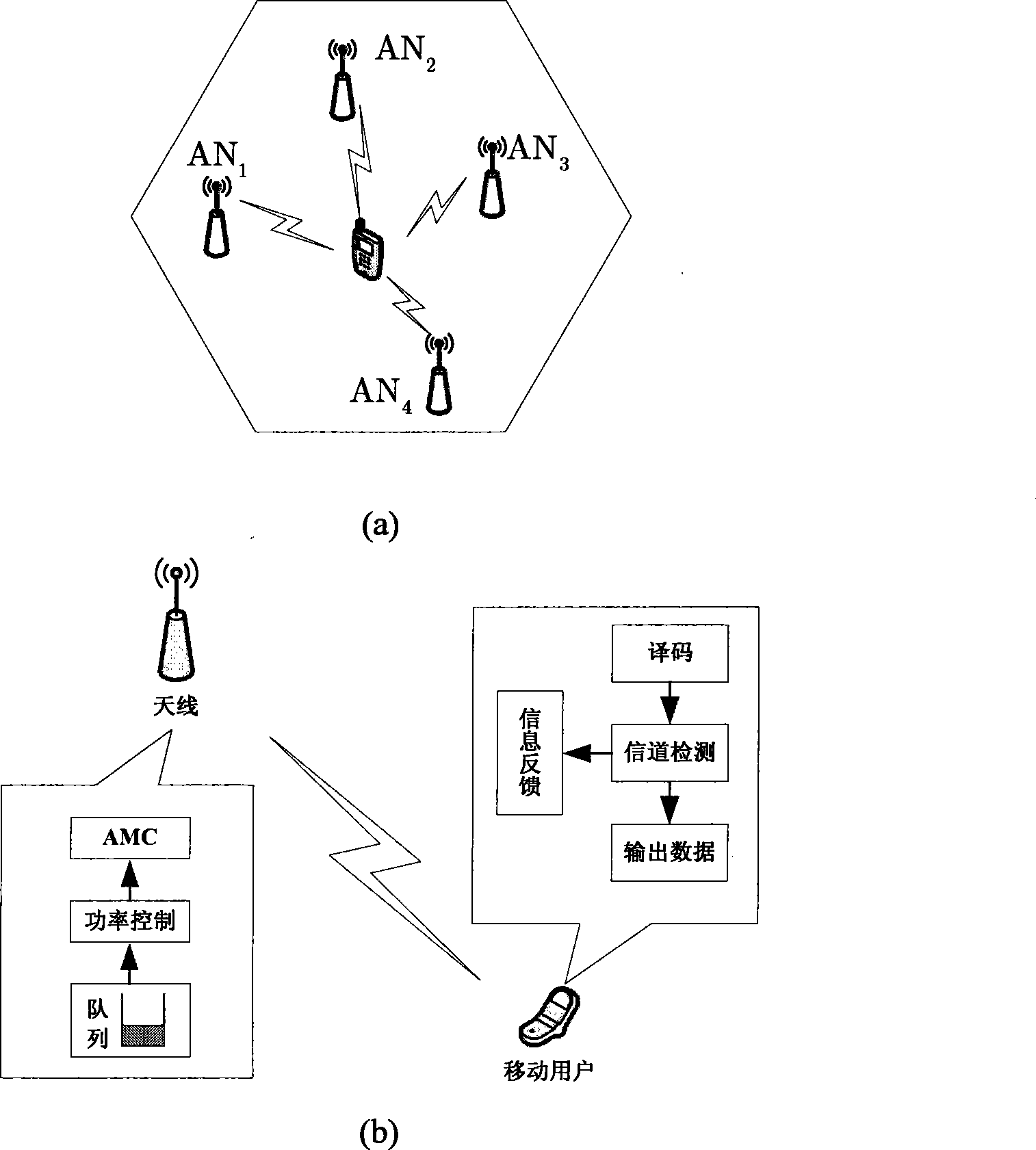
[0027] Step 1: The base station reads the queue status information of each user in the data link layer, and obtains the channel status information fed back by each user;
[0028] Step 2: The system uses the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm to perform cross-layer power allocation according to the queue state information and channel state information of each user.
[0029] In the above-mentioned discrete-rate cross-layer power allocation method applicable to distributed antenna systems, the queue status information of each user in the first step refers to the buffering amount u of the services of K users in the base station in a scheduling period 1 , u 2 ,...,u K , the channel state information fed back by each user refers to the channel fading coefficient h fed back by K users...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com