Efficient application of reduced variable transformation and conditional stability testing in reservoir simulation flash calculations
A reservoir and computer technology, applied in the field of reservoir simulation of components, can solve the problems of untaught stability testing, convergence difficulties, numerical convergence difficulties, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
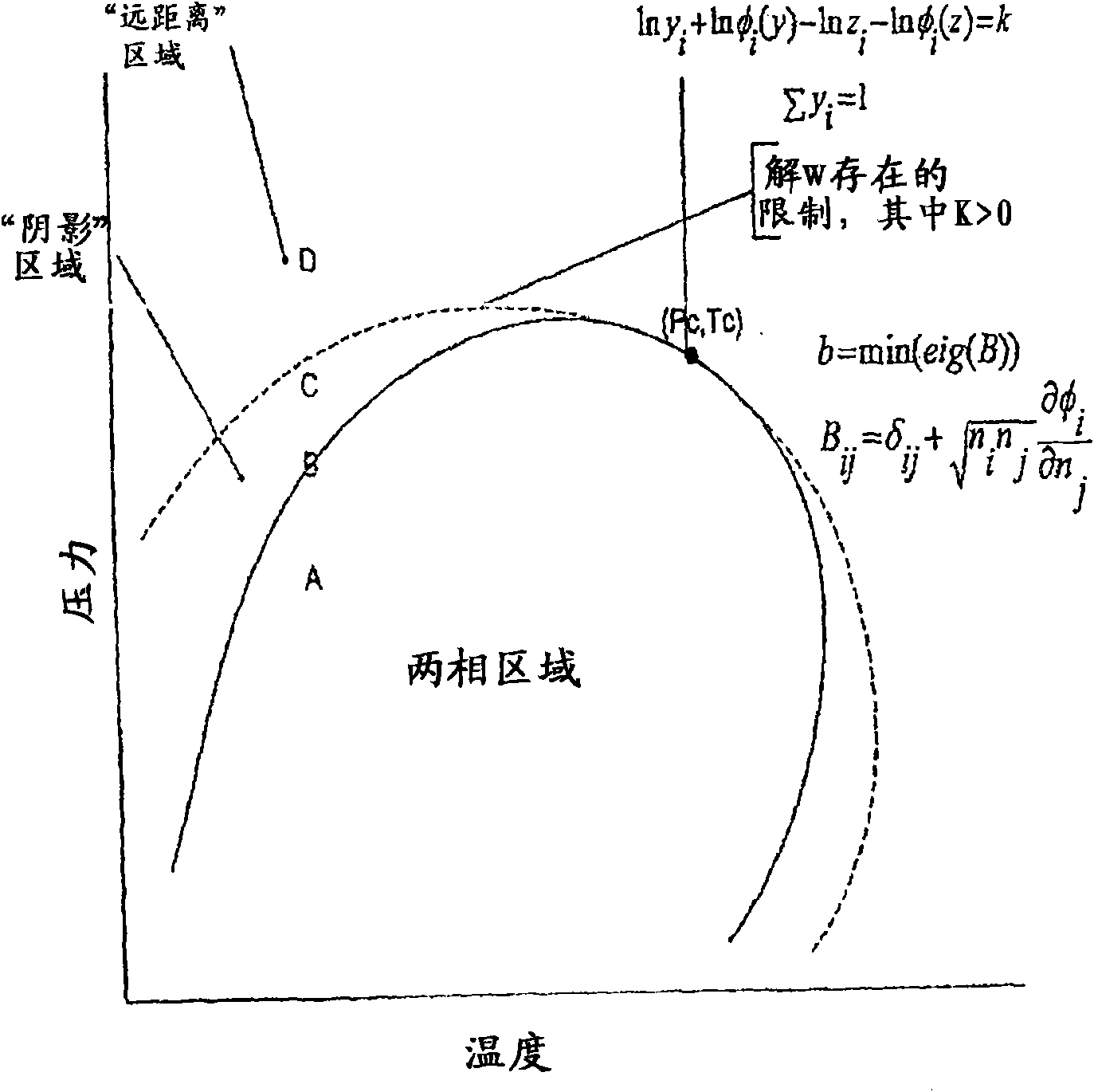
[0023] The following terms will be used in subsequent equations:
[0024] symbol
[0025] D = tangential distance (TPD)
[0026] G = Gibbs free energy function (GFE)
[0027] c = number of oil and gas components
[0028] m = number of non-zero eigenvalues
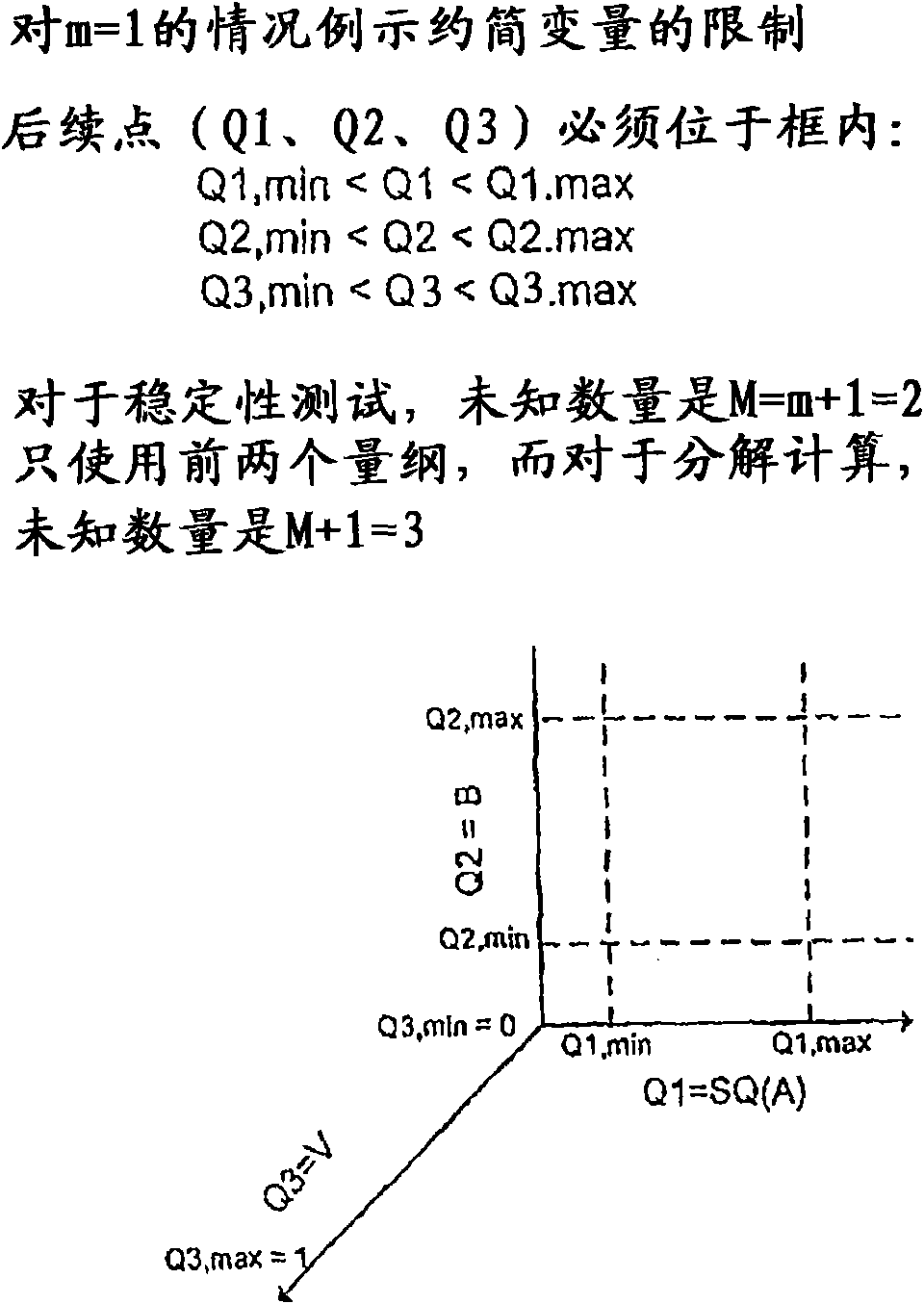
[0029] M = number of reduction parameters, equal to (m+1)
[0030] P = pressure
[0031] Q = element Q a The reduction variable (M-vector) of
[0032] Q = element q ij size M C The reduced coefficient matrix of
[0033] R = universal gas constant
[0034] T = temperature
[0035] x = liquid phase component (mol fraction)
[0036] y = gas phase component (mol fraction)
[0037] Y = unnormalized moles of test phase
[0038] z = raw material (feed) (total) component (mol fraction)
[0039] subscript
[0040] i, j = component index
[0041] α = reduced variable index
[0042] L = Fluid
[0043] V = gas
[0044] Superscript
[0045] F = feed phase
[0046] T = test phase
[0047] greek symbol
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com