Method and device for the quantitative real time analysis of fluorescent samples
A real-time analysis and sample technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, analysis materials, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problem of time-consuming analysis and achieve the effect of reducing the time period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
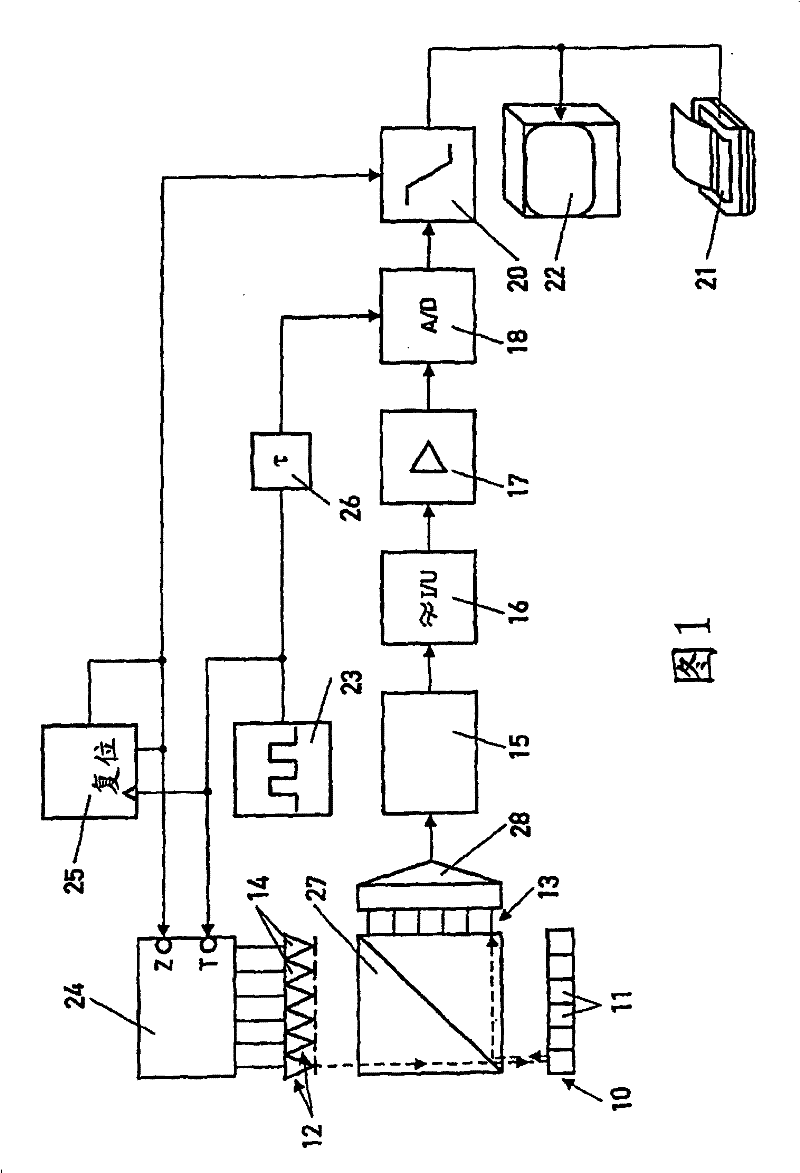
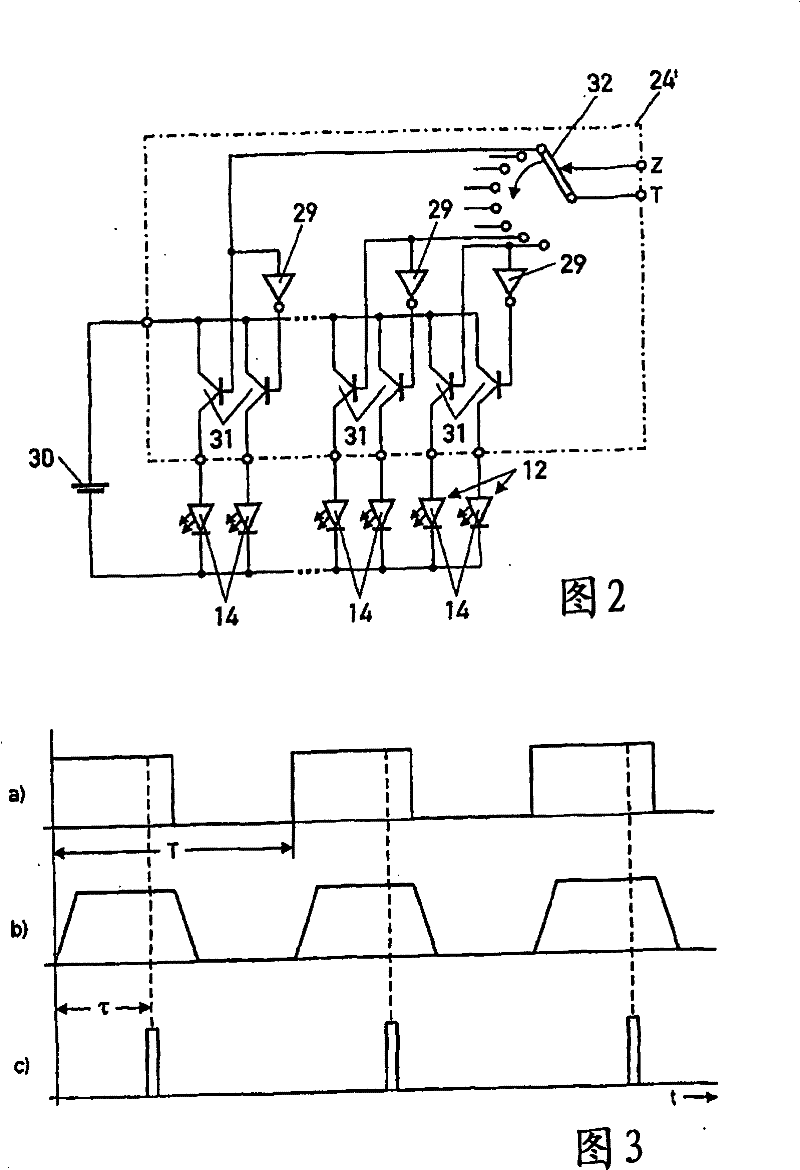
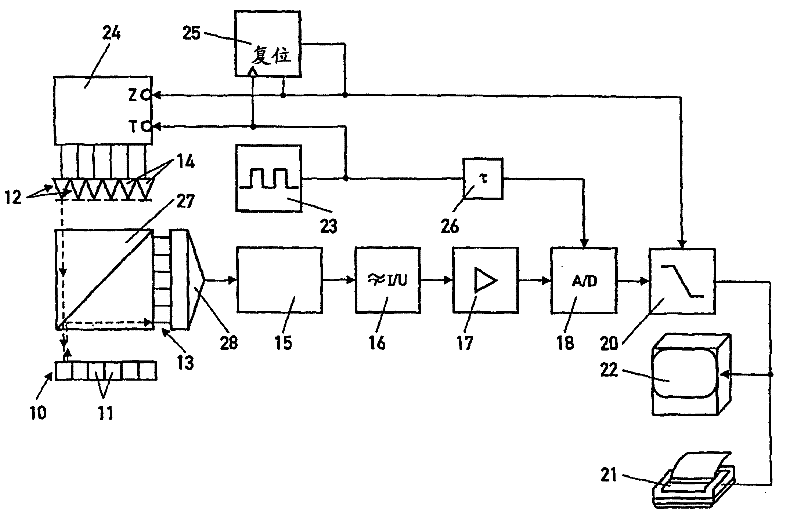
[0021] exist figure 1 A block diagram of an apparatus that can be used for quantitative real-time analysis of fluorescent samples is shown in . As an example, the device is used with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to determine the amount of DNA formed. Thus, multiple samples with DNA molecules to be replicated or amplified, respectively, are heated and annealed in repeated three-stage cycles as described above so that the fluorescent dye binds to the double-stranded DNA and fluoresces when excited by external light . To determine the amount of DNA replicated in each cycle in the sample, the intensity of light emitted by the sample is measured by the device.
[0022] The device provides a tray with a plurality of small containers 11 filled with samples with DNA molecules, primers, nucleotides and fluorescent dyes. The trays are alternately heated and annealed within the cycle described above. An electrical light source 12 is assigned to each container 11 in the tray, capab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com