Transmission method for broadcast/multicast feedback signaling
A transmission method and feedback signal technology, applied in the field of communication information, can solve the problems of consuming large spectrum resources, erroneous feedback, and large feedback overhead.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] The present invention proposes a set of feedback signaling transmission schemes for the success or failure of the transmission of layer 2 data packets of the broadcast / multicast system. The purpose of the feedback scheme is to enable the wireless communication system to support reliable and efficient broadcast / multicast communication.
[0053] The technical solution proposed by the present invention includes two parts: the uplink resource allocation process of the broadcast / multicast feedback, and the generation and transmission process of the broadcast / multicast feedback signal.
[0054] 1. Uplink resource allocation process for broadcast / multicast feedback
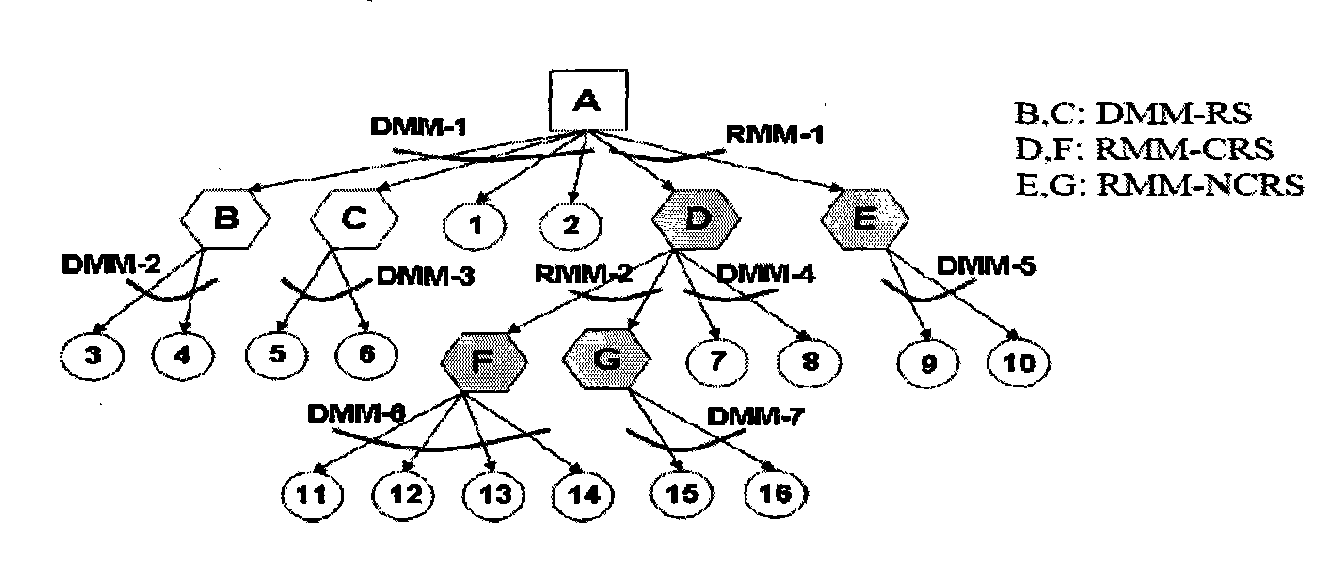
[0055] In uplink resource allocation, all nodes (hereinafter referred to as child nodes) that may feed back to the same node that sends broadcast / multicast signals (hereinafter referred to as parent nodes) are allocated the same time-frequency resource to support feedback information. The transmission of the order.
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Embodiment 2: A system in which the child node can estimate the transmission channel
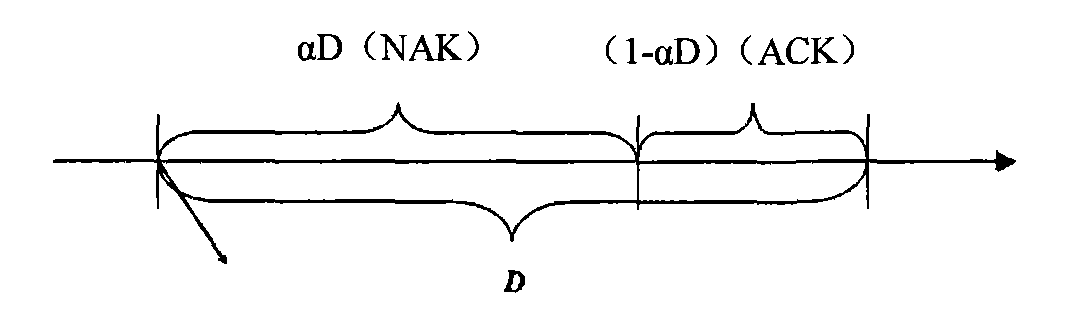
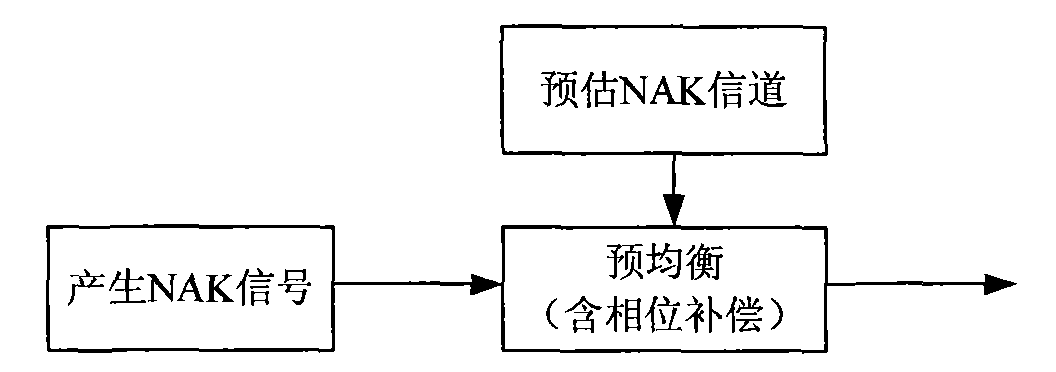
[0083] In some fixed wireless access systems in TDD mode, since the channel time becomes slow (for example, the 2.4GHz moving speed of 3km / h corresponds to the Doppler frequency of about 7Hz), when the frame length is short (for example, the IEEE802.16d standard) The frame length defined in includes options such as 2.5ms, 4ms, 5ms, etc.), and the channel in the uplink subframe may have reciprocity characteristics with the channel in the downlink subframe. Although the receiving end of the uplink channel and the receiving end of the downlink channel may face different interferences, the present invention mainly focuses on the channel experienced by the transmitted (NAK) useful signal itself.
[0084] When the system sends a broadcast / multicast signal, a stream identifier can be assigned to the data stream in the downlink resource allocation signaling, indicating which users the stream is se...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Embodiment 3: General system
[0096] In systems such as FDD, since the uplink and downlink channels are independent of each other, it is difficult for the child nodes to estimate its transmission channel. In this case, the first method based on pre-equalization cannot be used, and the second method suitable for general systems can only be used.
[0097] When the system sends a broadcast / multicast signal, a stream identifier can be assigned to the data stream in the downlink resource allocation signaling, indicating which users the stream is sent to, and indicating whether the stream supports feedback; while in the uplink resource allocation signaling In this frame, the corresponding uplink feedback resource can be allocated to the downlink broadcast / multicast data sent in this frame, indicating the downstream identifier corresponding to the feedback, and can uniquely determine each downstream data packet and the uplink feedback resource Correspondence between time-frequenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com