Method for measuring the shpericity of spherical profiles
A roundness measurement and profile technology, which is applied in the field of roundness measurement for round profiles, can solve problems such as inability to reflect profile features, uncertain center of circle, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] The invention will be described in more detail below with reference to examples, with reference to the schematic drawings, which illustrate the method steps according to the invention.
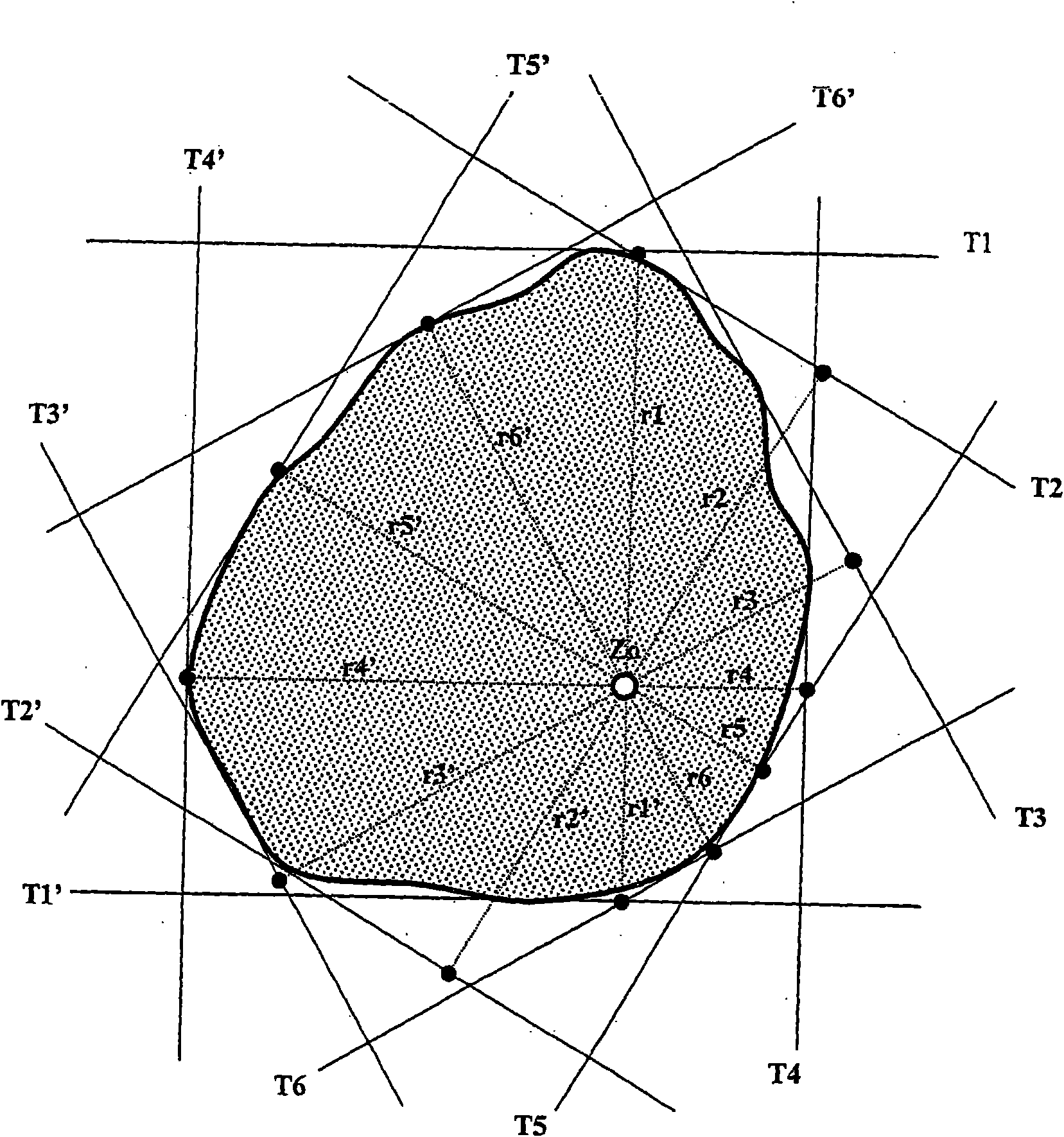
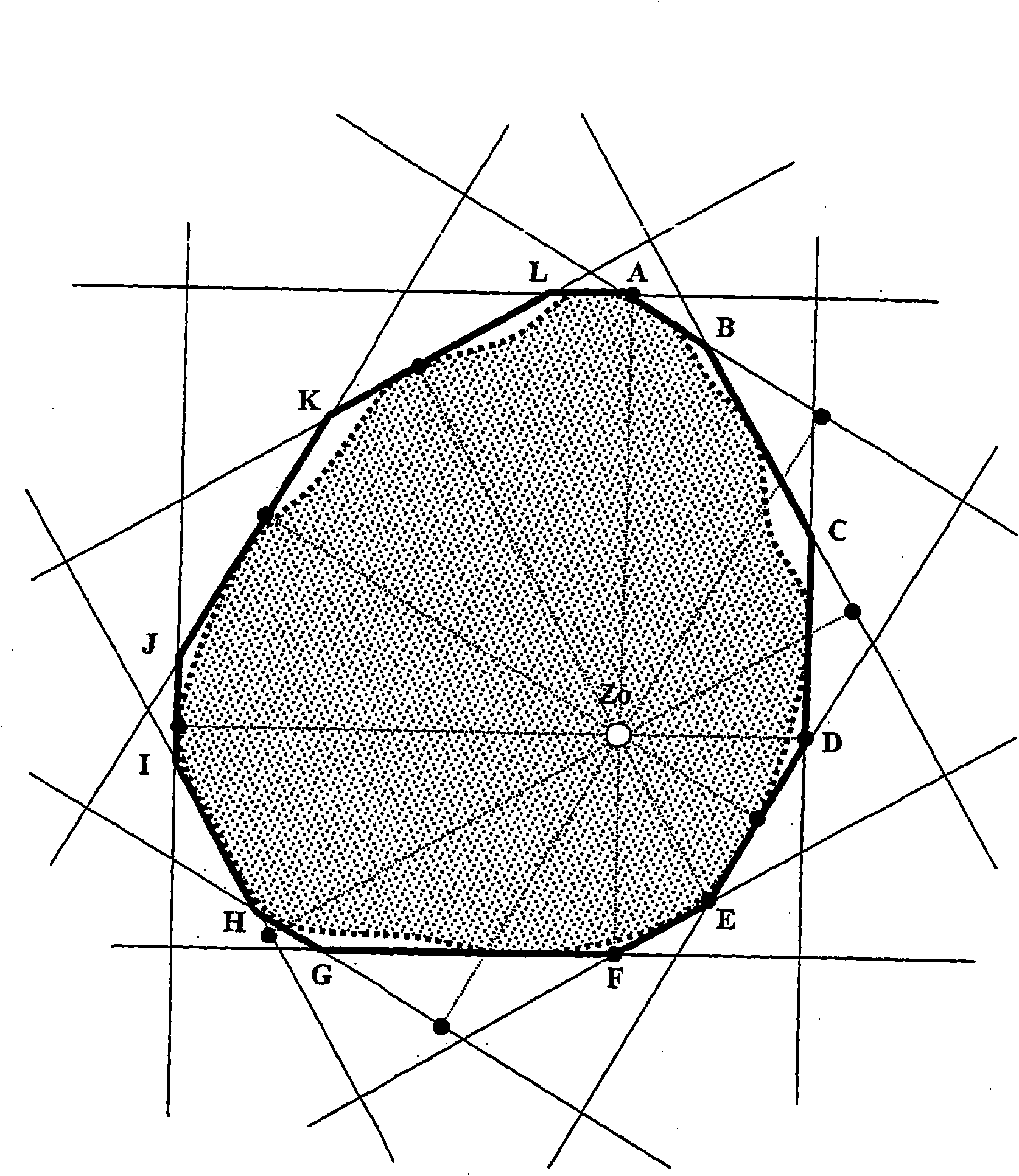
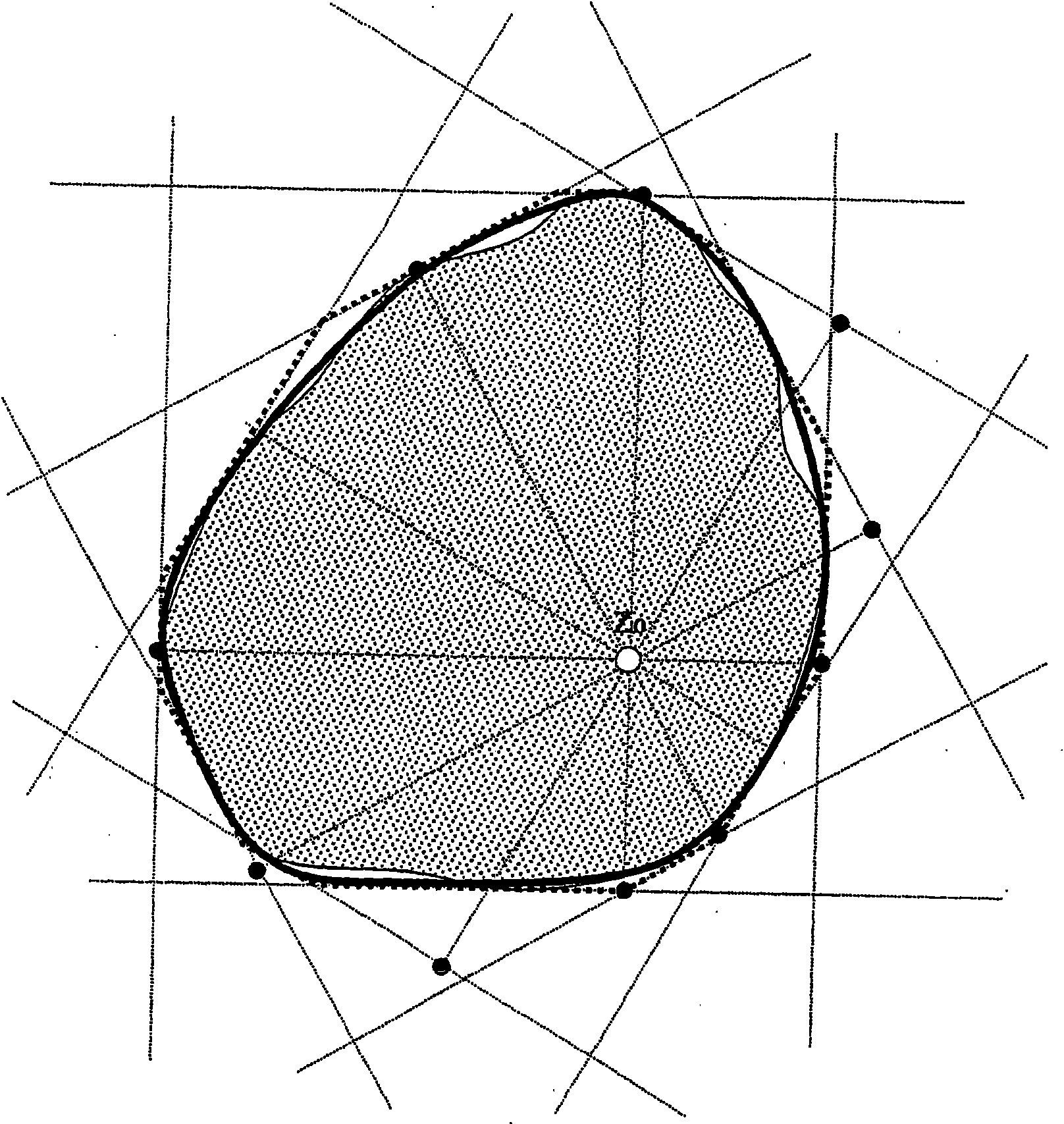
[0054] figure 1 A cross-section of a round profile to be tested is shown, and the outer contour of the round profile is shown by a thick solid line. On this round profile, a total of 12 projected edges are arranged by means of six laser scanners, said projected edges forming the tangent T 1 , T 2 , T 3 , T 4 , T 5 , and T 6 and T 1’ , T 2’ , T 3’ , T 4’ , T 5’ , and T 6’ . Here, the tangent to T 1 , T 1’ ; T 2 , T 2’ ; T 3 , T 3’ ; T 4 , T 4’ ; T 5 , T 5’ and T 6 , T 6’ Each belongs to a laser scanner. A total of six laser scanners are therefore used, the round profile to be measured being located entirely in the measuring field of these laser scanners.
[0055] The center Z of the measuring field of the measuring device is usually more precisely determined and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com