Method and device thereof used for dewatering textile
A dehydration device and a technology for textiles, applied in the field of textile processing, can solve the problems of prolonging drying time, reducing production efficiency, economic losses of users, etc., and achieving the effects of improving product qualification rate, improving production efficiency, and high dehydration efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
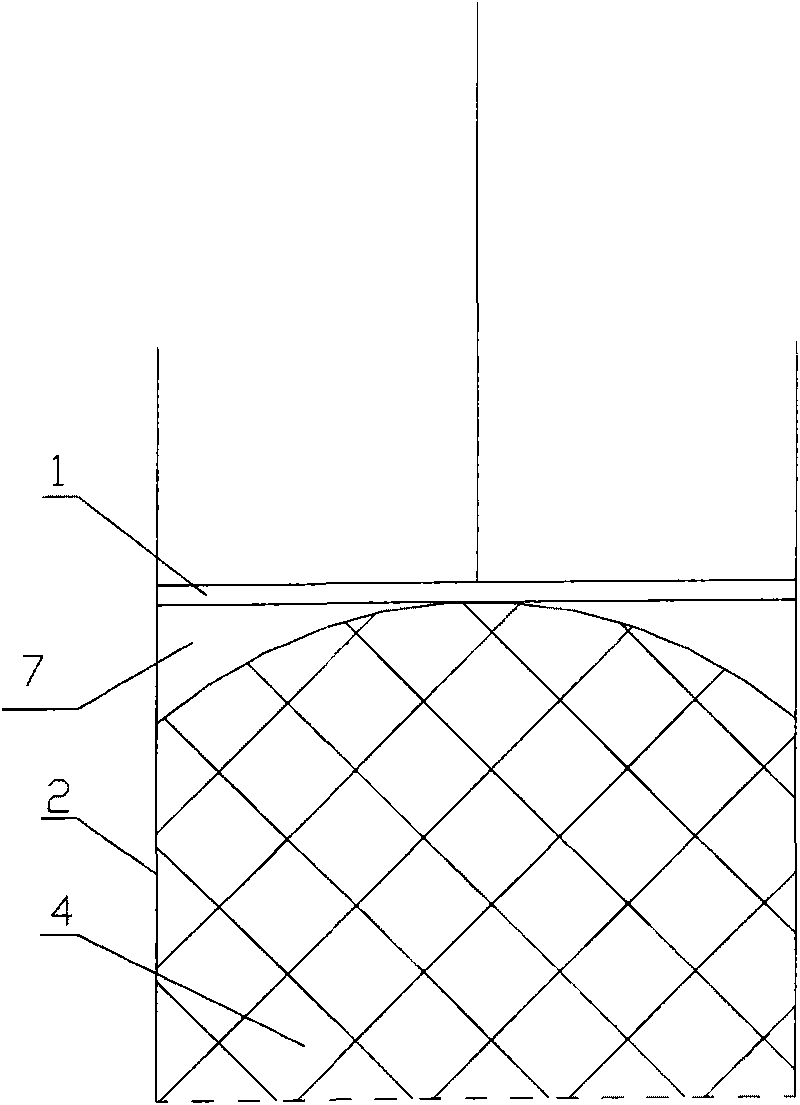
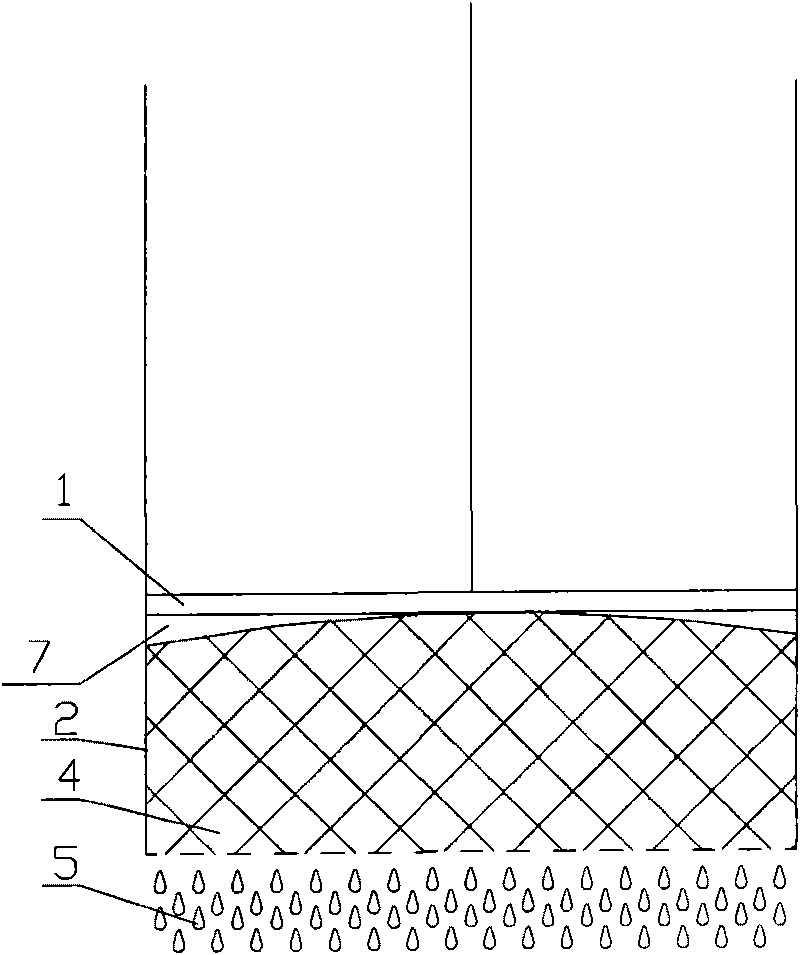
[0033] This embodiment is a dehydration method for textiles, in which the textiles are extruded by a deformable extrusion block in the working space to realize the dehydration of the textiles, specifically as image 3 and Figure 4 As shown, when the working head 1 moves toward the textile in the cylinder body 2, it first acts on the deformable extruding block 3, and the deformable extruding block 3 is deformed, and its lower surface is close to the top of the textile 4, and is filled with the textile 4 and the working The gap 7 between the heads 1; continue to pressurize the deformable extruding block 3, and the deformable extruding block 3 squeezes the textile 4 so that the moisture 5 in the textile 4 is discharged from the dehydration hole at the bottom of the cylinder body 2.
[0034] A kind of dehydration device for textiles that this embodiment is used for above-mentioned method, its structure is as follows image 3 As shown, it includes a cylinder body 2 and a working ...
Embodiment 2
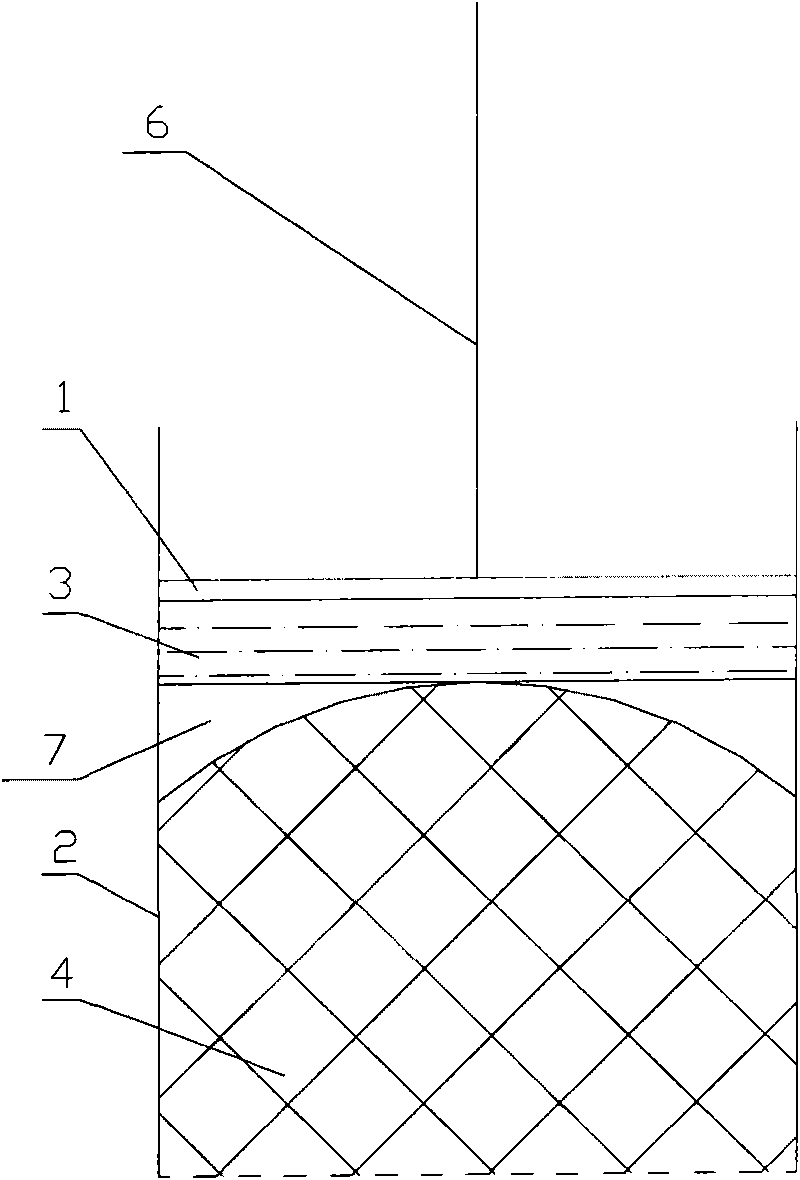
[0040] This embodiment is a dehydration device for textiles. Compared with Embodiment 1, the difference is that the deformable extrusion block 3 of this embodiment adopts a liquid bag, and the liquid bag can be a sealed and fixed structure filled with liquid. , or the liquid capsule can also be a volume-adjustable structure with an external liquid source mechanism.
[0041] Since the deformable extruding block 3 of this embodiment adopts a liquid bag, the dehydration method of this embodiment is different from that of Embodiment 1 in that when the deformable extruding block 3 continues to be pressurized, the working head can 1 continues to move in the direction of the textile to pressurize the liquid bag; or the working head 1 can be kept still after it is located at the set working position, and then fill the liquid bag with filling liquid through the liquid source mechanism to pressurize the liquid bag.
Embodiment 3
[0043] This embodiment is a dehydration device for textiles. Compared with Embodiment 1, the difference is that the deformable extrusion block 3 of this embodiment adopts a high-elastic sponge layer, and the cross-sectional shape of the high-elastic sponge layer is similar to that of the cylinder. The cross-sectional shapes of body 2 are the same or similar.
[0044] Since the deformable extruded block 3 of this embodiment adopts a high-elastic sponge layer, the dehydration method of this embodiment differs from that of Embodiment 1 in that when the deformable extruded block 3 continues to be pressurized, by working The head 1 continues to move towards the textile to pressurize the high elastic sponge layer.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com