Target tracking method of passive multi-sensor based on layered particle filtering
A target tracking, multi-sensor technology, applied in the field of target tracking, can solve problems such as inability to observe distance information, difficulty in obtaining noise intensity, filter divergence, etc., to improve accuracy and stability, facilitate parallel implementation, and avoid tracking errors. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
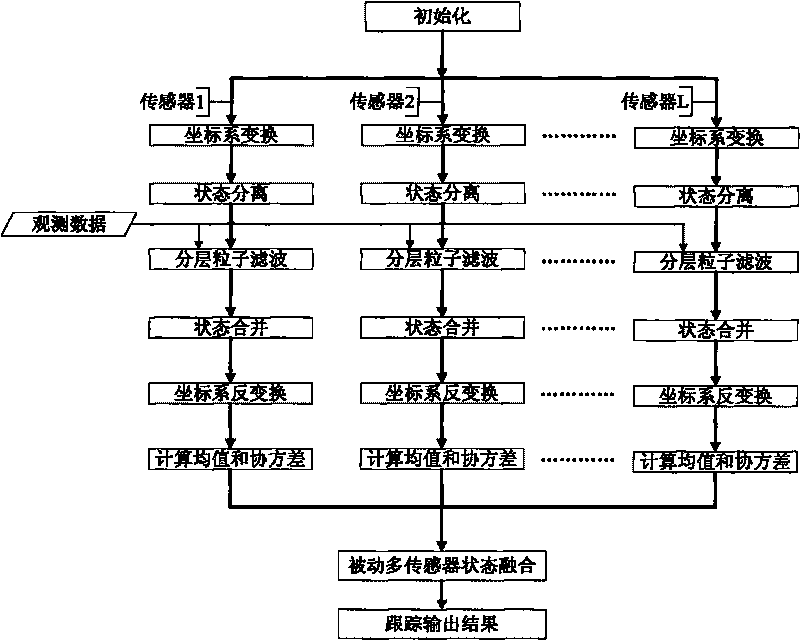
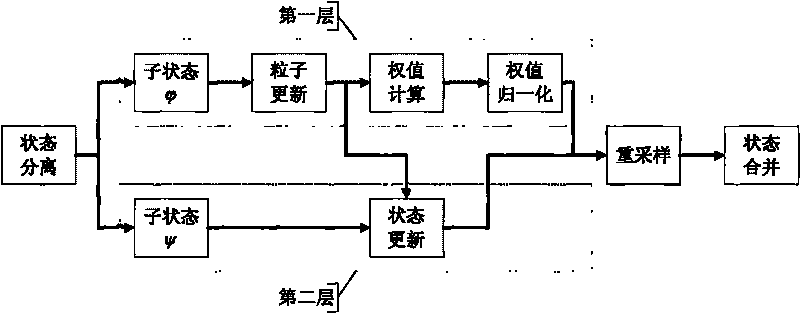
[0027] 1. Introduction to basic theory
[0028] 1. System equations
[0029] In the Cartesian coordinate system, the system state takes the position and velocity in the x and y directions, and the following nonlinear dynamic system model can be established:
[0030] x k+1 =Fx k +σv k
[0031] 1)
[0032] z k =h(x k )+ω k
[0033] in is the state of the system at time k, F is the one-step transition matrix, and σ is the process noise intensity. The function h( ) represents the observation model, v k , ω k are process noise and observation noise, respectively.
[0034] In the present invention, it is assumed that the passive sensor can only observe the angle information of the target, so h is defined as follows:
[0035] h ( x k ) = Δ a tan y k x ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com