Raw material-saving one-dimensional stock-cutting method
A technology of raw materials, waste materials, used in the field of computer applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
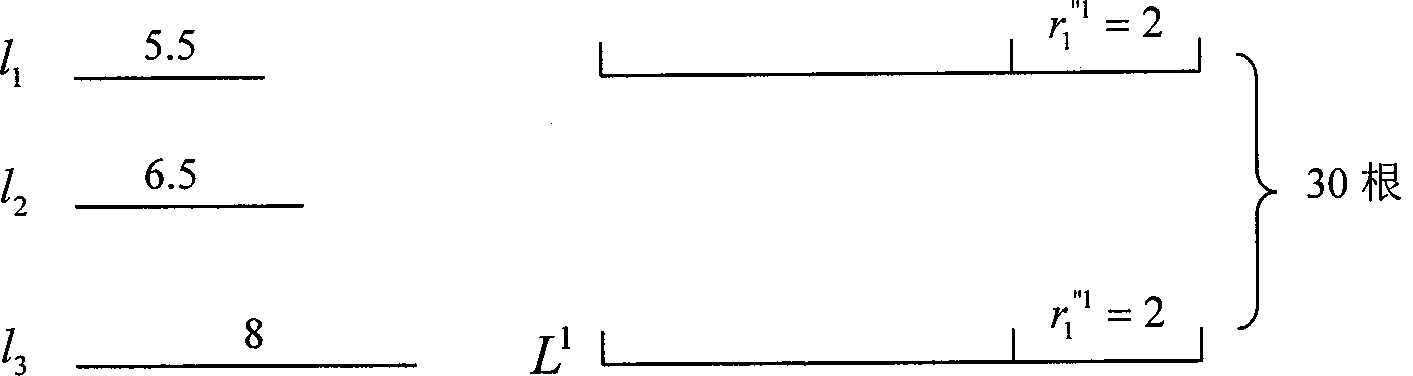
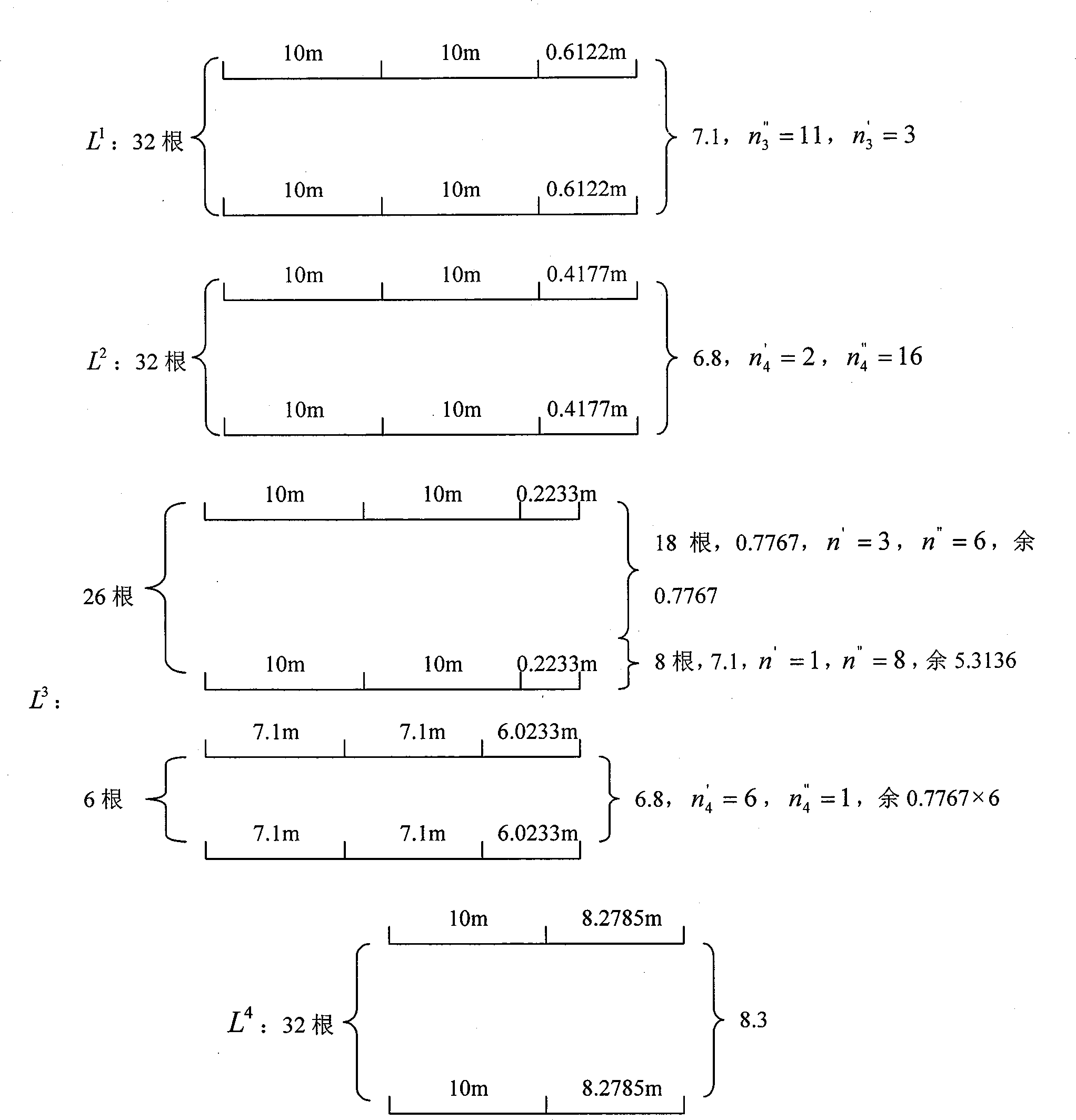
[0110] input: l 1 = 10m, l 2 =8.3m, l3 =7.1m, l 4 = 6.8m. no 1 =212,n 2 =32,n 3 =16,n 4 =8. a j =1. l j have the same priority. D=4,m 1 =m 2 =m 3 =m 4 =32,L 1 =20.6122m,L 2 =20.4177m,L 3 =20.2233m, L 4 = 18.2785m. max I i =3.
[0111] Unsplicable interval:
[0112]
[0113] R 1 = 0.2, R 2 = 0.5.
[0114] Output: I 1 =I 2 =I 4 = 1, I 3 = 2, the splicing result is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0115] Results The total length of the material was 2545.0144m, the length of the remaining material was 6.2916m, and the total length of the raw material was 2553.6m.
[0116] Clipping rate ρ = 2551.306 2553.6 = 99.91 % , The number of interfaces is 224.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com