Coaxial digital holography method capable of effectively inhibiting zero-order and conjugate images
A digital holographic and conjugate technology, applied in the field of holography, can solve problems such as complex calculations of multiple holograms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
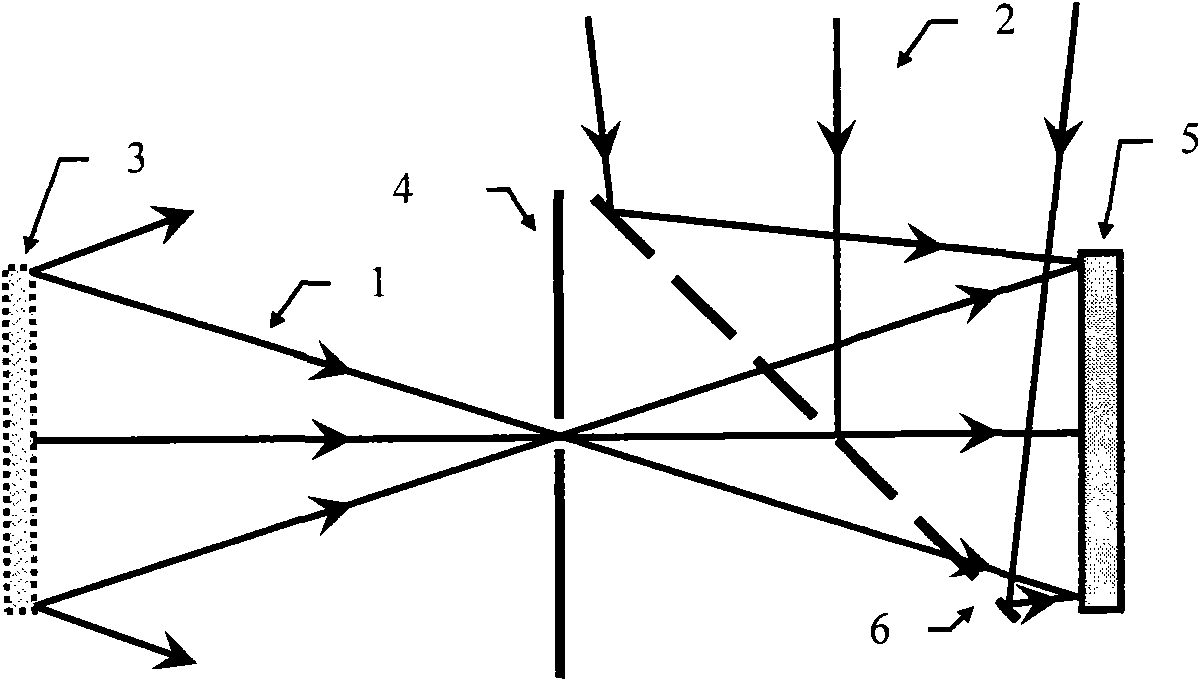
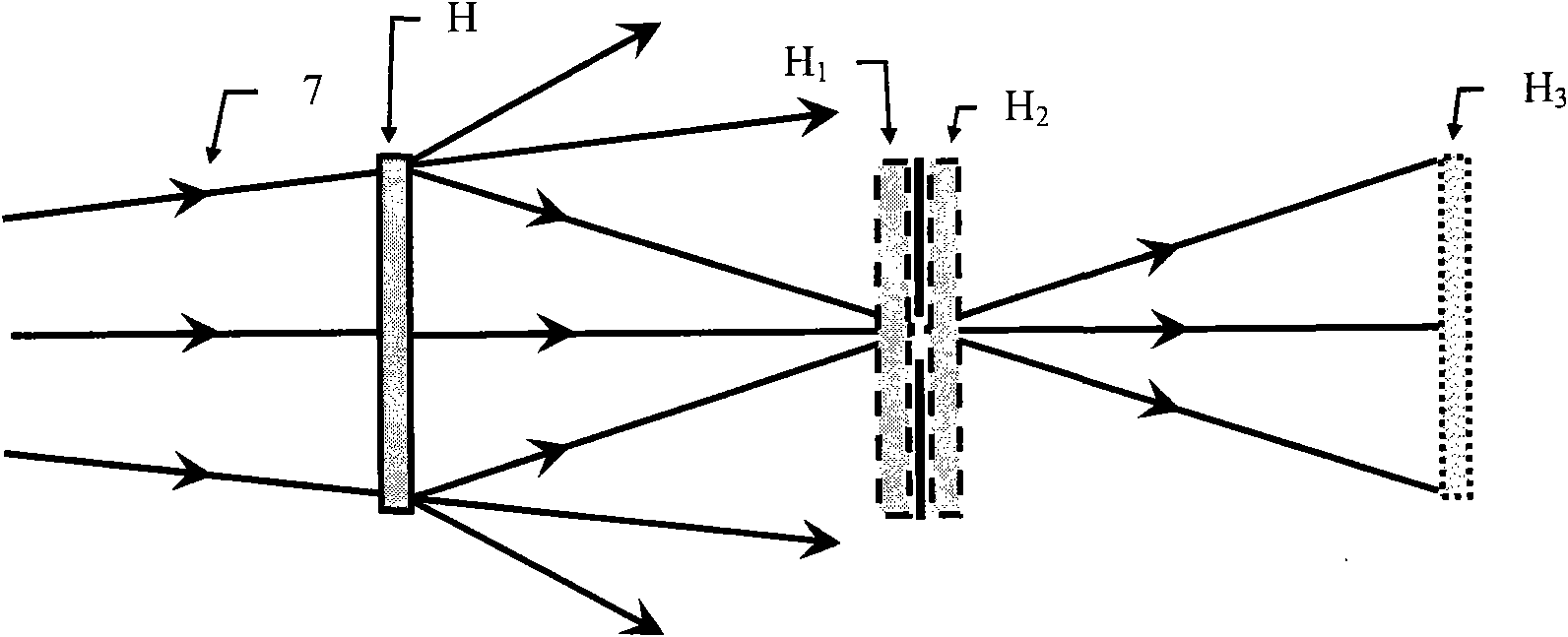
[0042] Example 1: See figure 1 and figure 2 . This embodiment is a coaxial digital holographic method that can effectively suppress zero-order diffraction and conjugate images for wooden chess pieces of diffuse objects. This embodiment includes a diffuse object to be measured 3, a CCD camera 5, and a small hole. Aperture 4, beam splitting device 6, laser beam 1 reflected or transmitted from diffuse object 3, reference light wave 2 coherent with laser beam 1, reproduced illumination light wave 7 conjugated to reference light wave 2, and holographic interferogram H, diffraction Pattern H 1 、H 2 and H 3 .
[0043] The working process of this embodiment is: a pinhole diaphragm 4 is set between the diffuse reflection type object 3 to be measured and the CCD camera 5 for digitally recording the holographic interferogram, and the laser light is irradiated and passed through the diffuse type object 3 or from the diffuse type The laser beam 1 reflected by the surface of the obje...
Embodiment 2
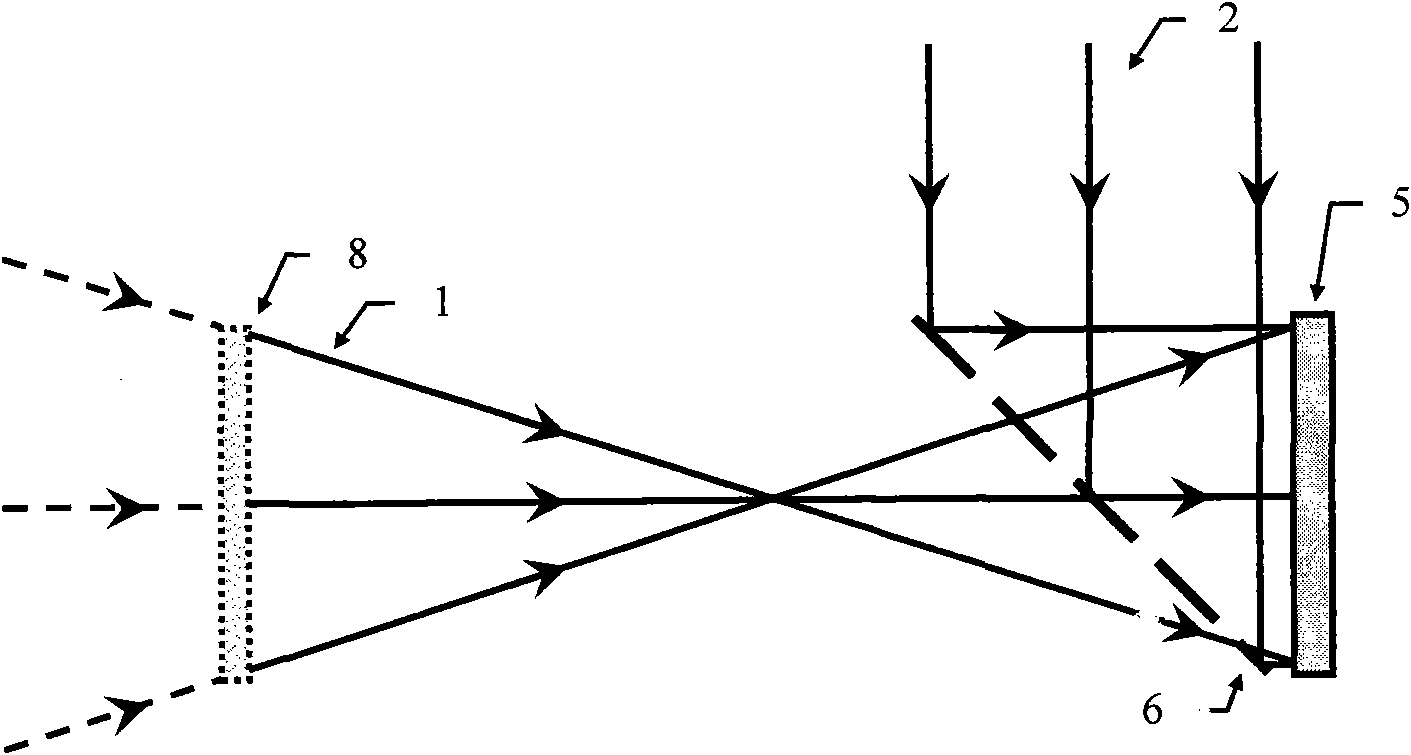
[0056] Example 2: See image 3 and Figure 4 . This embodiment is a coaxial digital holography method that can effectively suppress zero-order diffraction and conjugate images for transparent biological cell slices of transmission objects. This embodiment includes a transmission object to be measured 8, a CCD camera 5, a spectroscopic device 6, a transmission The converging spherical laser beam 1 of the diffuse object 8, the reference light wave 2 coherent with the laser beam 1, the reconstructed illumination light wave 7 conjugated with the reference light wave 2, and the holographic interferogram H, the diffraction pattern H 1 、H 2 and H 3 .
[0057] The working process of this embodiment is as follows: irradiate with the converging laser beam 1 and pass through the transmission type object 8 to be measured to reach the CCD camera 5 of the digitally recorded holographic interferogram to form an object light wave, and the object light wave interferes with the reference li...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3: See Figure 5 and Figure 6 . This embodiment is a coaxial digital holographic method that can effectively suppress zero-order diffraction and conjugate images for red blood cell slices of transmission-type objects. This embodiment includes a transmission-type object to be measured 8, an imaging lens 9, a CCD camera 5, and a spectroscopic device 6. The parallel laser beam 1 passing through the diffuse object 8, the reference light wave 2 coherent with the laser beam 1, the reproduced illumination light wave 7 conjugated with the reference light wave 2, and the holographic interferogram H, the diffraction pattern H 1 、H 2 、H 3 and H 4 .
[0070] The working process of this embodiment is: an imaging lens 9 is set between the transmission-type object 8 to be measured and the CCD camera 5 for digitally recording the holographic interferogram, and the parallel laser beam 1 is irradiated and passed through the object 8 to be measured, and converged through the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com