Method for recovering silicon carbide and polyethylene glycol cutting fluid from waste silicon wafer cutting fluid
A technology of cutting waste fluid and polyethylene glycol, applied in silicates, alkali metal silicates, lubricating compositions, etc., can solve the problems of increasing environmental burden, low purity of silicon carbide, and inability to reuse water, etc. The effect of saving energy consumption, simple recycling method and avoiding pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
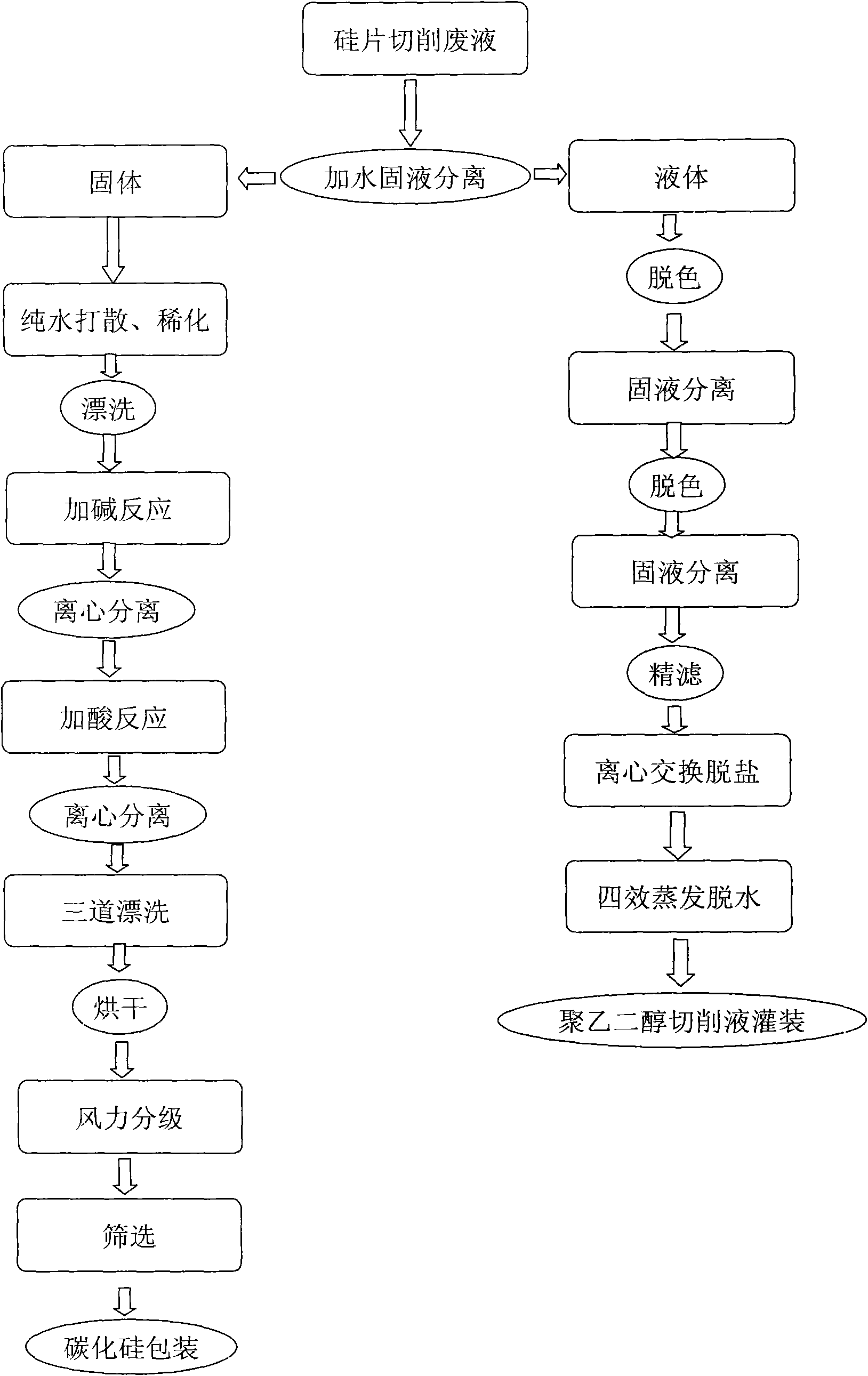
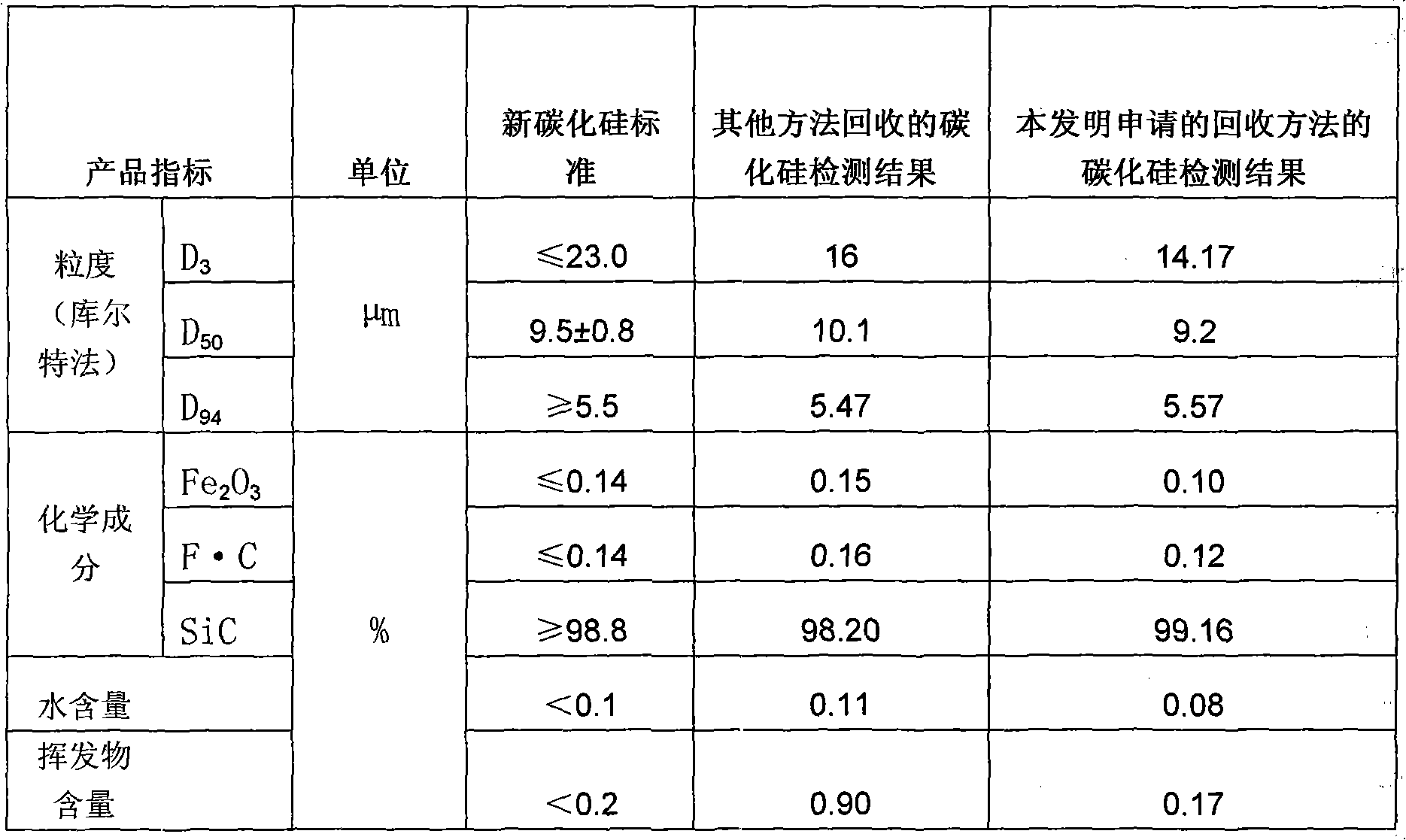
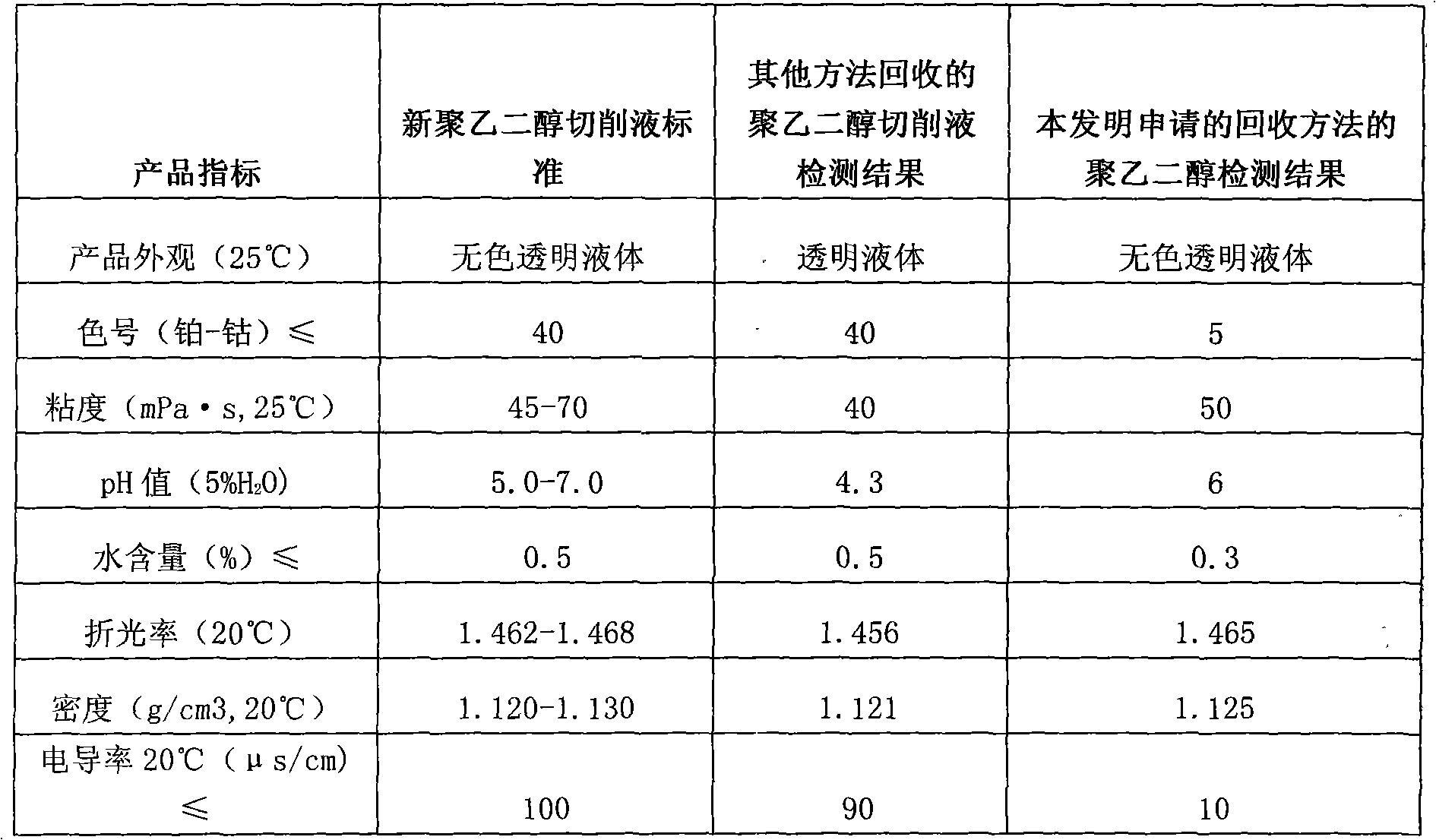
[0042]Weigh 1000g of silicon chip cutting waste liquid, stir it evenly with a stirrer, control its temperature at 25°C, add 10g of normal temperature tap water, the ratio of water addition is 1%, and pour the cutting waste liquid mixed with water into the filter press, The pressure is controlled at 0.5 bar; under this pressure, the filter press performs solid-liquid separation, and most of the solids such as silicon carbide, silicon, and iron remain in the filter cloth to form a filter cake, while most of the polyethylene glycol is cut Liquid and water permeate filter cloth to form filtrate, obtain 450g solid, 850g liquid: comprise most of silicon carbide in the solid (filter cake), silicon and a small amount of iron; In the liquid (filtrate), comprise all Polyethylene Glycol, Moisture and traces of silicon carbide, silicon;
[0043] The solid obtained by solid-liquid separation is added with a ratio of 1 times of 10°C pure water, and a uniform suspension is formed after stirr...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Weigh 2000g of silicon chip cutting waste liquid, stir it evenly with a stirrer, control its temperature at 60°C, add 1200g of distilled water, the proportion of water added is 60%, put the cutting waste liquid mixed with water into the filter press, press Control at 6bar; under this pressure, the filter press performs solid-liquid separation: most of the solids such as silicon carbide, silicon, and iron remain in the filter cloth to form a filter cake, while most of the polyethylene glycol cutting fluid and Water passes through the filter cloth to form a filtrate, and 120g of solid and 1600g of liquid are obtained: the solid contains most of the silicon carbide, silicon and a small amount of iron; the liquid contains all the polyethylene glycol, moisture and traces of silicon carbide and silicon;
[0054] The solid obtained through solid-liquid separation is added with 60°C pure water at a ratio of 5 times, and after stirring, the water is filtered by a belt filter, and...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Weigh 2000g of silicon chip cutting waste liquid, stir it evenly with a stirrer, control its temperature at 60°C, add 400g of distilled water, the proportion of water added is 40%, put the cutting waste liquid mixed with water into the filter press, press Control at 6bar; under this pressure, the filter press performs solid-liquid separation: most of the solids such as silicon carbide, silicon, and iron remain in the filter cloth to form a filter cake, while most of the polyethylene glycol cutting fluid and Water passes through the filter cloth to form a filtrate, and 120g of solid and 1600g of liquid are obtained: the solid contains most of the silicon carbide, silicon and a small amount of iron; the liquid contains all the polyethylene glycol, moisture and traces of silicon carbide and silicon;
[0064] After solid-liquid separation, add 60°C pure water with a ratio of 5 times. After stirring, use a belt filter to filter out the water. Add potassium hydroxide with a co...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap