Driving circuit of pixel and method for driving pixel
A driving circuit and pixel technology, applied in instruments, static indicators, etc., can solve problems such as difference in driving current, uneven brightness of the panel, and afterimage, so as to improve the brightness attenuation, improve the uneven brightness of the panel, and reduce the driving current. the effect of the difference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
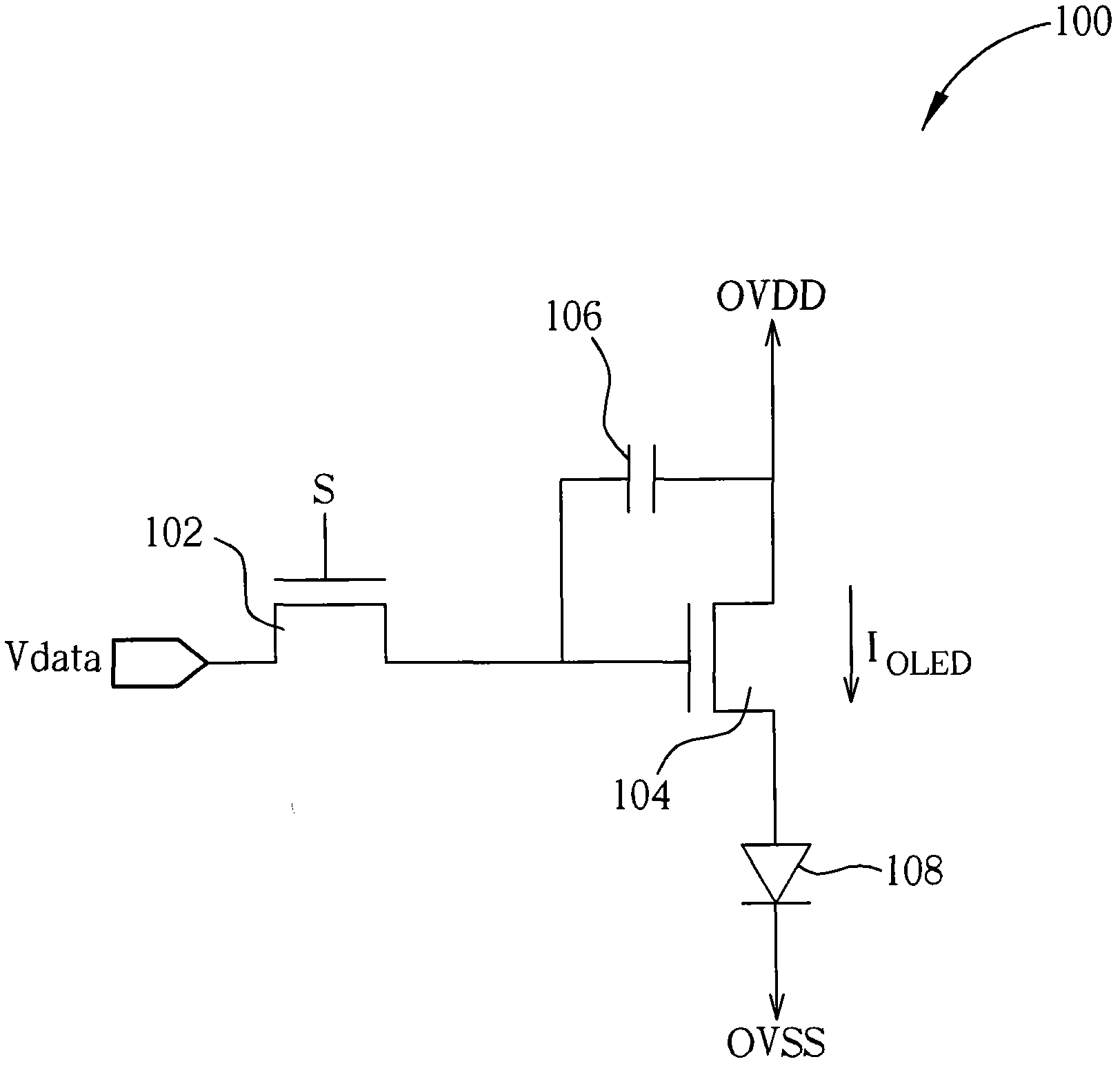
[0035] Please refer to figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic diagram illustrating a pixel driving circuit 100 of an active matrix organic light emitting diode (active matrix OLED, AMOLED) display. Such as figure 1 As shown, the driving circuit 100 is a 2T1C circuit, including two N-type thin film transistors 102 , 104 , a capacitor 106 and an organic light emitting diode 108 . The N-type thin film transistor 102 is a switch, and the N-type thin film transistor 104 provides the driving current I of the organic light emitting diode 108. OLED , wherein the OVSS terminals of the driving circuit 100 of each pixel on the panel are electrically connected together, and the OVDD terminals are also electrically connected together. When the driving circuit 100 drives the pixels, there will be a driving current I at the OVSS end. OLED flow past.
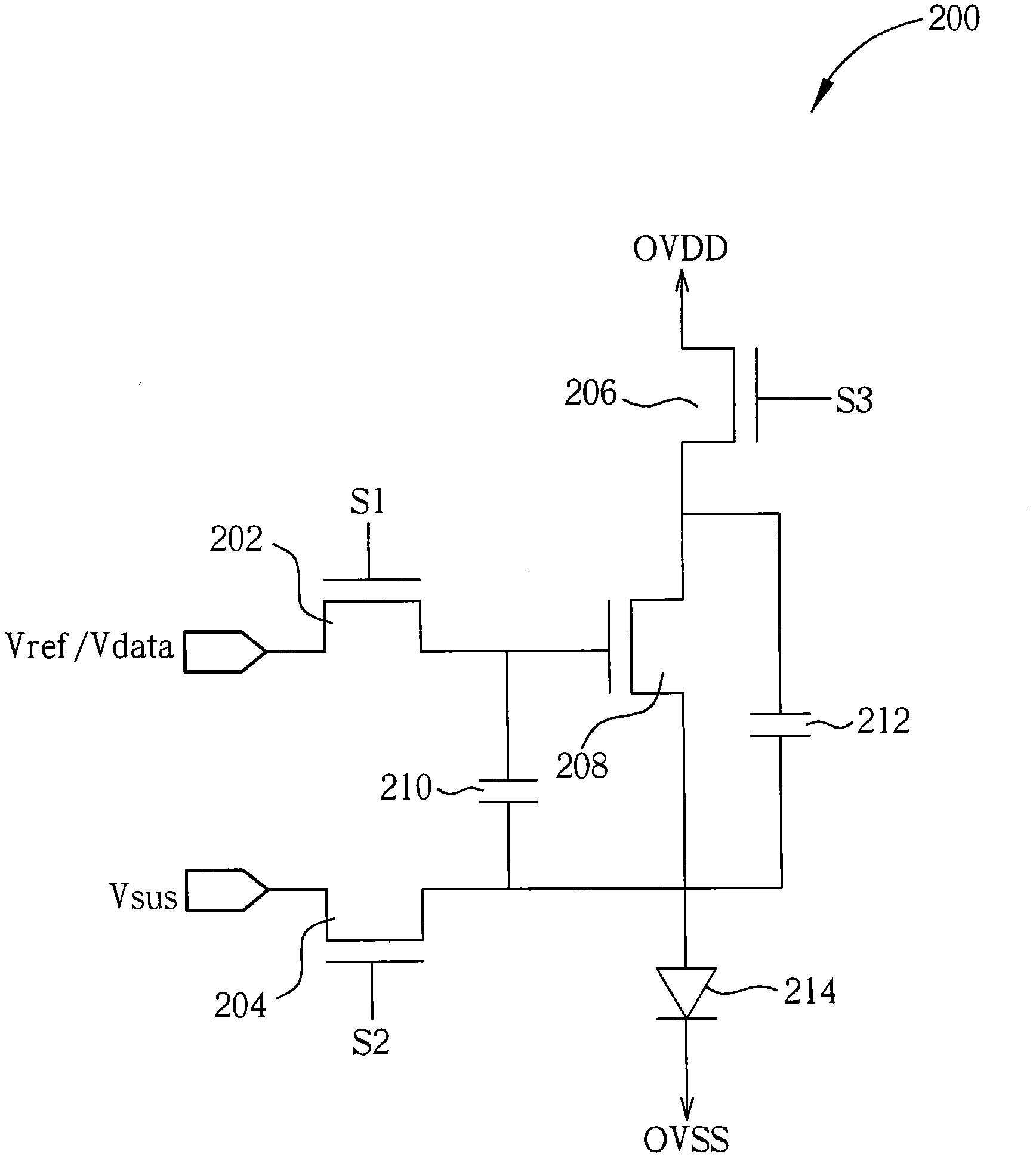
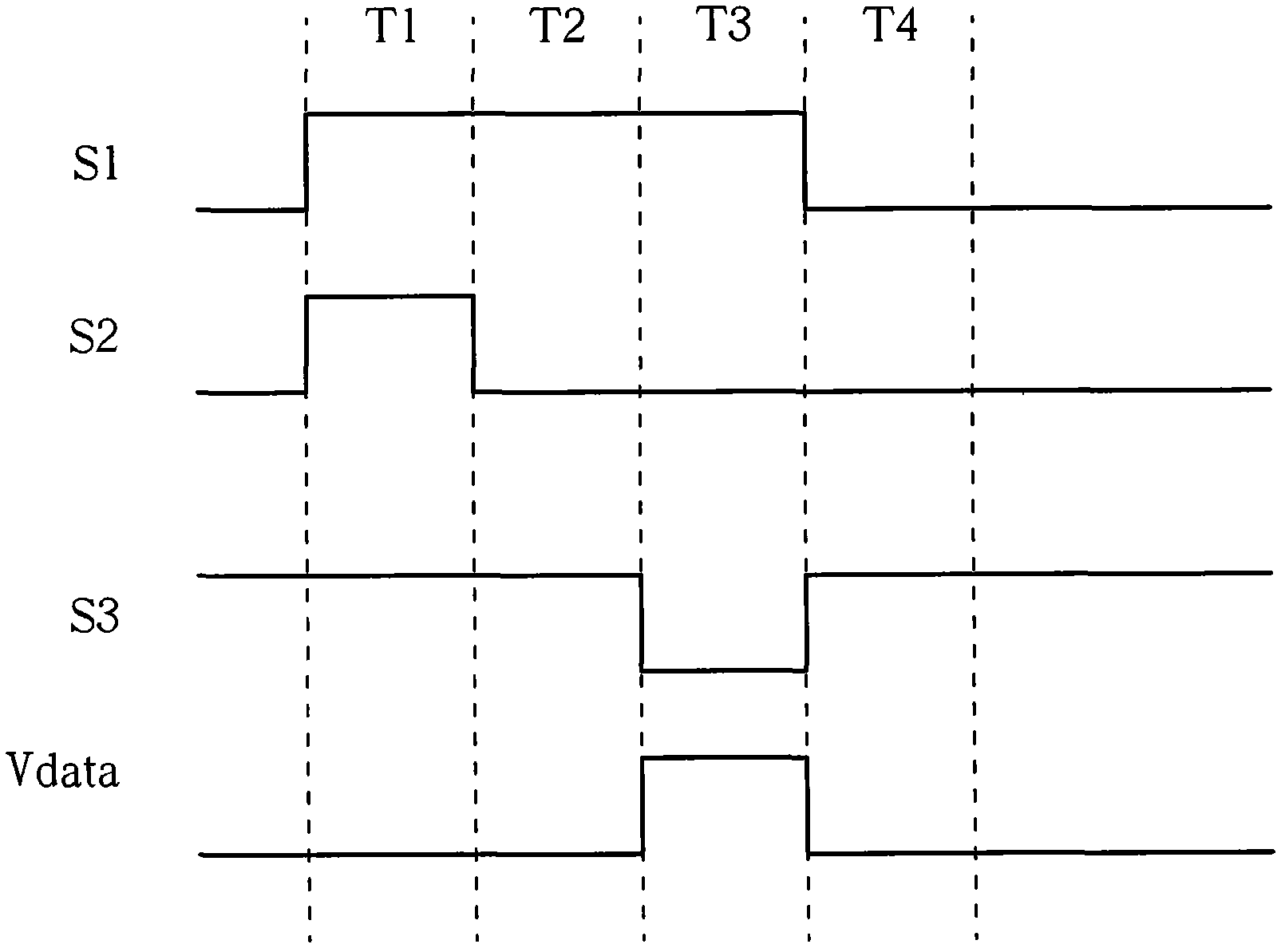
[0036] Please refer to figure 2 , figure 2 A schematic diagram illustrating a pixel driving circuit 200 of an active matrix organic li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com