Double reciprocation pump
A reciprocating and moving technology, applied in the direction of pumps, piston pumps, pump components, etc., can solve the problems of unstable flow, increased liquid inertia resistance, mixing, etc., and achieve the effect of suppressing pulsation and stabilizing pump action
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
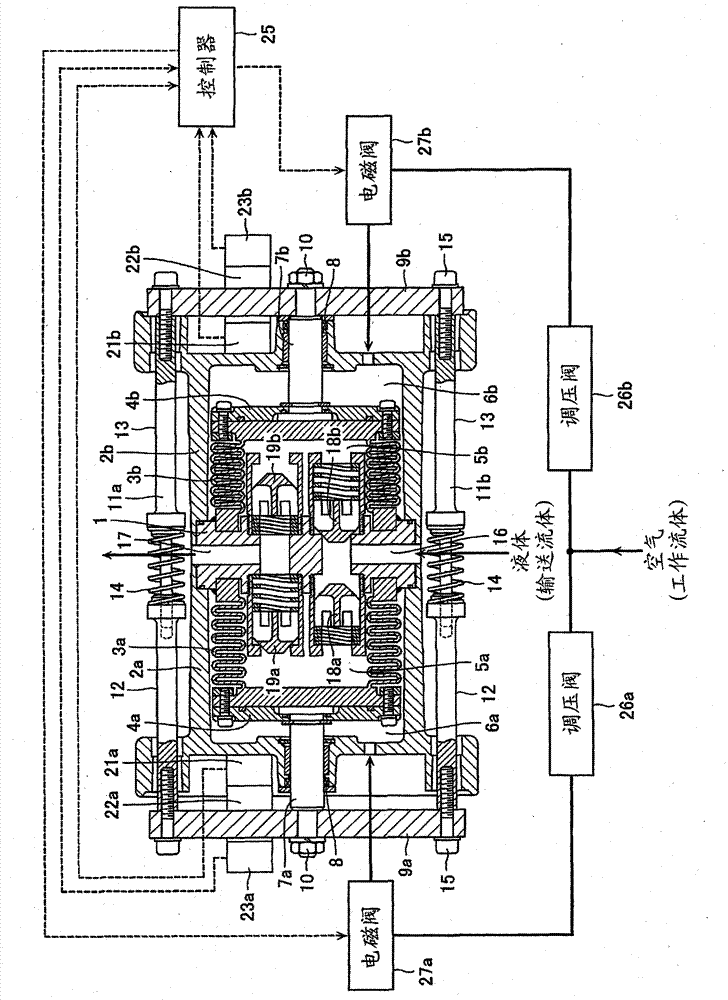
[0036] figure 1 It is a sectional view of a double reciprocating bellows pump according to the first embodiment of the present invention and a view showing its peripheral mechanism. Bottomed cylindrical air cylinders 2a, 2b serving as casing members are coaxially arranged on both sides of the pump head 1 arranged in the center, and a pair of spaces are formed inside the air cylinders 2a, 2b. Bottomed cylindrical bellows 3a, 3b are arranged coaxially in these spaces, respectively. Open ends of the bellows 3a, 3b are fixed to the pump head 1, and shaft fixing plates 4a, 4b are fixed to the bottoms of the bellows 3a, 3b. The inner side of the bellows 3a, 3b is used as the pump chamber 5a, 5b, and the outer side is used as the working chamber 6a, 6b, whereby the bellows 3a, 3b constitute a movable partition member for partitioning the internal space of the cylinder 2a, 2b.
[0037]One ends of shafts 7a, 7b extending coaxially are fixed to the shaft fixing plates 4a, 4b. The oth...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
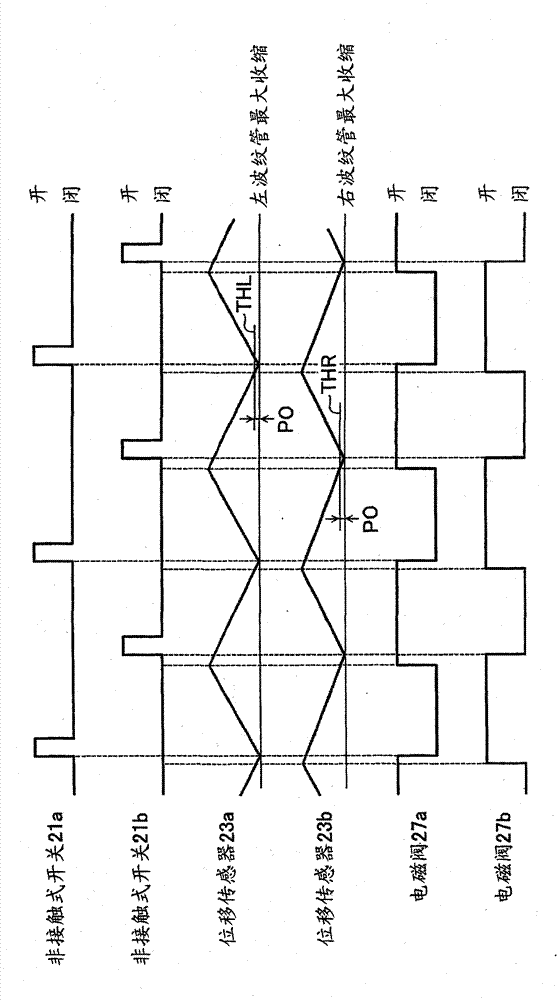
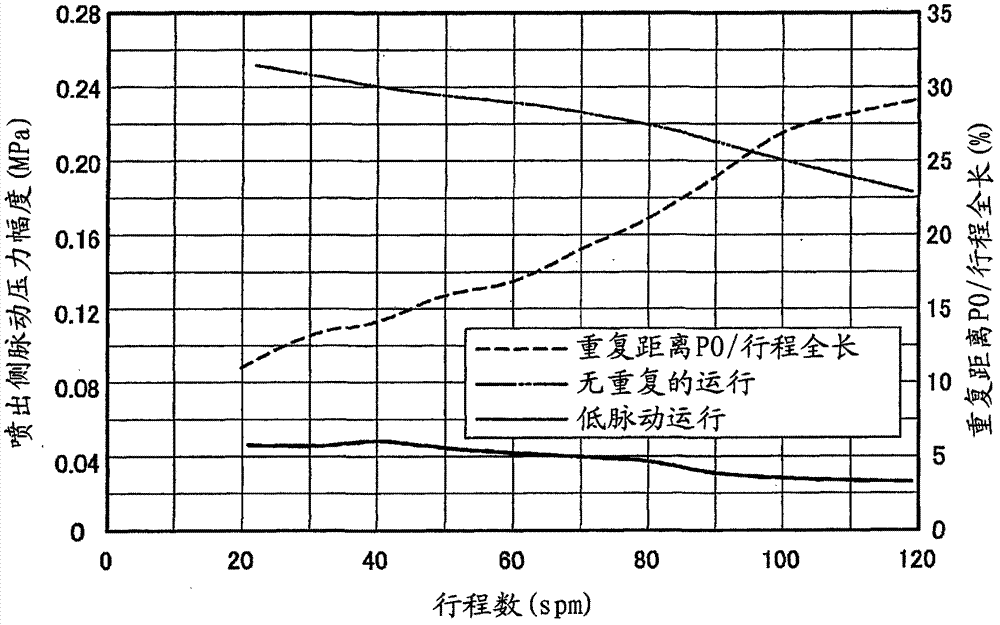
[0051] In the previous embodiments, it is not specifically mentioned that the repetition rate has a critical value, but if the repetition rate is too large, the force advancing one of the movable partition parts and the force advancing the other movable partition part will oppose and cause Pump action stops. Thus, the repetition rate at which pump action stops will be referred to hereinafter as the "critical repetition rate".
[0052] Figure 3B The critical repetition rate for each number of strokes under a certain condition is shown in . In order not to stop the operation of the pump, it is preferable to control the operation of the pump so as not to exceed the critical repetition rate, and to maintain the repetition rate within the range of pulsation reduction (pulsation elimination) indicated by the hatching in the figure. More preferably, the repetition rate is preferably maintained at a repetition rate that is several percent (eg, 1-3%) lower than the critical repetiti...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0059] Figure 4 It is a partial sectional view of the connecting shaft 31a (31b) used in the double reciprocating pump according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
[0060] In the first embodiment, the coil spring 14 is used as the telescopic member connecting the shafts 11a and 11b, but in this embodiment, an air shock absorber is used as the telescopic member. That is, the connection shaft 31a (31b) is comprised from the shaft part 32,33 and the air damper part 34 which connects them. The air damper portion 34 is composed of an air cylinder 35 attached to the end of the shaft portion 33 and a piston 36 attached to the end of the shaft portion 32 , and air of a predetermined pressure is supplied to the air cylinder 35 through the air inlet 37 .
[0061] According to the present embodiment, not only the optimal repetition rate but also the optimal elastic pressure (barne pressure) can be easily set. In addition, it is also possible to vary the elastic pressur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com