Zernike moment-based rapid image comparison method
A technology of image comparison and alignment method, which is applied in image analysis, image data processing, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to obtain high-level image content, color features that cannot capture local features well, and lack of mathematical models
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
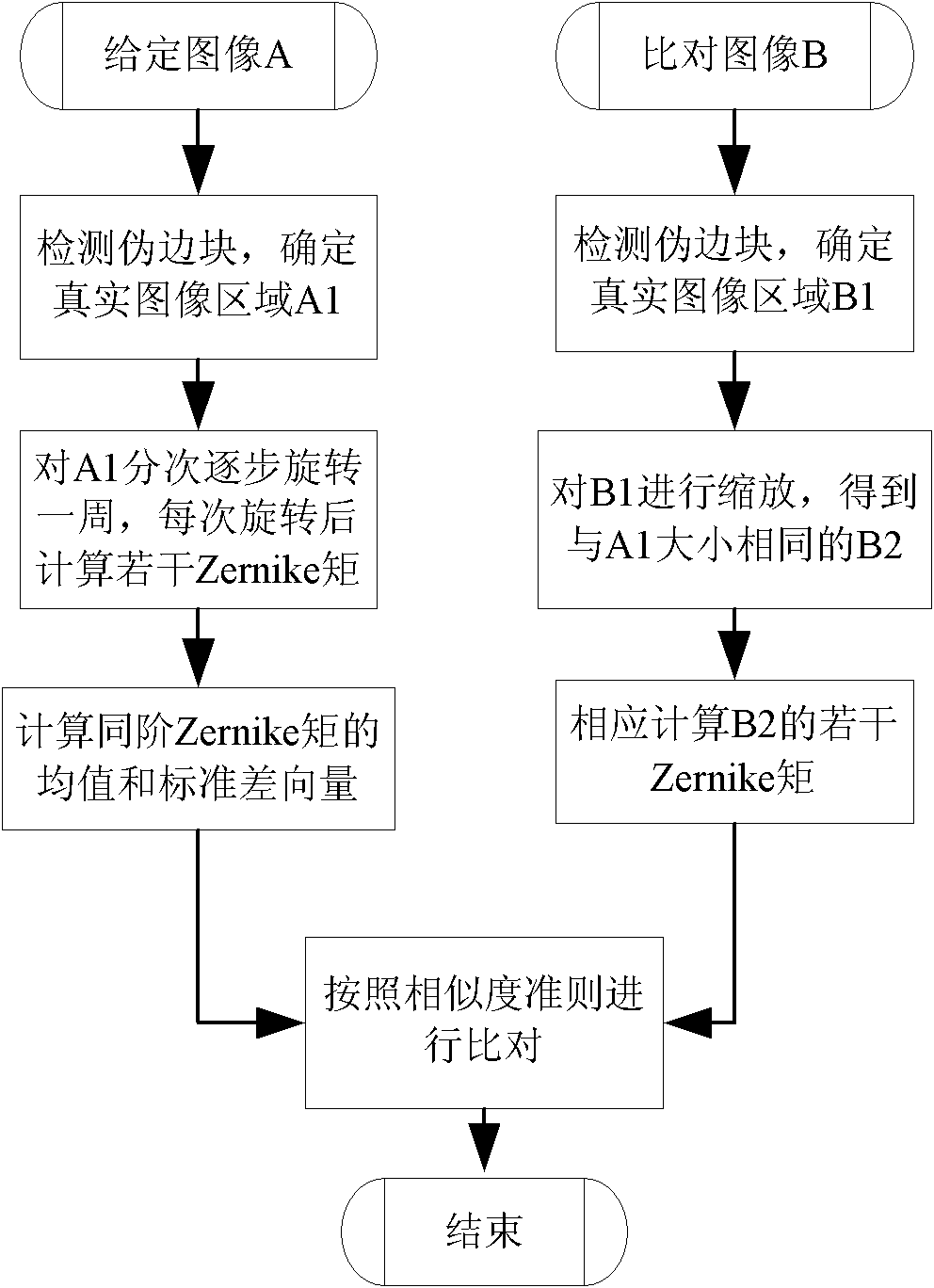
[0062] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of this example are as follows:
[0063] The first step is to detect the false edge blocks that may exist in the given image and the comparison image, and determine the real area.
[0064] (1.1) Scan the pixel values near the four sides of the given image and compare the statistical distribution. Usually, the distribution of pixel values in normal natural images should be relatively uniform, and no one pixel value will occupy the majority. In the case of proportion, if the occurrence frequency of a certain pixel value is higher than 50%, it is considered that the pixel value is the pixel value of the pseudo edge block caused by rotation, and the pixel connected area near the four edges with the pixel value is considered as a pseudo edge piece;
[0065] (1.2) Take the pixel value of the given image and the pseudo-edge block of the comparison image as the critical threshold, and then perform binarization processing to obt...
Embodiment 2
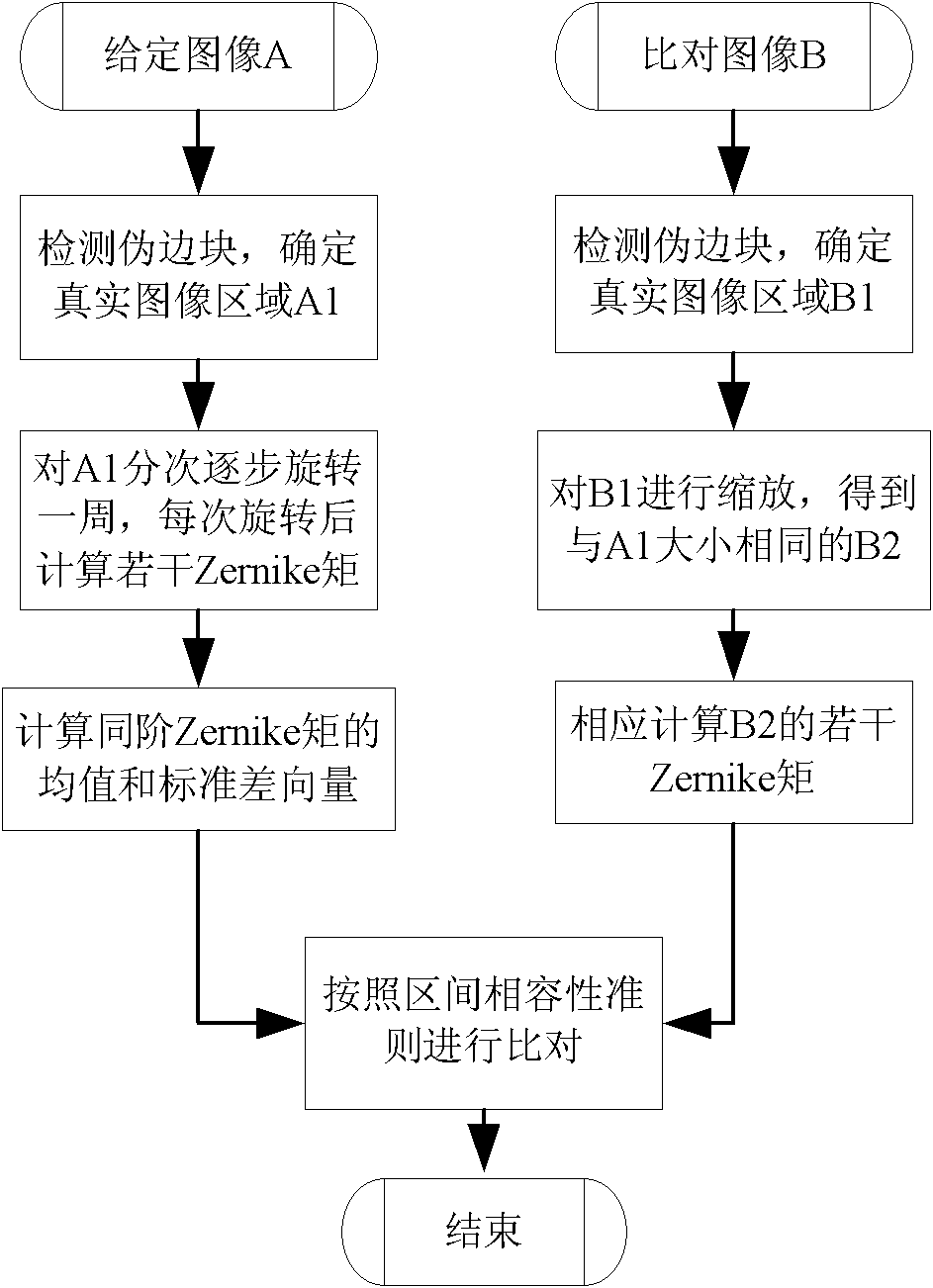
[0103] refer to figure 2 , the implementation steps of this example are as follows:
[0104] The first four steps are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0105] The fifth step is to use interval compatibility for comparison
[0106] refer to Figure 4 , the specific implementation of this step is as follows:
[0107] (5a) According to the mean vector of the Zernike moment value of the given image, the standard deviation vector and a set weight α (α>0), an allowable interval P of the i-th Zernike moment value of the given image is obtained:
[0108] P ⊆ [ K ‾ i - α D i , K ‾ i + α D i ] ; i = 1,2 , L , T ;
[0109] T represents the number of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com