Sub-surface damage detection method based on temperature field finite element analysis and simulation
A sub-surface damage and detection method technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and low precision, and achieve the effects of low cost, simple equipment operation and short detection cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
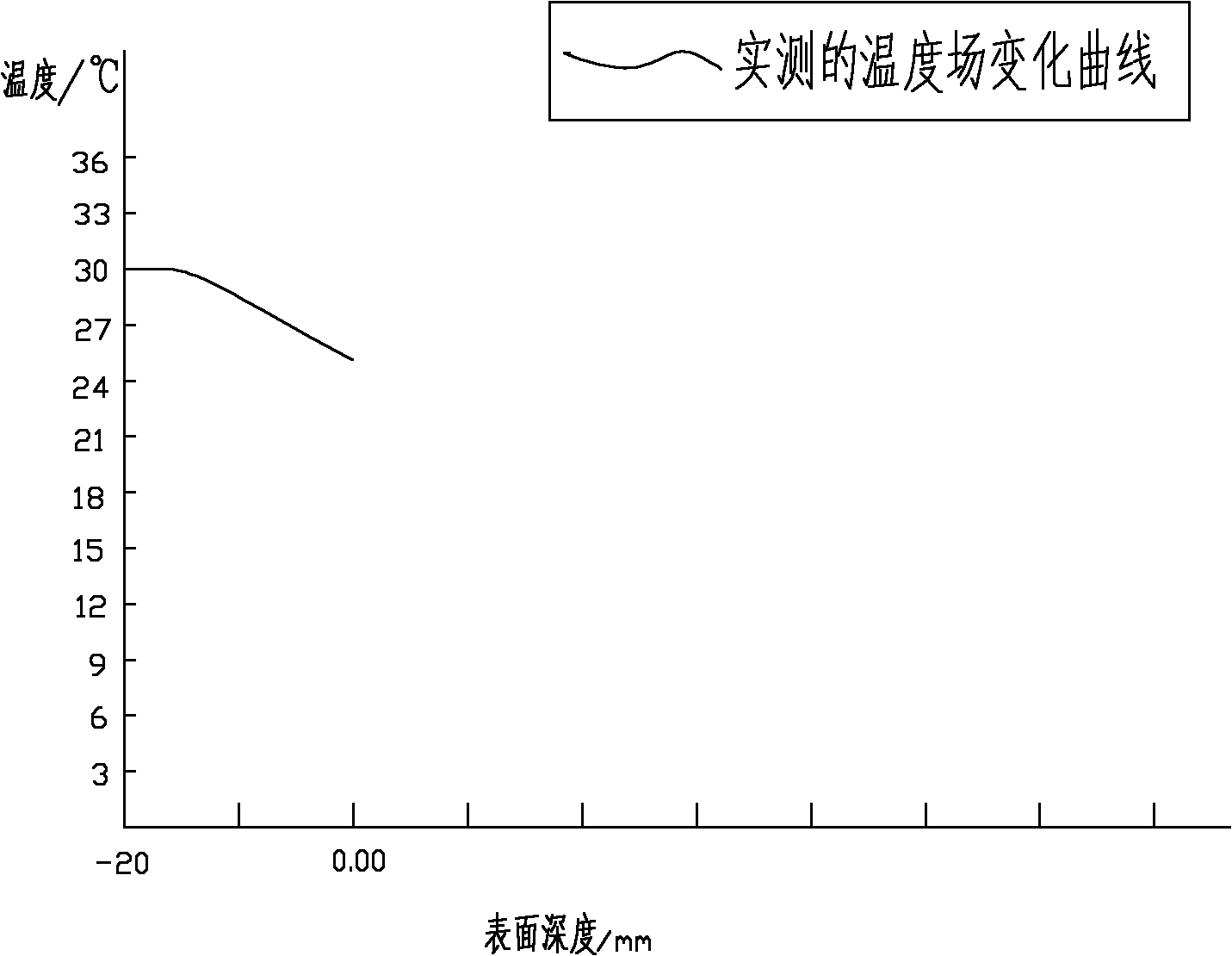
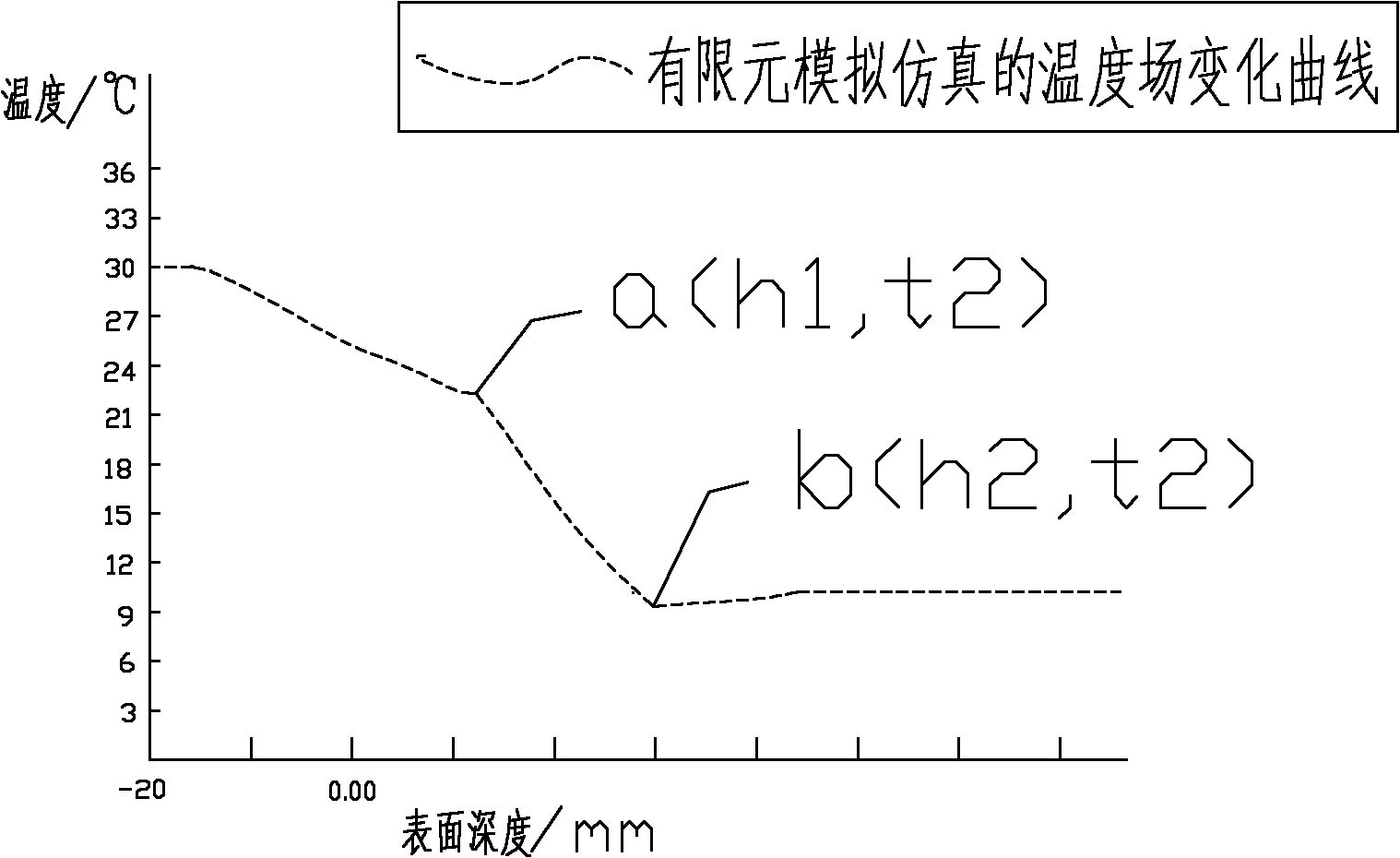
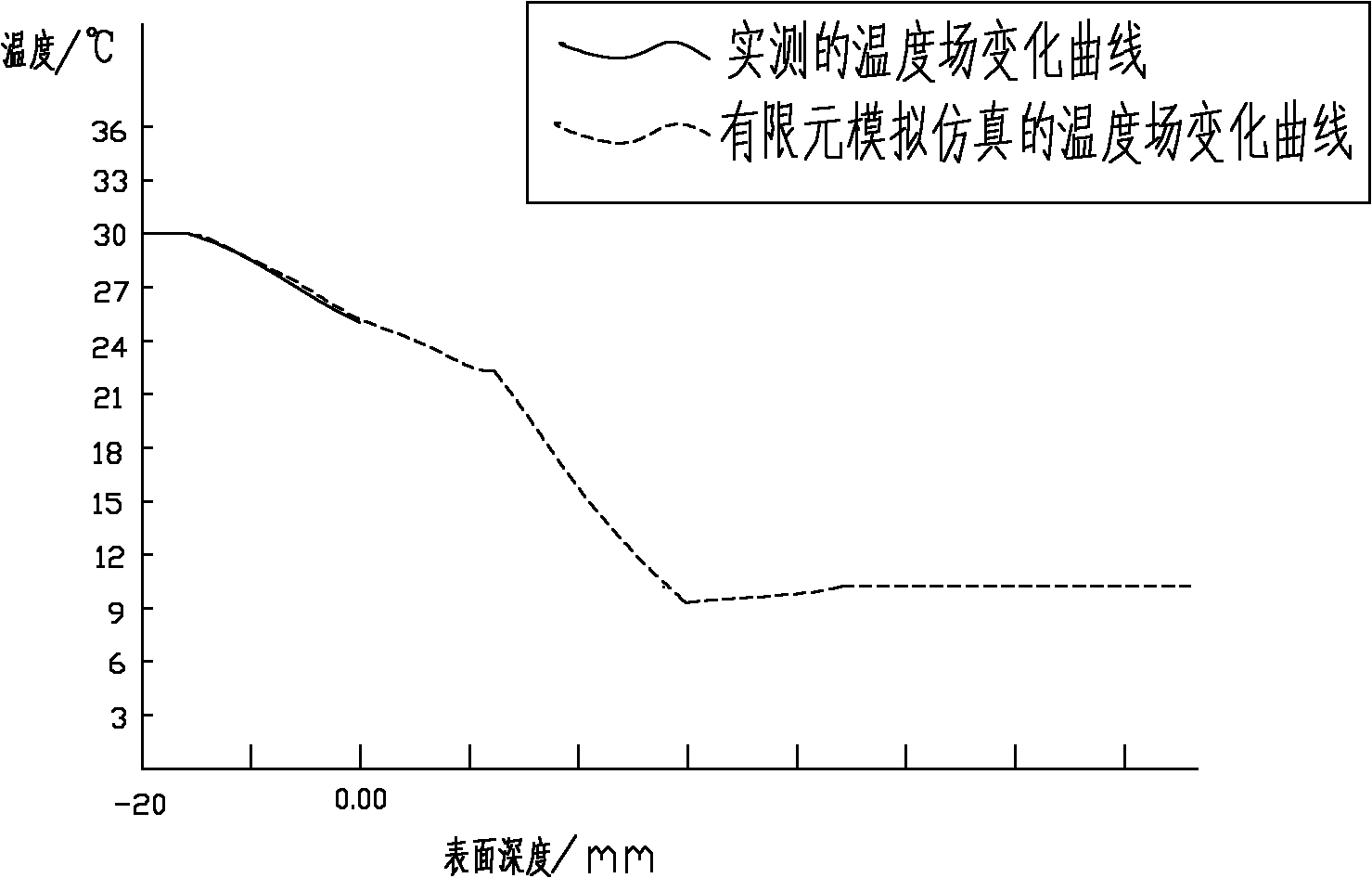
[0022] The depth of the subsurface damage layer produced by the grinding process of optical materials can directly affect the long-term stability, service strength and laser damage resistance threshold of optical parts. Therefore, it is extremely important to non-destructively detect subsurface damage of optical parts. The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with specific examples.
[0023] The subsurface damage detection method based on the finite element analysis and simulation of the temperature field includes the following steps:
[0024] (1) Set the heating constant temperature source T1 (10°C) on the upper surface of the optical k9 glass part, and set the heating constant temperature source T2 (30°C) on the lower surface with a heating plate, T2>T1, the temperature difference between the upper and lower surfaces of the constant temperature source is 20°C, Heat for a period of time until the heat transfer reaches a dynamic equilibri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com