Patents
Literature
80 results about "Inelastic deformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
For the amorphous polymers, the volumetric strain ceases to decrease after the yield peak and is held constant in spite of an increase in the inelastic deformation. This inelastic deformation is in the form of crazes, which usually initiate at a stress concentration site.
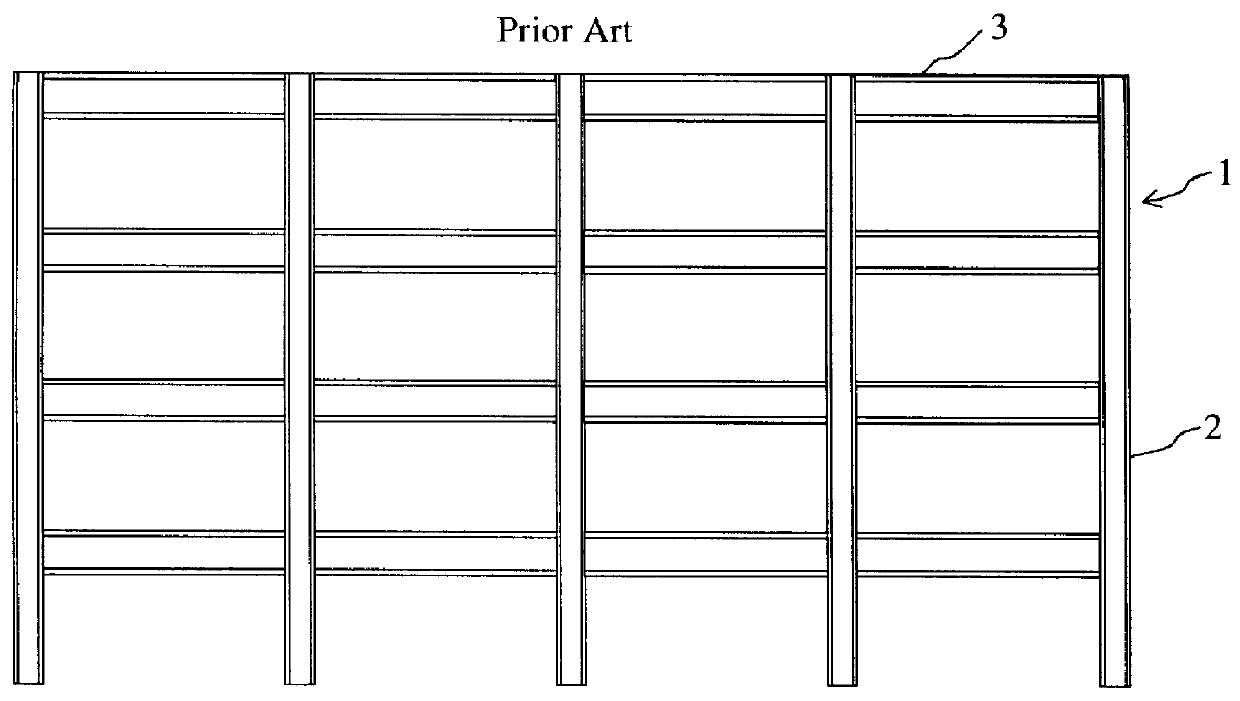
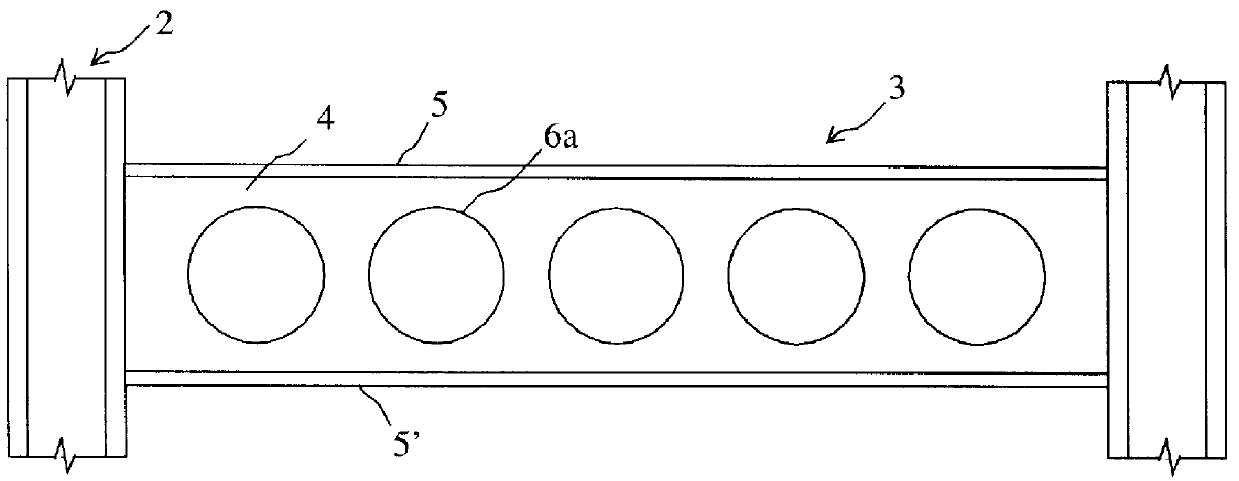
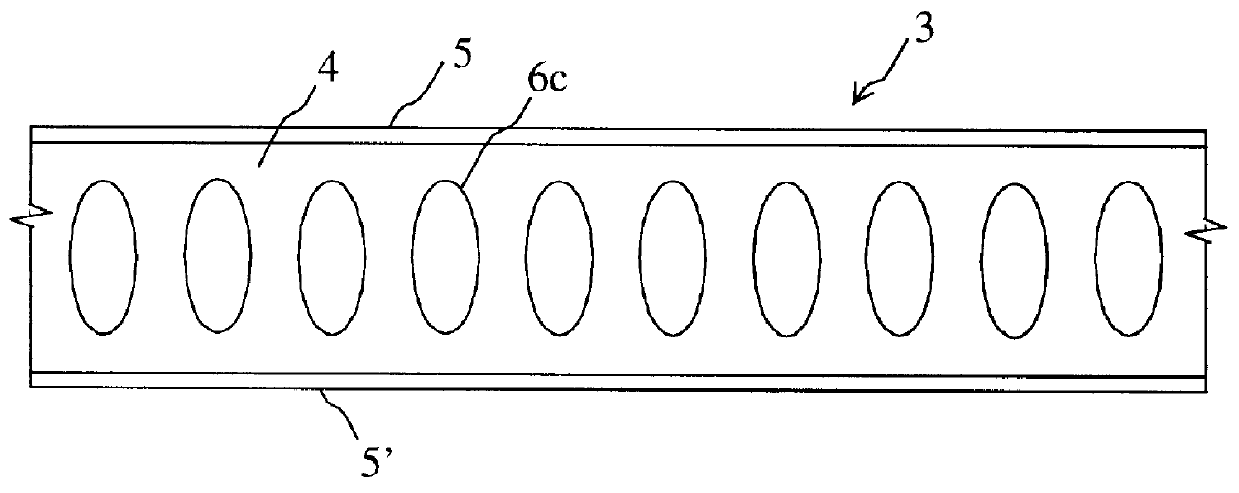
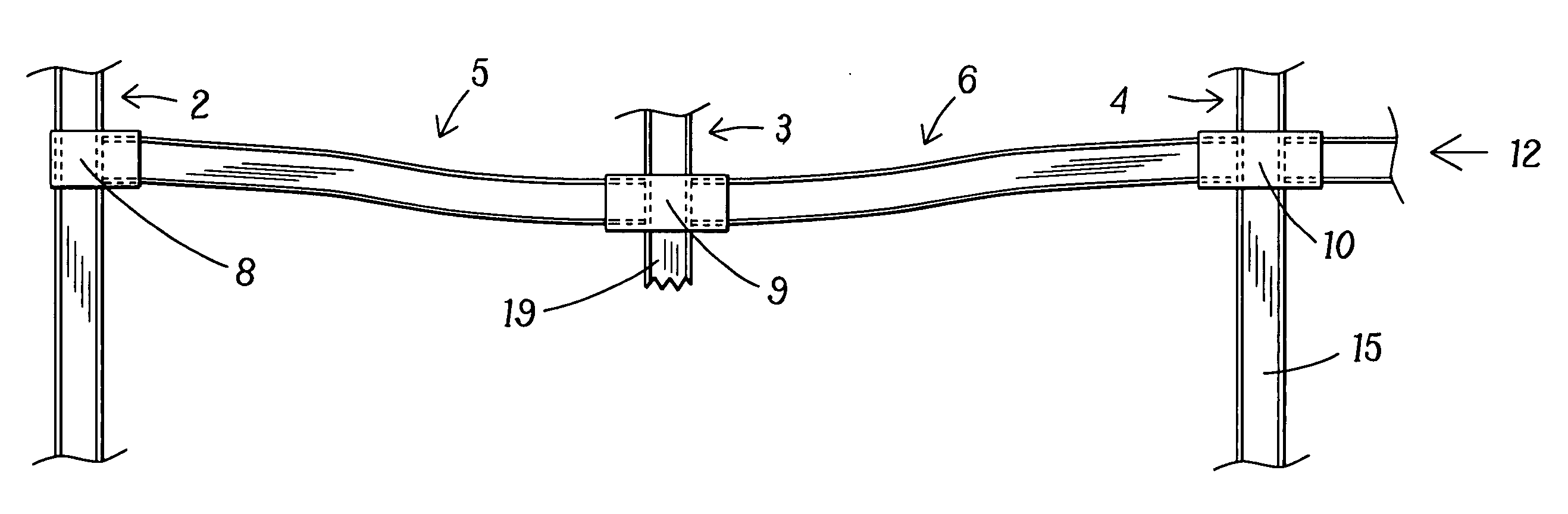
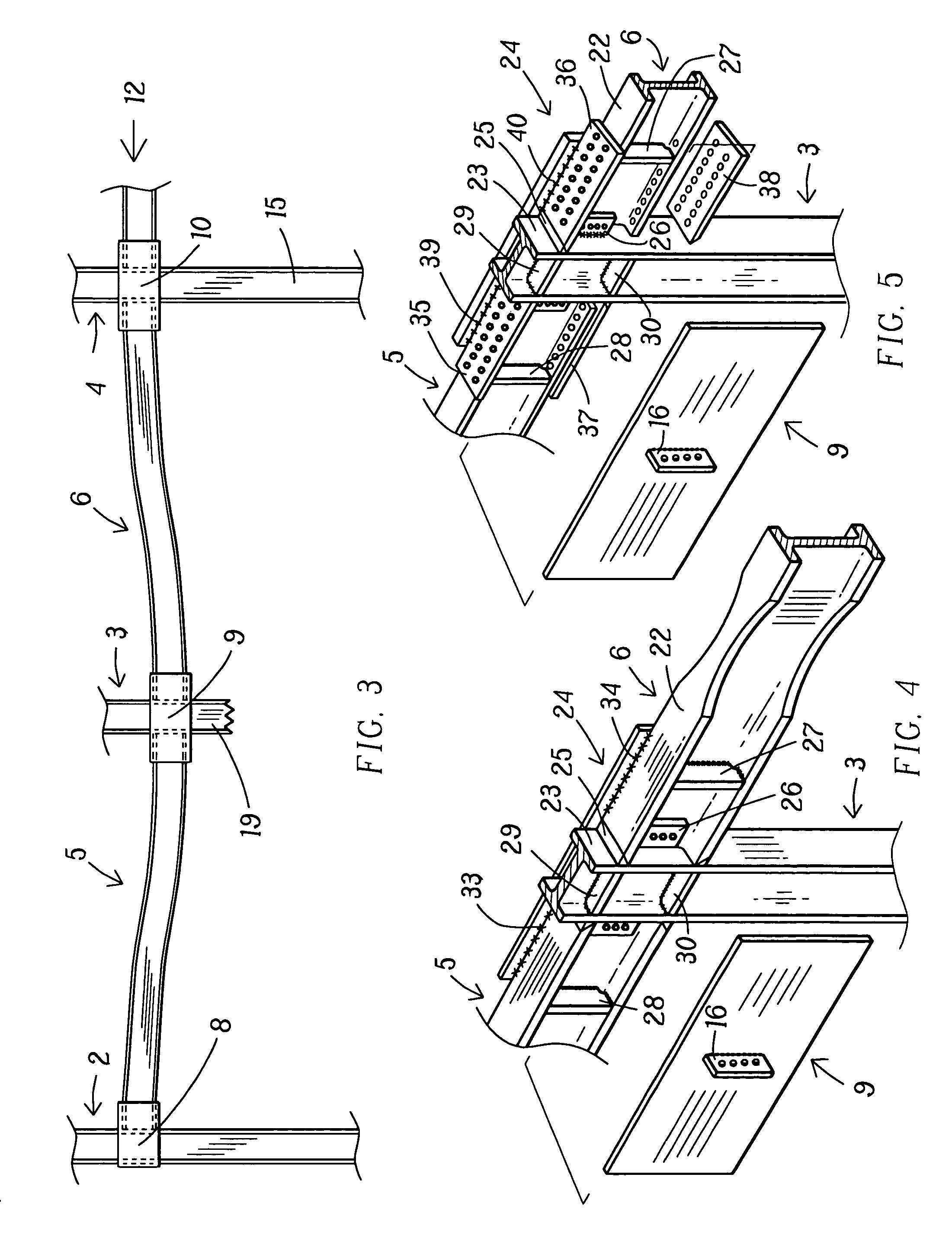
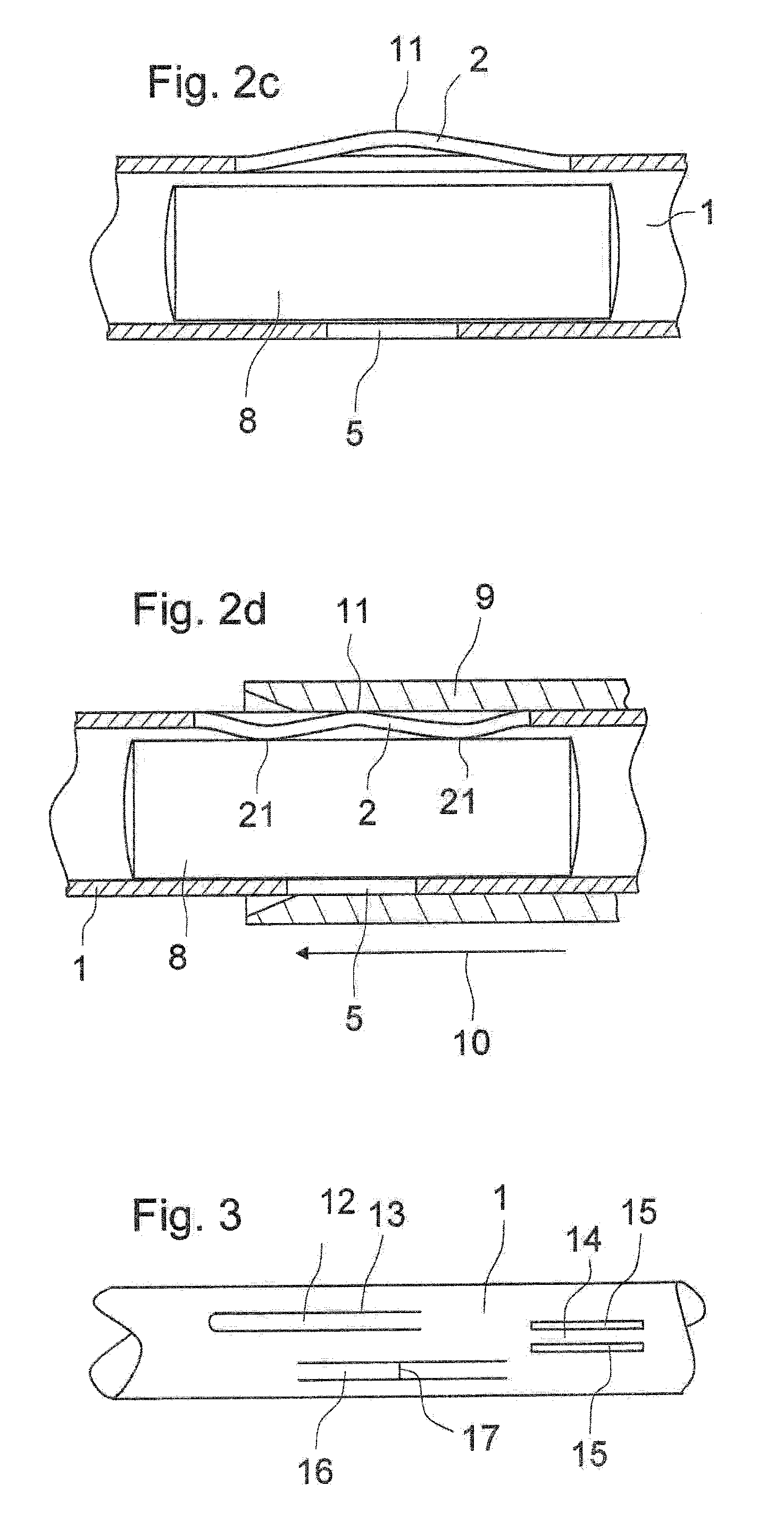
Moment-resistant structure, sustainer and method of resisting episodic loads
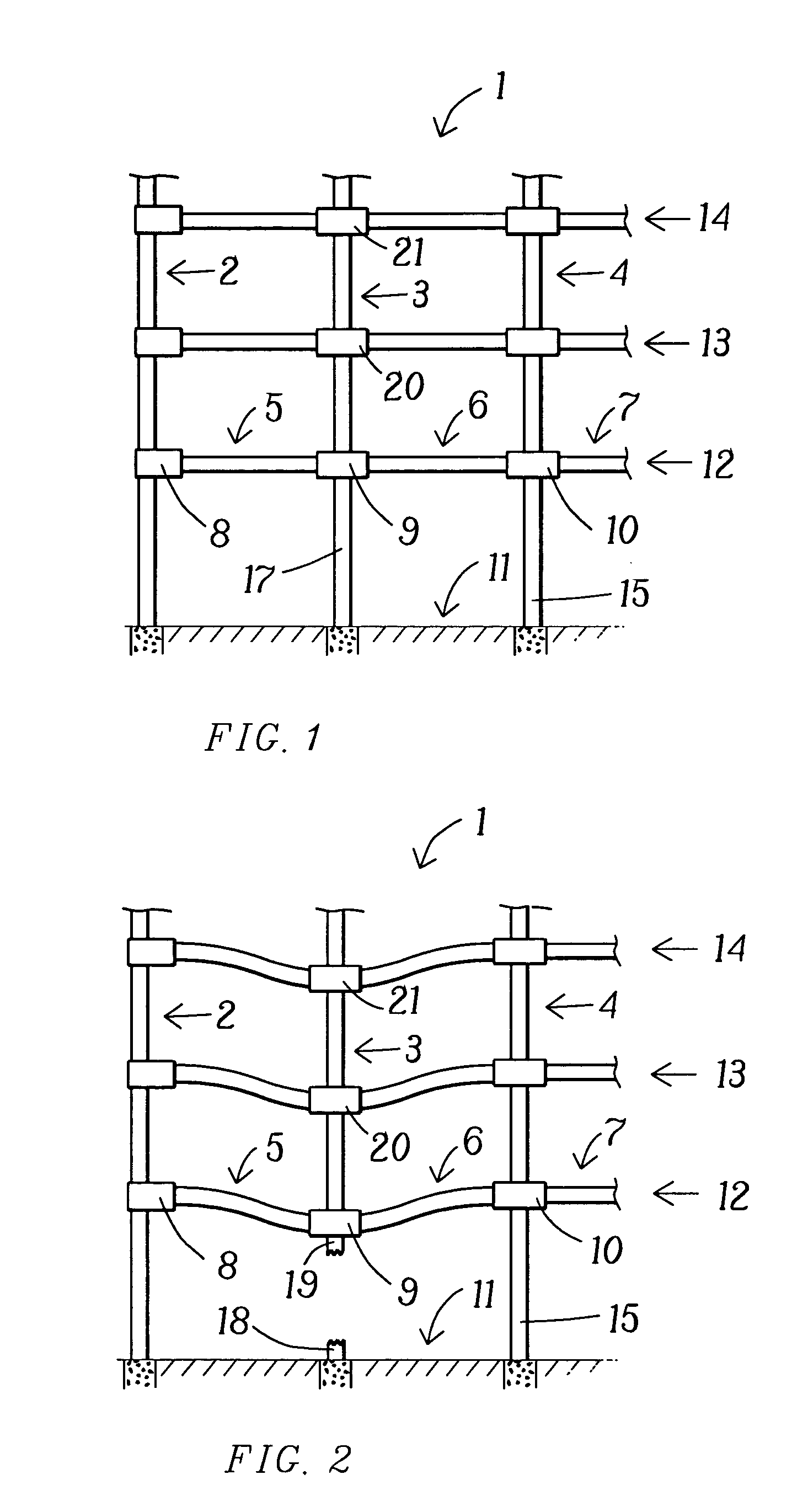
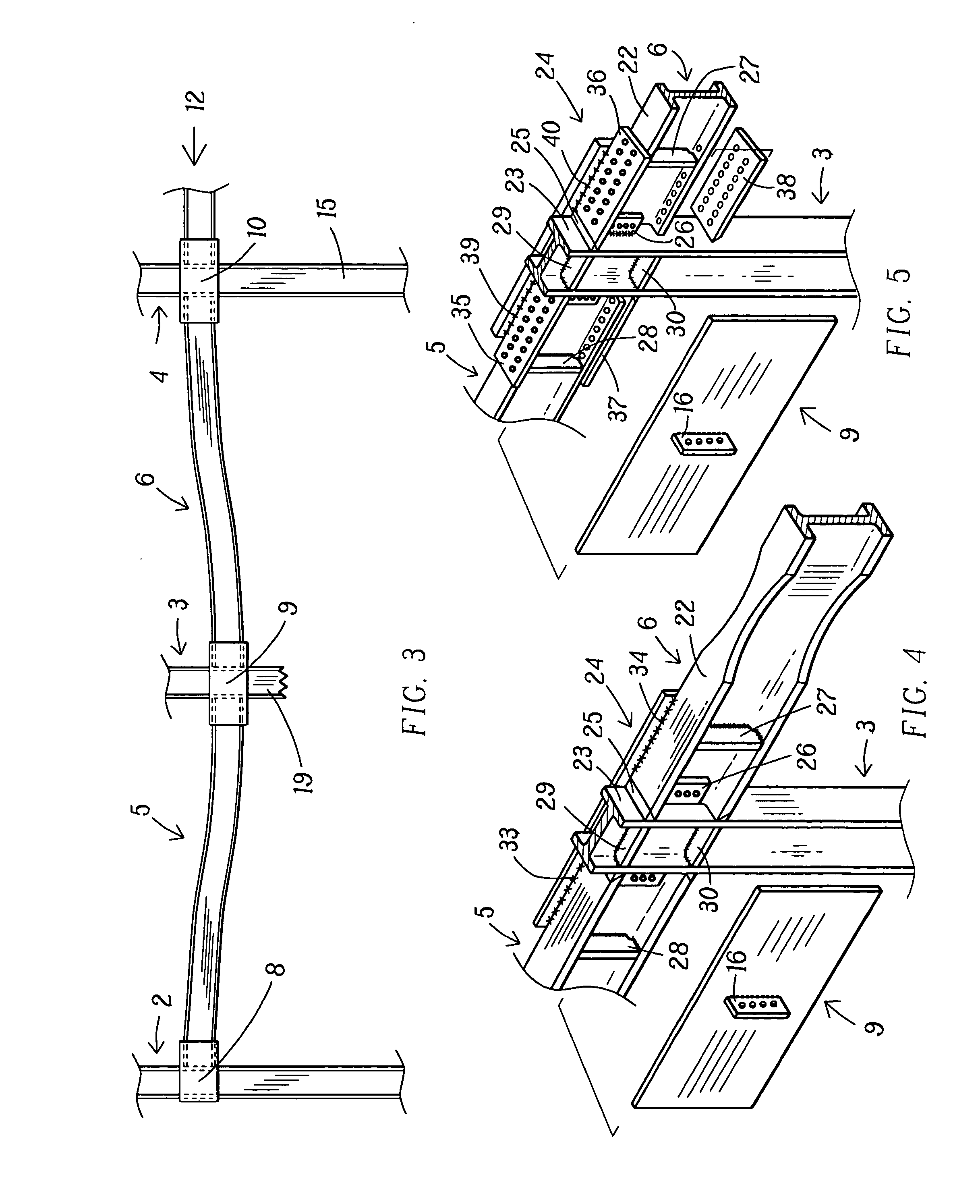
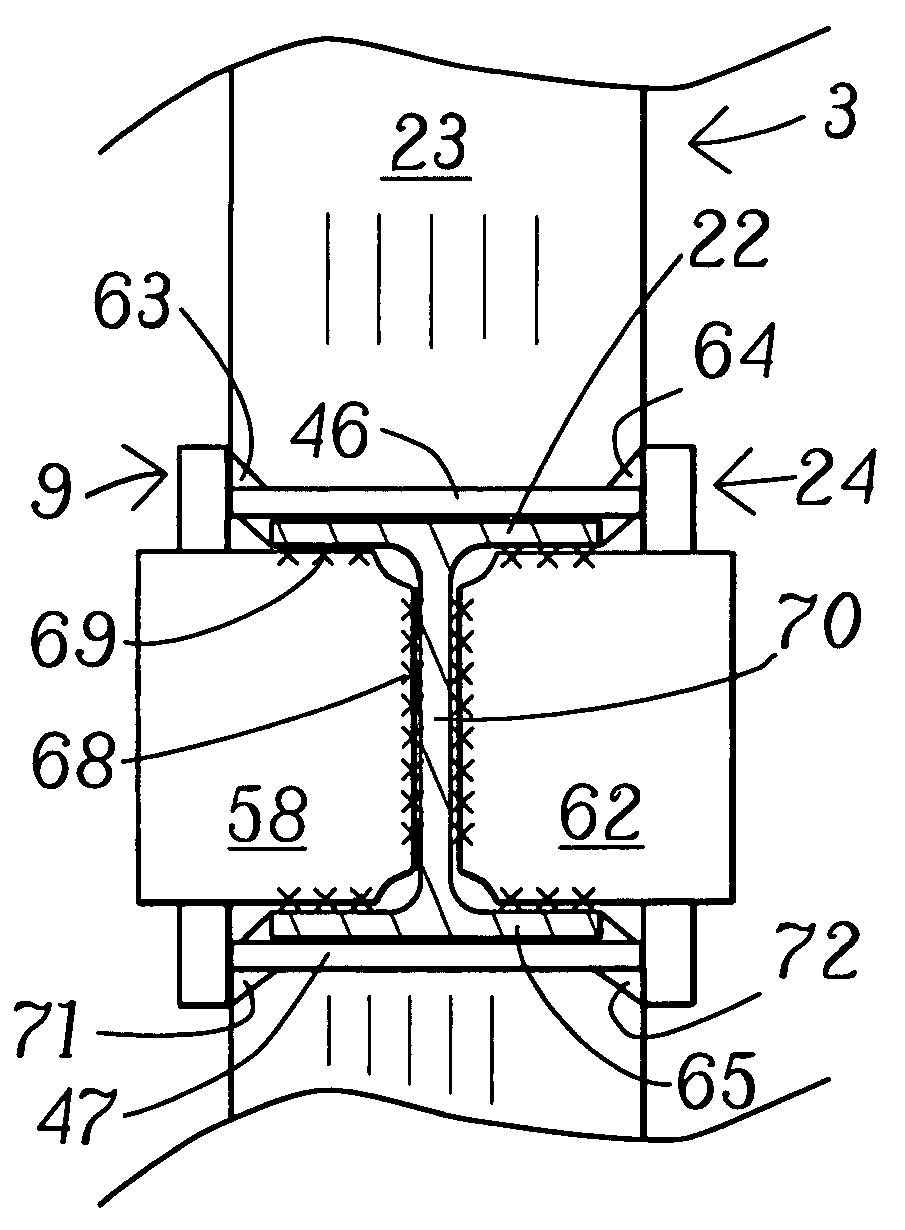
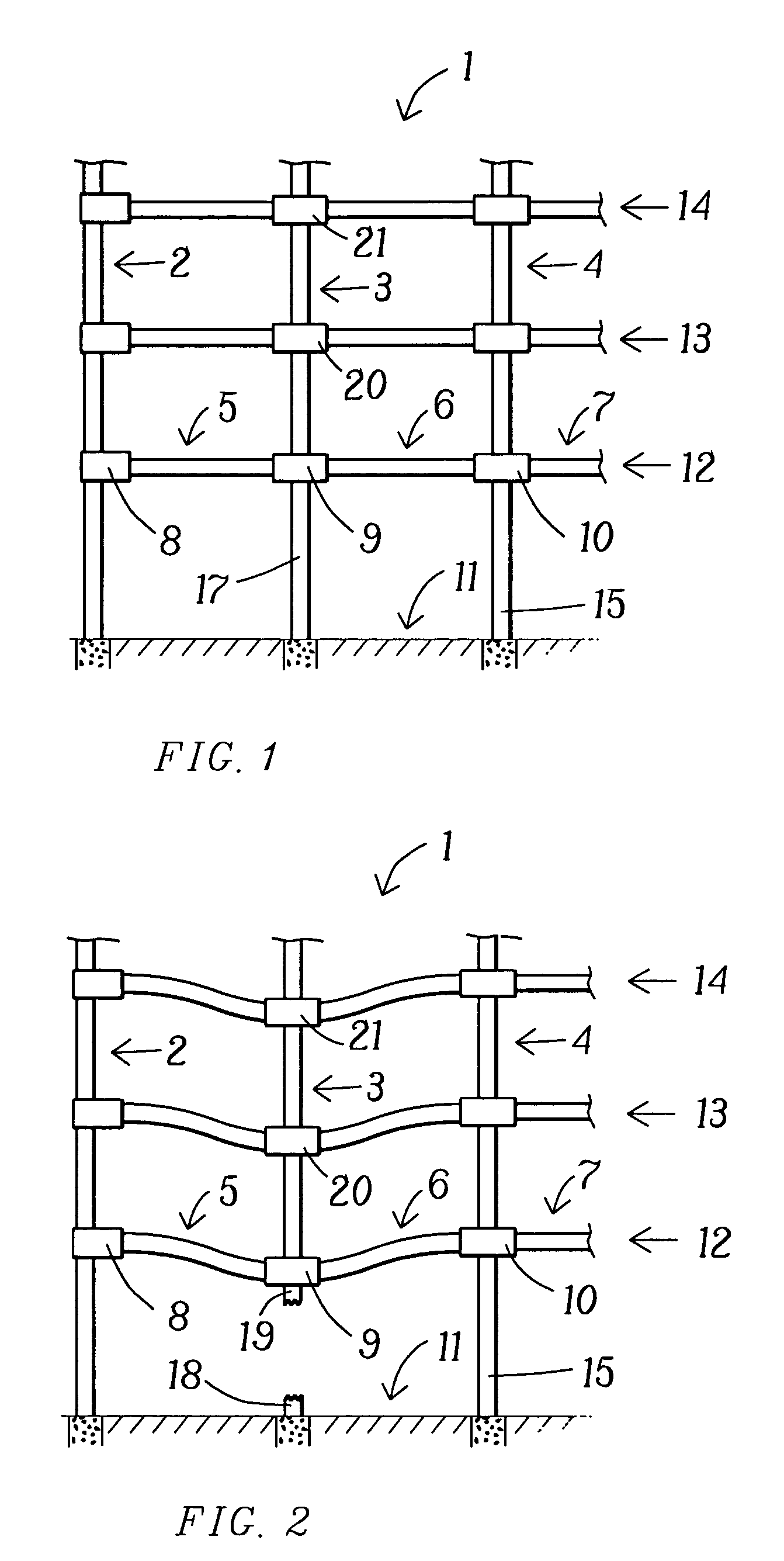
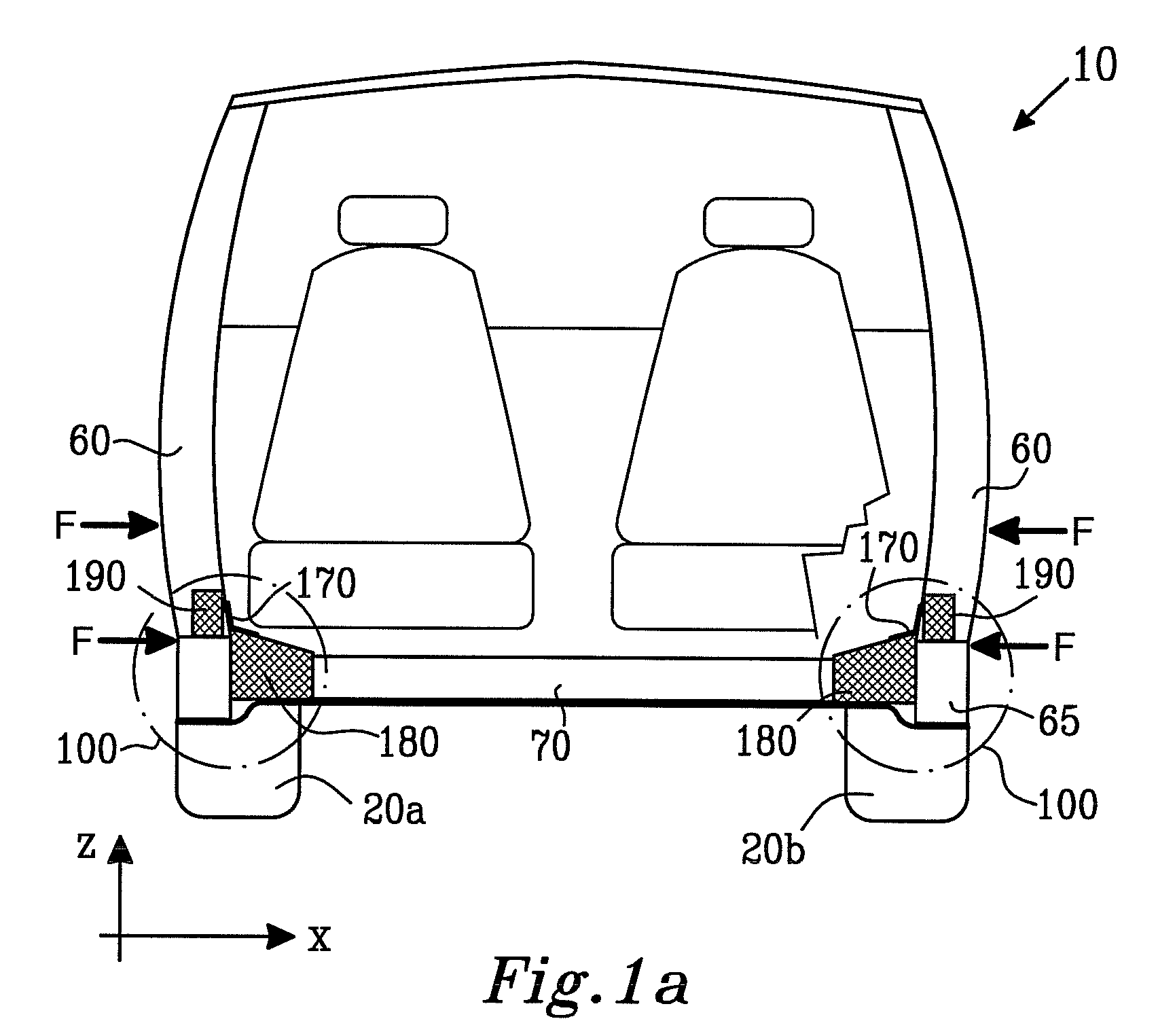
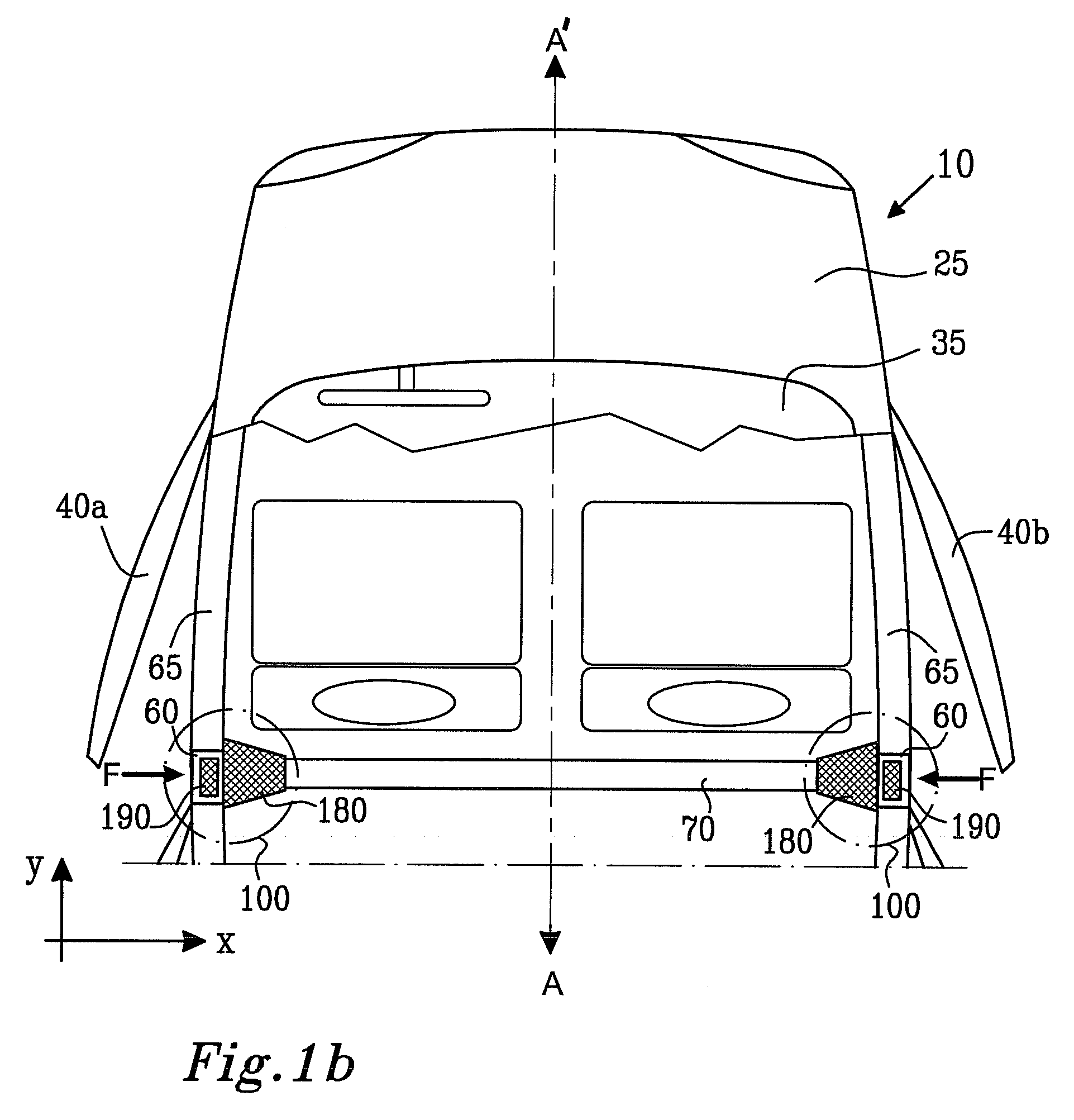
The present invention relates to a moment-resistant structure, sustainer, and method of construction for deformably resisting episodic loads, particularly those of high intensity. The episodic loads may be due to earthquake, impact, or other intense episodic sources. The structure and sustainer may be in buildings, bridges, or other civil works, land vehicles, watercraft, aircraft, spacecraft, machinery, or other structural systems or apparati. Deformation capacity is enhanced by the use of multiple dissipative zones. Dissipative zones that function in a manner similar to plastic hinges are determined by one or more voids that are located in the web of a sustainer. The one or more voids are of a size, shape, and configuration to assure that the dissipative zones deform inelastically when a critical stress, i.e., a maximum allowable demand, is reached, thereby developing the action of a structural fuse, preventing the occurrence of stress and strain demands sufficient to cause fracture of the connection welds or adjacent heat-affected zones, i.e., preventing the stress and strain demands from exceeding the strength capacity of the connection welds or adjacent heat-affected zones. The sustainers may be removably connected to the remainder of the structure, facilitating their replacement after inelastic deformation. The structure, sustainer, and method of construction may be utilized in new construction and in the rehabilitation of existing construction. Mechanical equipment and utilities may pass through the voids.
Owner:ASCHHEIM MARK AMOS
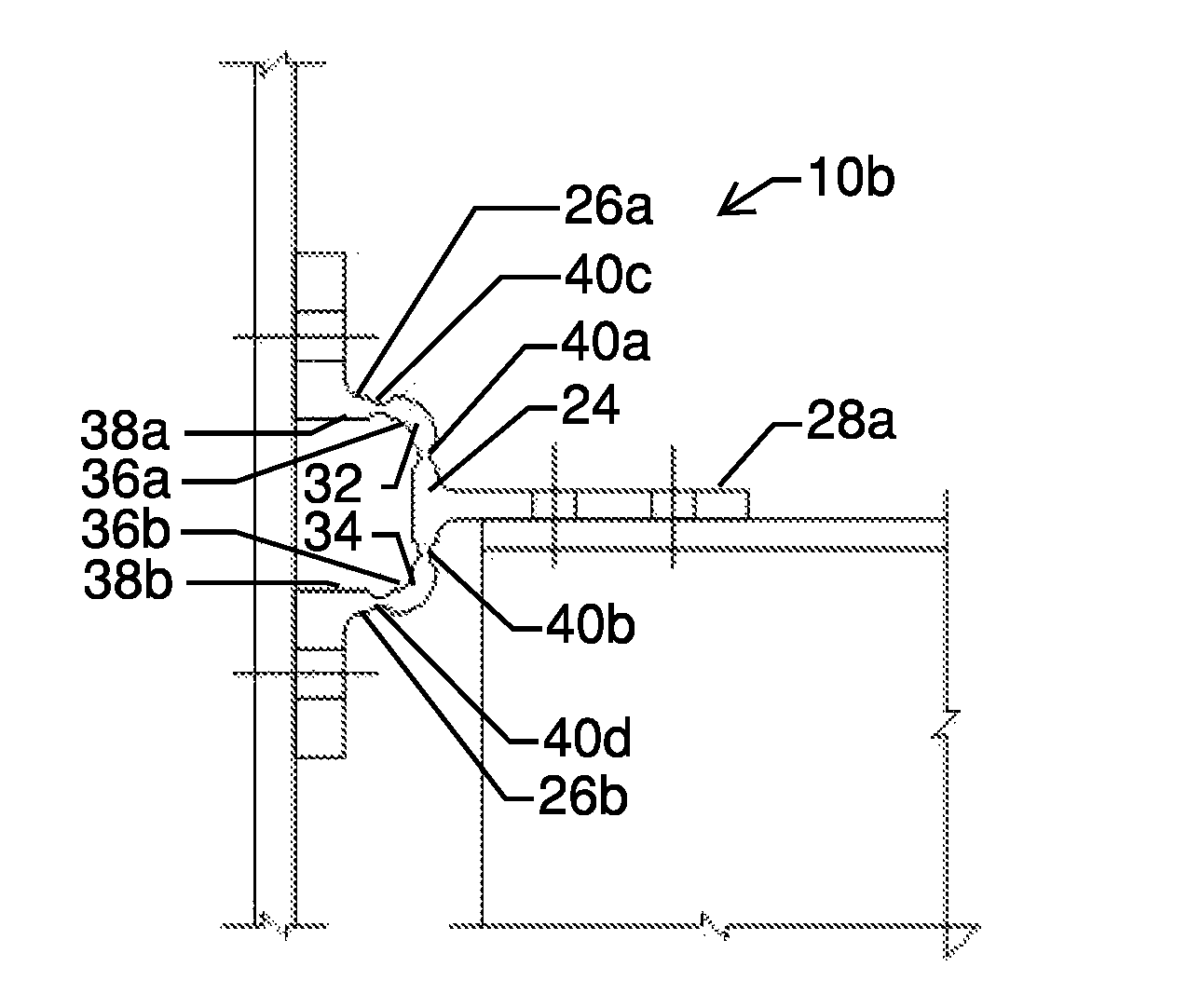
Structural joint connection providing blast resistance and a beam-to-beam connection resistant to moments, tension and torsion across a column
ActiveUS20050204684A1Mitigates likelihood of progressive collapseTremendous tensile pull and vertical moment demandBuilding roofsFloorsGusset plateEngineering
At a beams-to-column joint connection of two beams to a column, in which the joint connection comprises both a gravity load-carrying connection and a moment-resisting connection, there is added a beam-to-beam connection across the column, using two gusset plates, facing each other, on opposite sides of the joint connection. The gusset plates, which are not connected to the column in a moment-resisting connection, connect the two beams, in a tension and moment-resisting connection with respect to each other, by longitudinal welds between the gusset plates and the beams, and provide the capability of withstanding disastrous events, including loss of column support and / or loss of integrity of the beams-to-column joint connection and severe torsional and lateral inelastic deformation due to direct blast pressure. When subjected to such violent conditions and upon loss of column support, and, the likely loss of integrity of the beams-to-column joint connection, the two beams and two gusset plates provide independent beam-to-beam structural continuity, causing the two beams to act as one long beam, or, in other words, a “double-span” condition is created. Such beam-to-beam connection is capable of carrying the tension, torsional and moment loads placed upon the beams, to the ultimate capacity of the beams. Inasmuch as a gusset plate is disposed on each side of the beams-to-column joint connections, substantial shielding of those connections against blast and impact forces is also achieved.
Owner:MITEK HLDG INC
Structural joint connection providing blast resistance and a beam-to-beam connection resistant to moments, tension and torsion across a column
ActiveUS7178296B2Tremendous tensile pull and vertical moment demandBuilding roofsFloorsGusset plateEngineering
Owner:MITEK HLDG INC
Shape engineered aligner - auto shaping
InactiveUS20100055635A1Reducing and eliminating desirable contact forceReduce the amount requiredOthrodonticsDental toolsInelastic deformationOrthodontics
Owner:ALIGN TECH
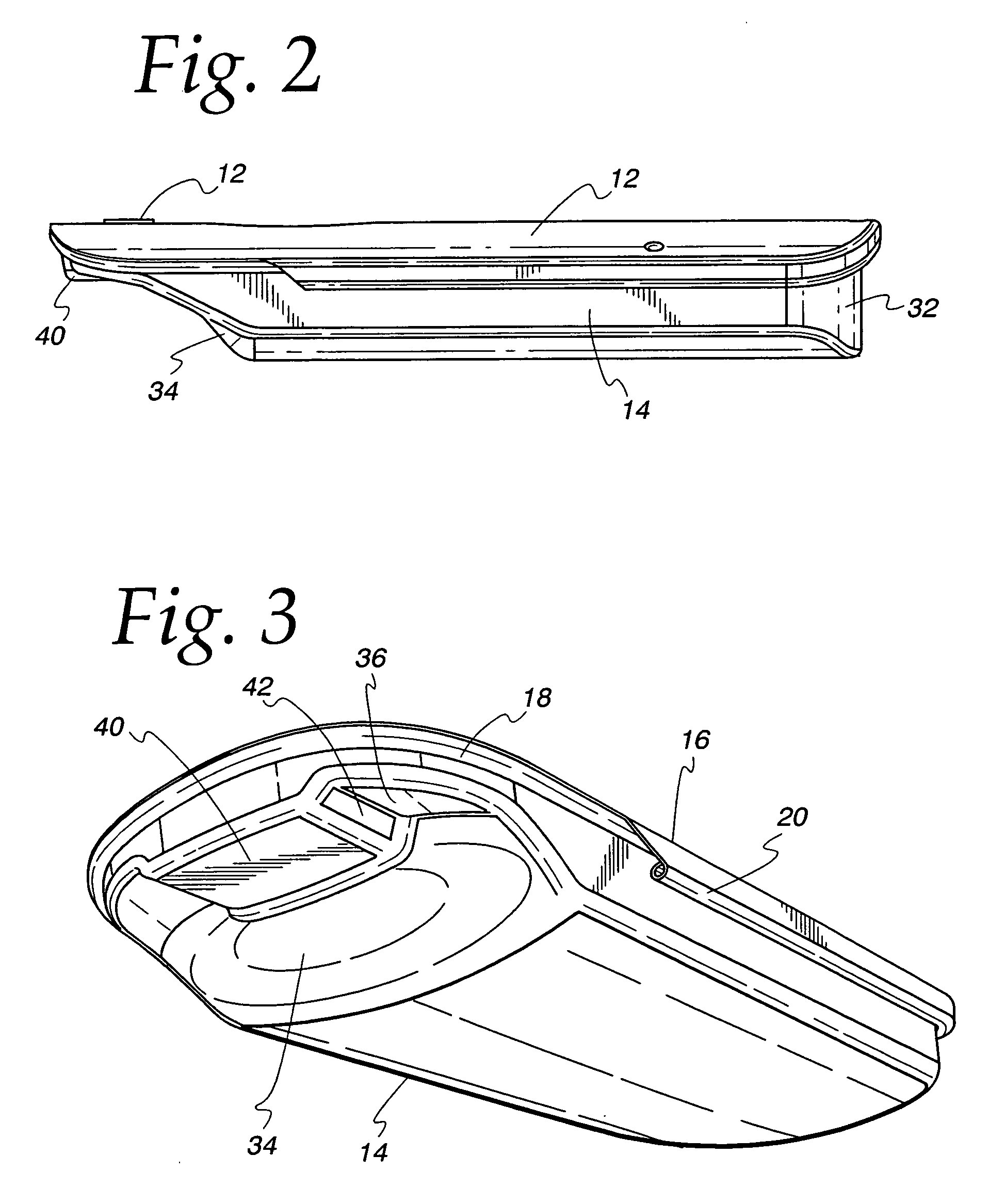
Wire cable reinforced carrying strap
InactiveUS20090140020A1Neat loopPrevent permanent deformationTravelling sacksOther accessoriesConvex sideEngineering
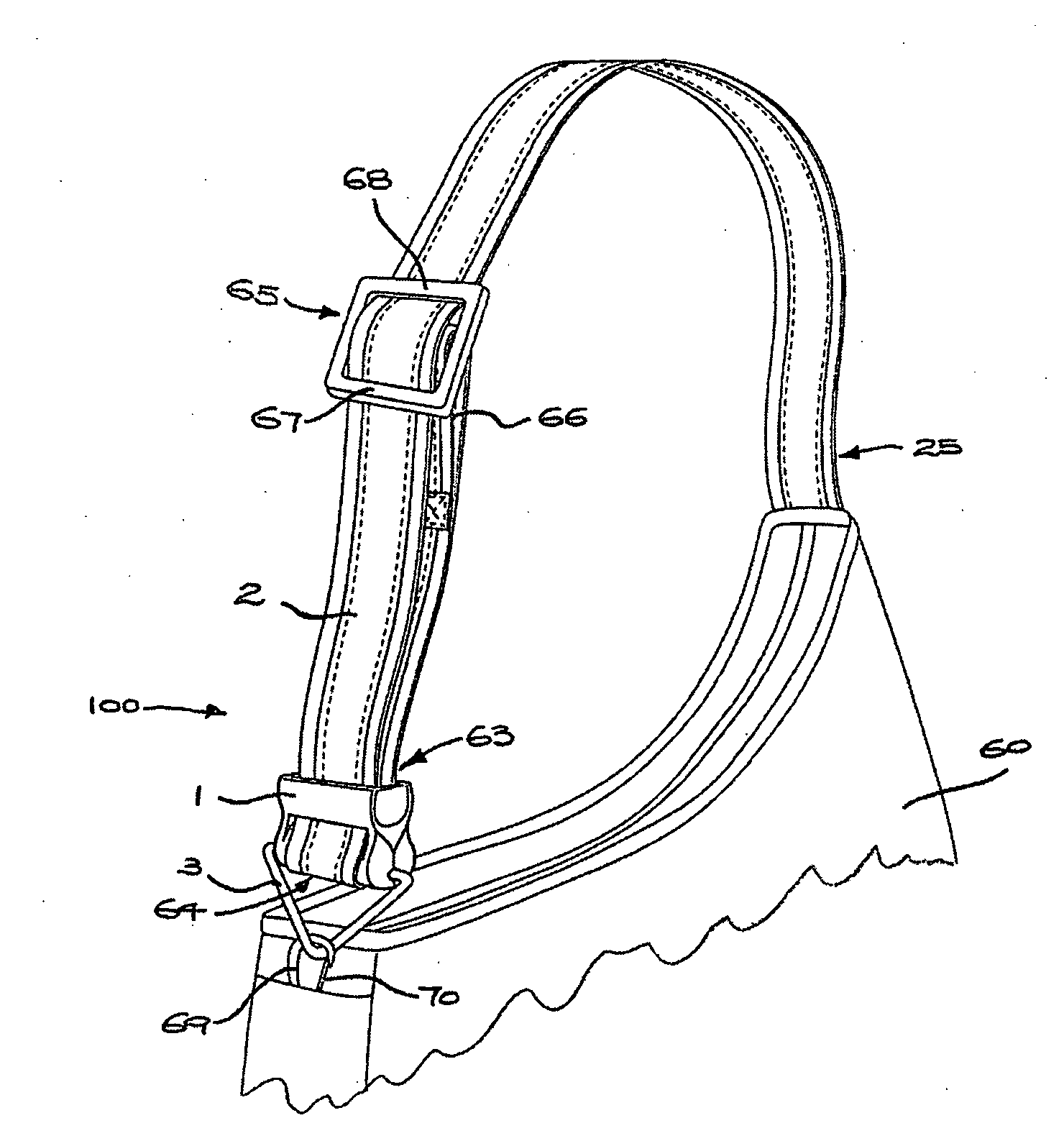
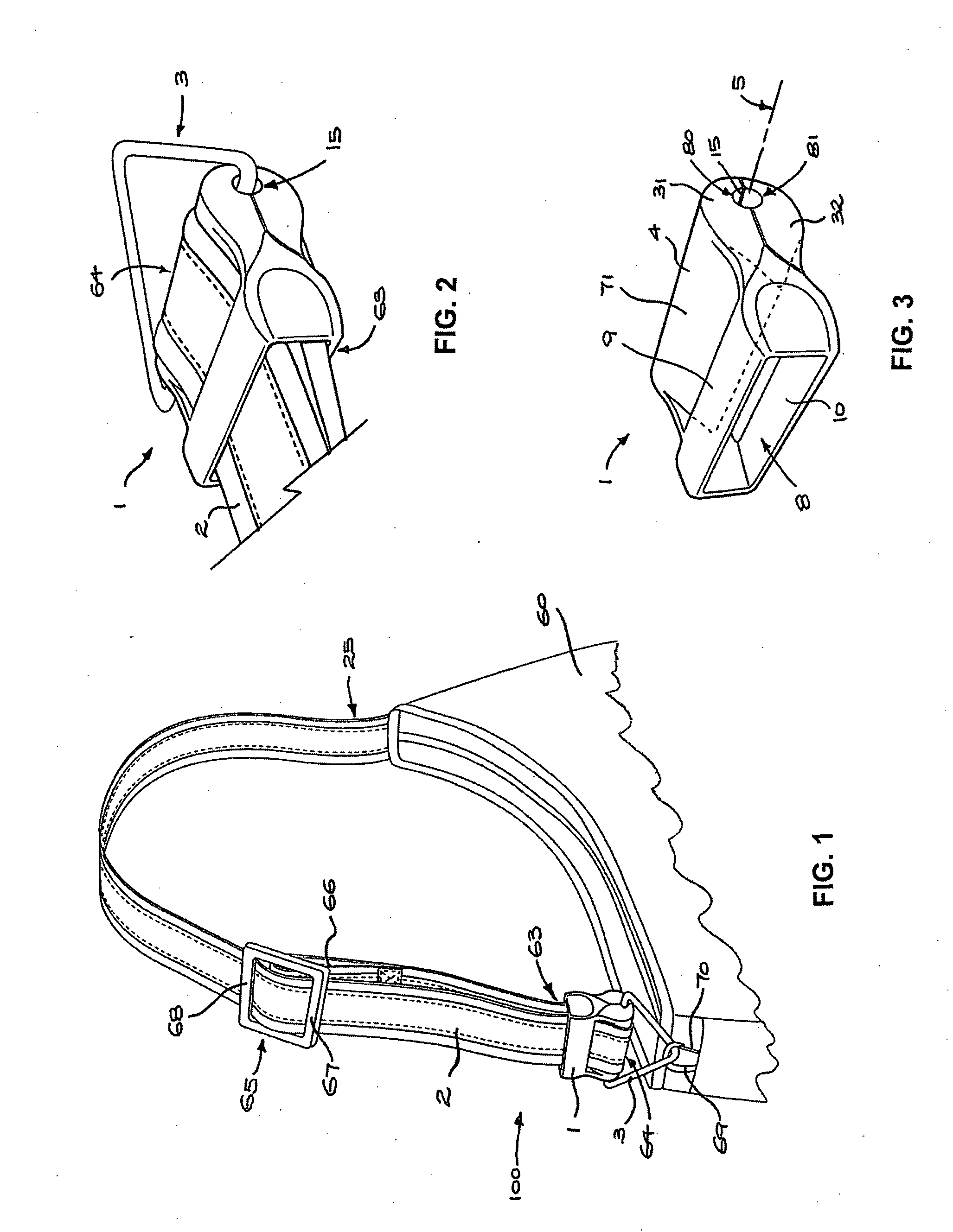
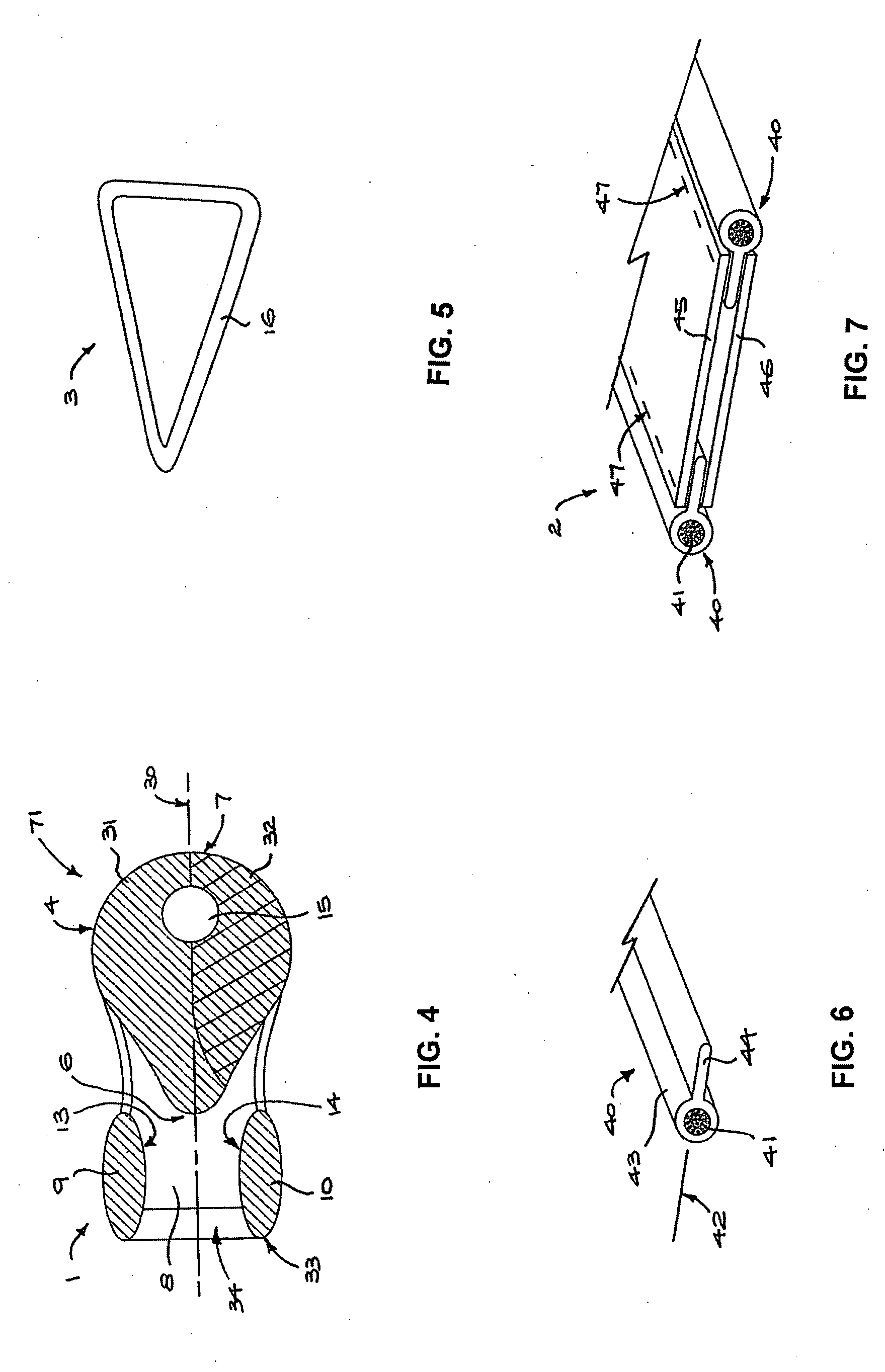
An elongate carrying strap reinforced by longitudinally extending multi-strand wire cables (41) is engaged with a fitting (1) for forming a loop (64) at an end of the strap (2) so as to avoid inelastic deformation of the cable. A pair of multi-strand wire cables are received in parallel envelopes (43) disposed on opposite longitudinal edges of the strap, each envelope is tubular and formed in a flexible polymer strip (40) extruded over the cable. The fitting has a transverse bar portion (71) having a convex face abutting the inner side of the loop and a pair of transverse arm portions (9, 10) defining an opening therebetween, the opening receiving a neck (63) of the loop and having opposing strap-engaging surfaces abutting the outer side of the strap and cooperating to hold the inner side against the convex face (4) of the bar portion (71).
Owner:MRM HK
Method and system for printing onto a deformable cast polymer article
A printing system configured to print an image onto a deformable cast polymer article comprising: (a) means for supporting a deformable cast polymer article in preparation for printing thereon, the means for supporting comprising a pressure platen, the deformable cast polymer comprising a finished surface to be printed on and a secondary surface; (b) an image transfer medium located contiguous with the finished surface, the image transfer medium configured to produce the image on the finished surface upon transfer of an ink image, comprising one or more inks, supported by the image transfer medium; (c) means for applying pressure to the deformable cast polymer article in the form of a deformable pressure applicator, such as a flexible membrane, the means for applying being flexible and configured to deform and conform to a surface of the deformable cast polymer article, and to cause an opposing surface of the deformable cast polymer article, under heat, to inelastically deform and conform to the pressure platen, the means for applying also being configured to cause the image transfer medium to conform to the finished surface such that substantially all of the ink image is caused to be in contact with the finished surface; and (d) means for heating at least a portion of the cast polymer to a pre-determined temperature for a pre-determined time sufficient to achieve the inelastic deformation of at least a portion of the cast polymer article, and to effectuate the transfer of the ink image to the finished surface.
Owner:TRUSTONE PROD
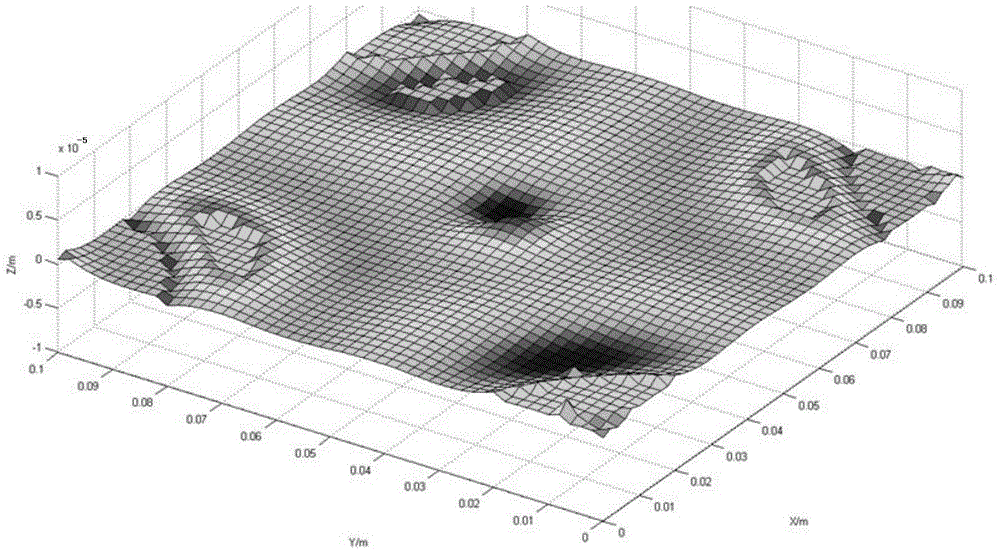
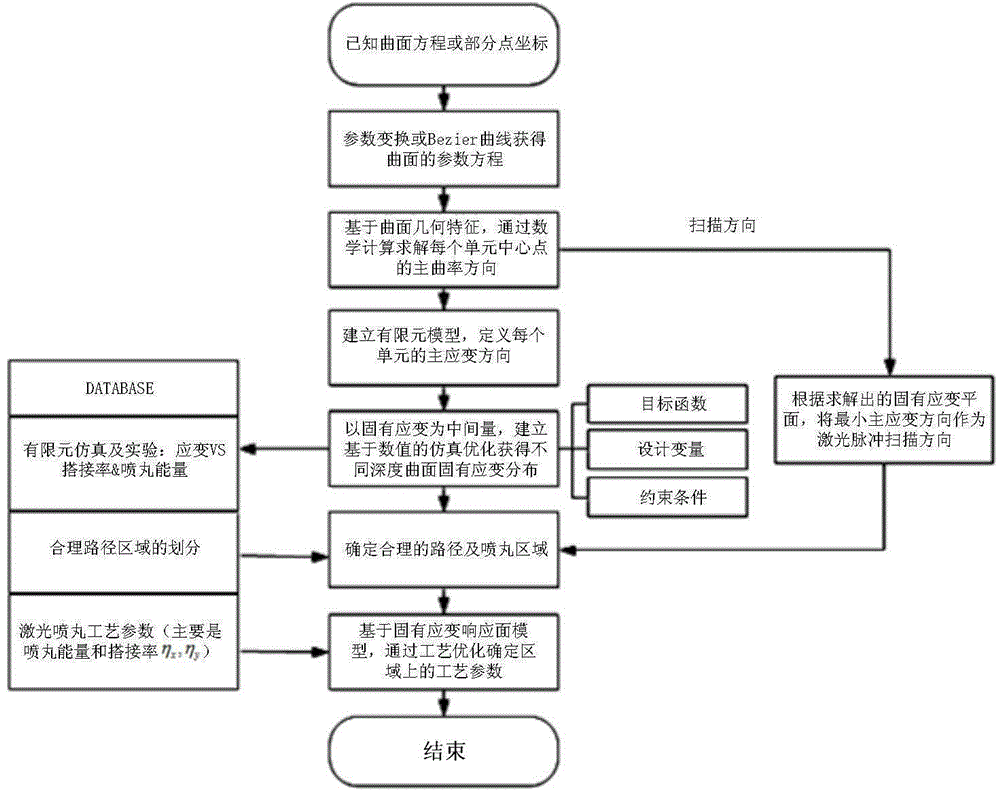
Method for determining laser peening forming process parameter of complex curved-surface-shaped workpiece
ActiveCN104899345AImprove fatigue resistanceAccelerated corrosionSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelStrain response
The invention provides a method for determining a laser peening forming process parameter of a complex curved-surface-shaped workpiece. The method comprises the following steps: according to a curved surface parameter equation of the workpiece, carrying out geometrical characteristic analysis on the curved surface of the workpiece to calculate a main strain direction so as to obtain a laser pulse scanning direction in laser peening forming; establishing a workpiece bending deformation finite element model which takes depth-direction inherent strain distribution as a deformation source, and optimizing an inherent strain field to obtain the inherent strain distribution of different positions of the workpiece along the depth direction, wherein an inherent strain direction is the main strain direction; and according to inherent strain response surface models under different laser peening forming process parameters and the inherent strain of different positions of the workpiece along the depth direction, optimizing the laser peening forming process parameters, and obtaining an optimal laser peening forming process parameter corresponding to different inherent strain fields on the surface of the workpiece. A non-elastic deformation problem can be converted into an elastic deformation problem to improve the efficiency and the precision of finite element simulation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
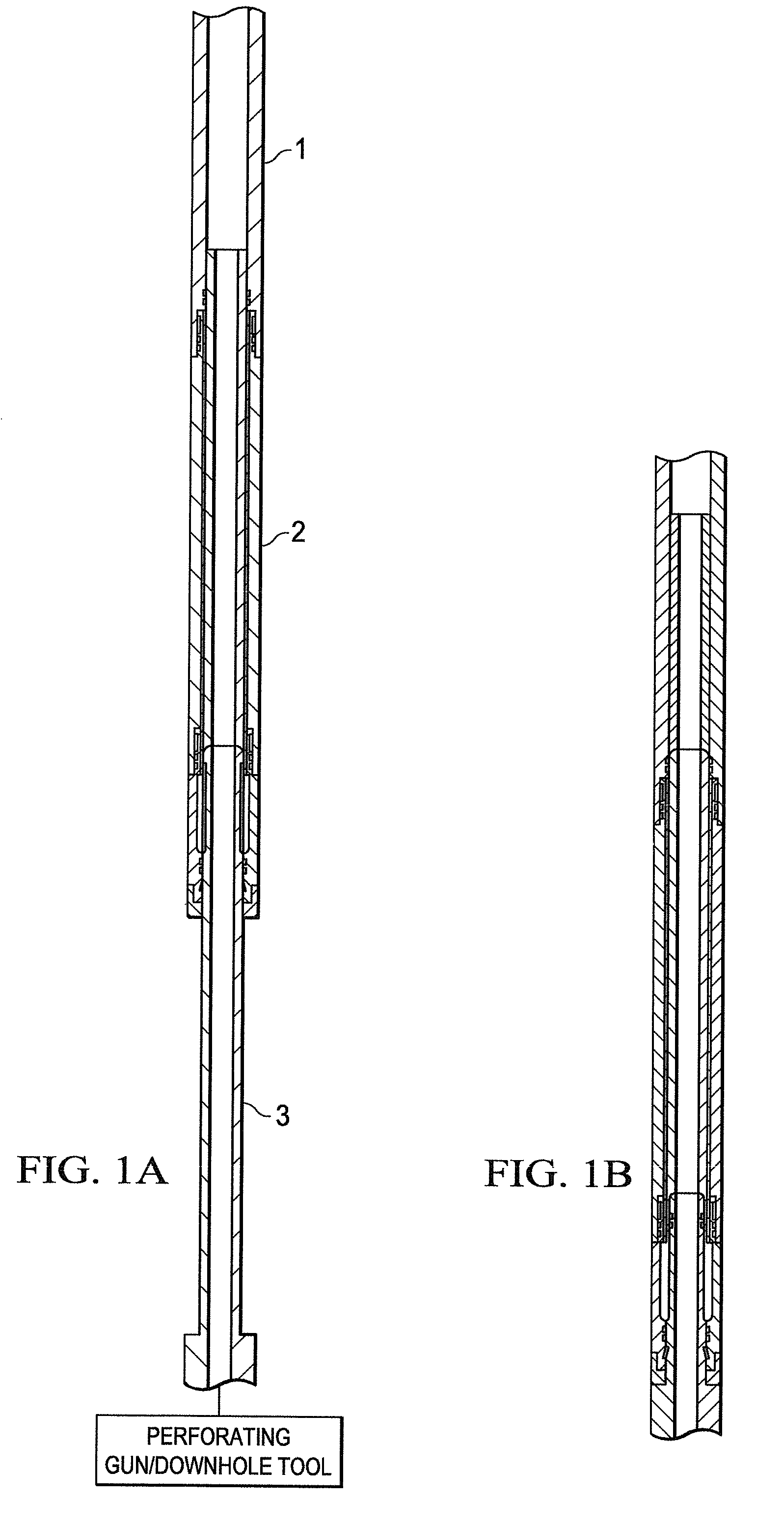
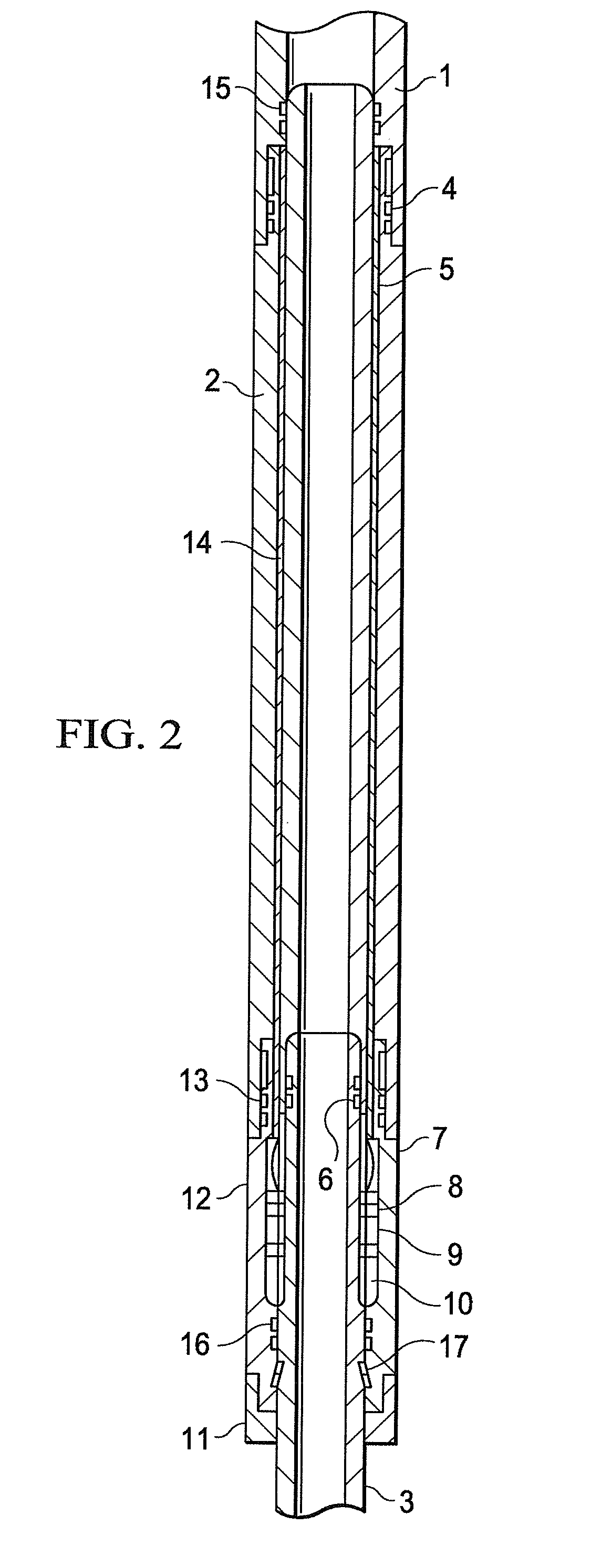
System and method for providing a downhole mechanical energy absorber
InactiveUS20100132939A1Maximizes limit loadMinimizing shock loadingPortable framesDrilling rodsMechanical energyEngineering
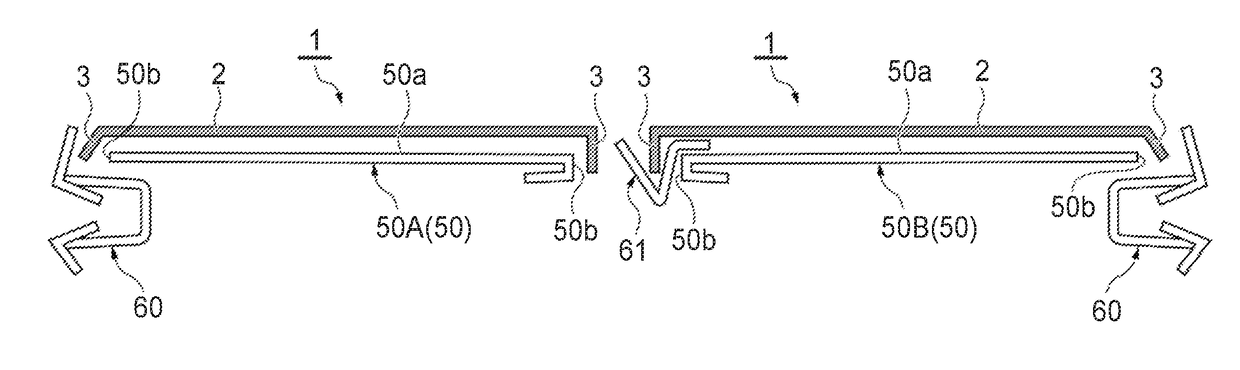
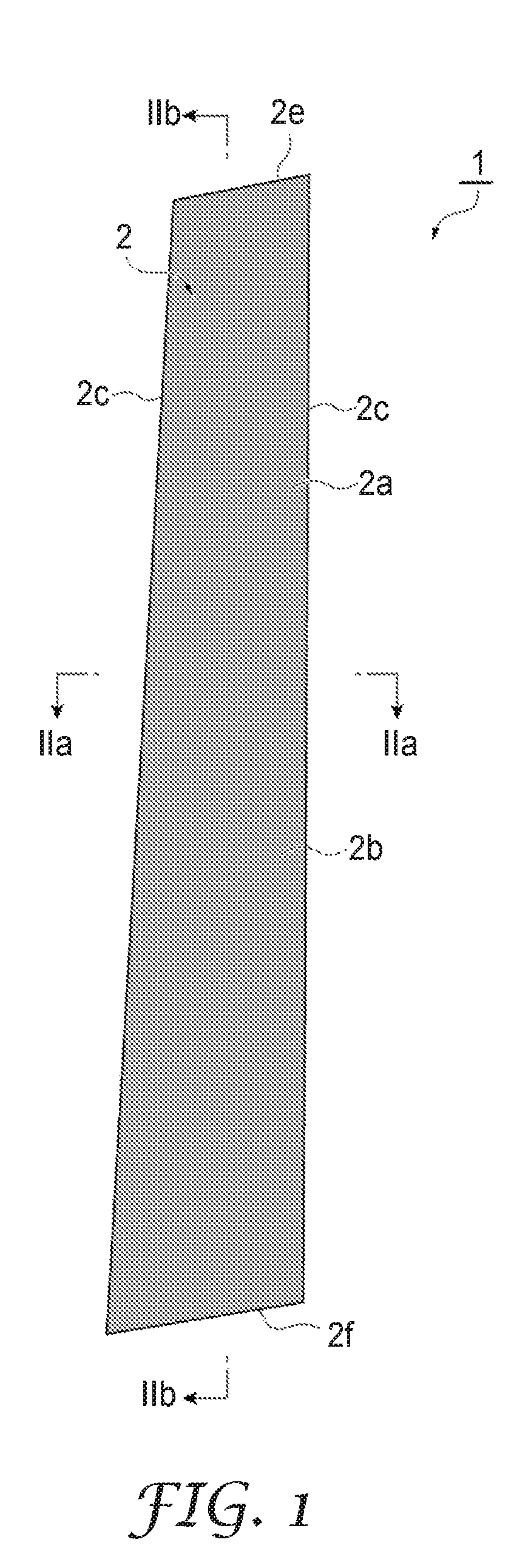
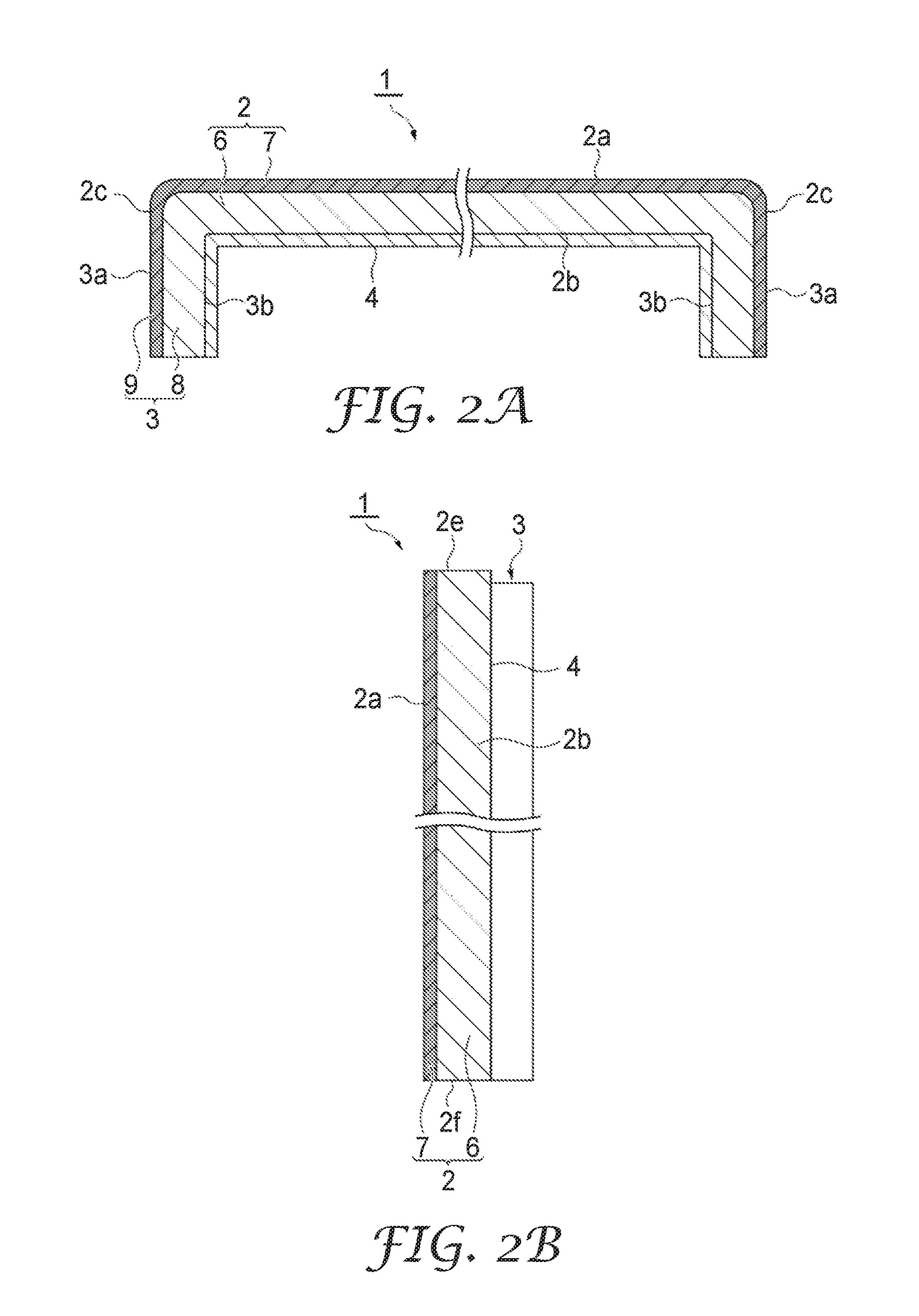
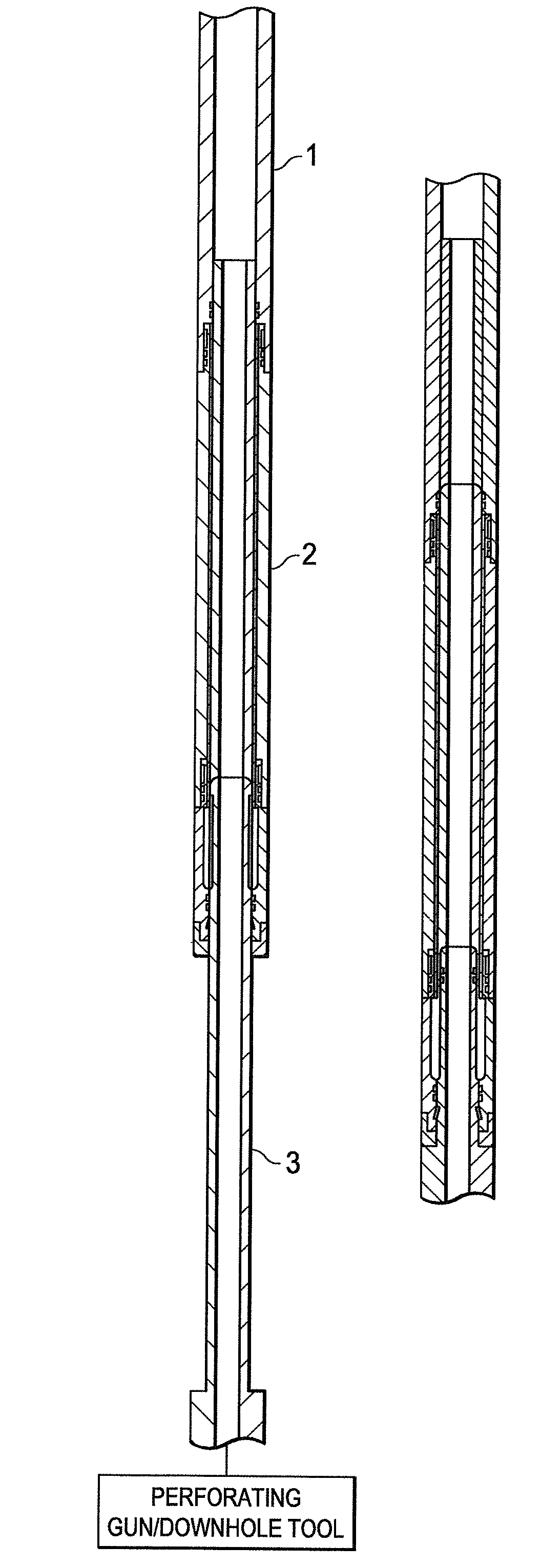
A system and a method are disclosed for providing a downhole mechanical energy absorber that protects downhole tools from impact loads and shock loads that occur during run-in contacts, tool drops, perforating blasts, and other impact events. A continuous localized inelastic deformation of a tube is a primary energy absorber in a load limiting design of the downhole mechanical energy absorber.
Owner:STARBOARD INNOVATIONS
Impact Energy Absorption Block Arrangement
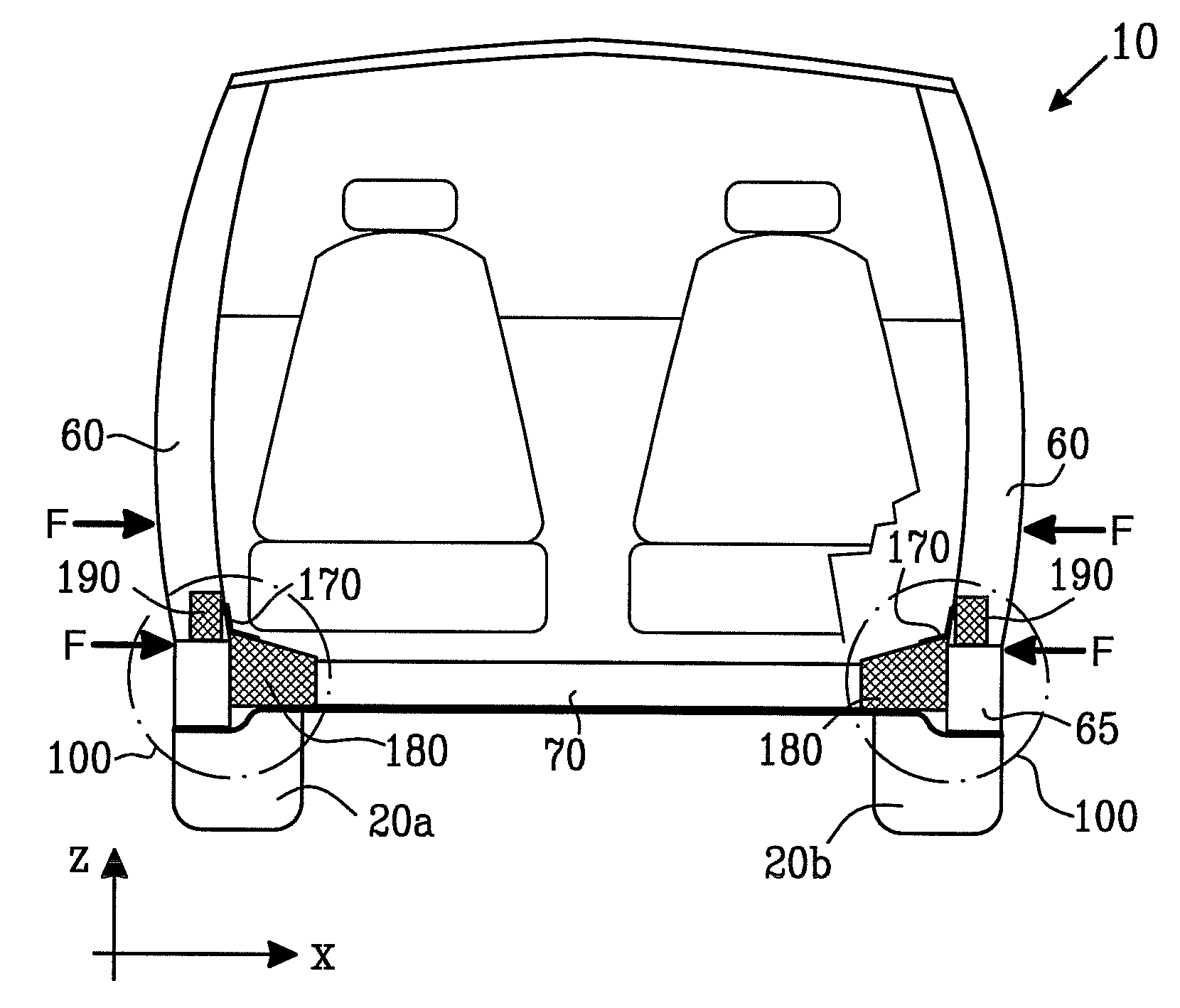
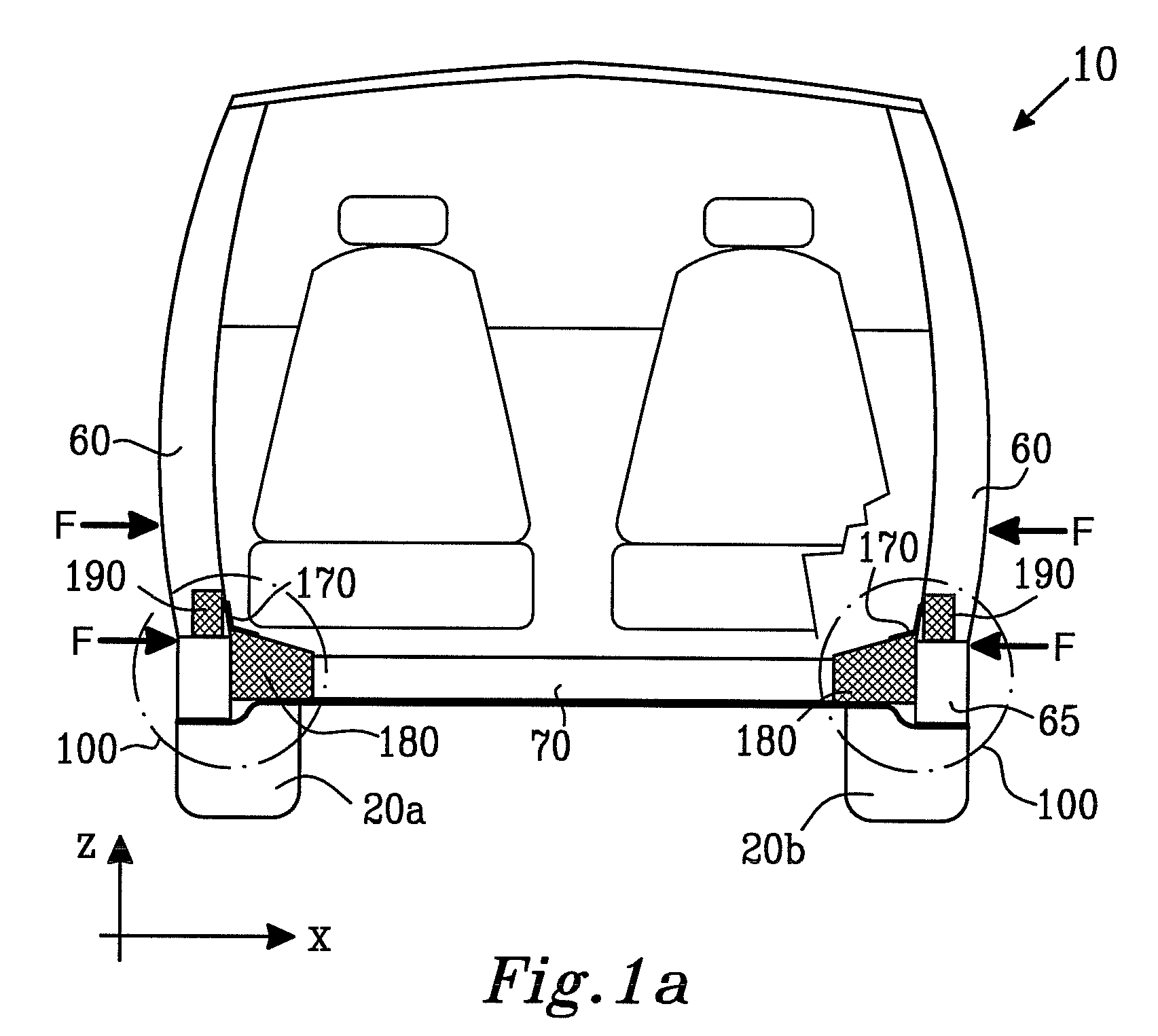
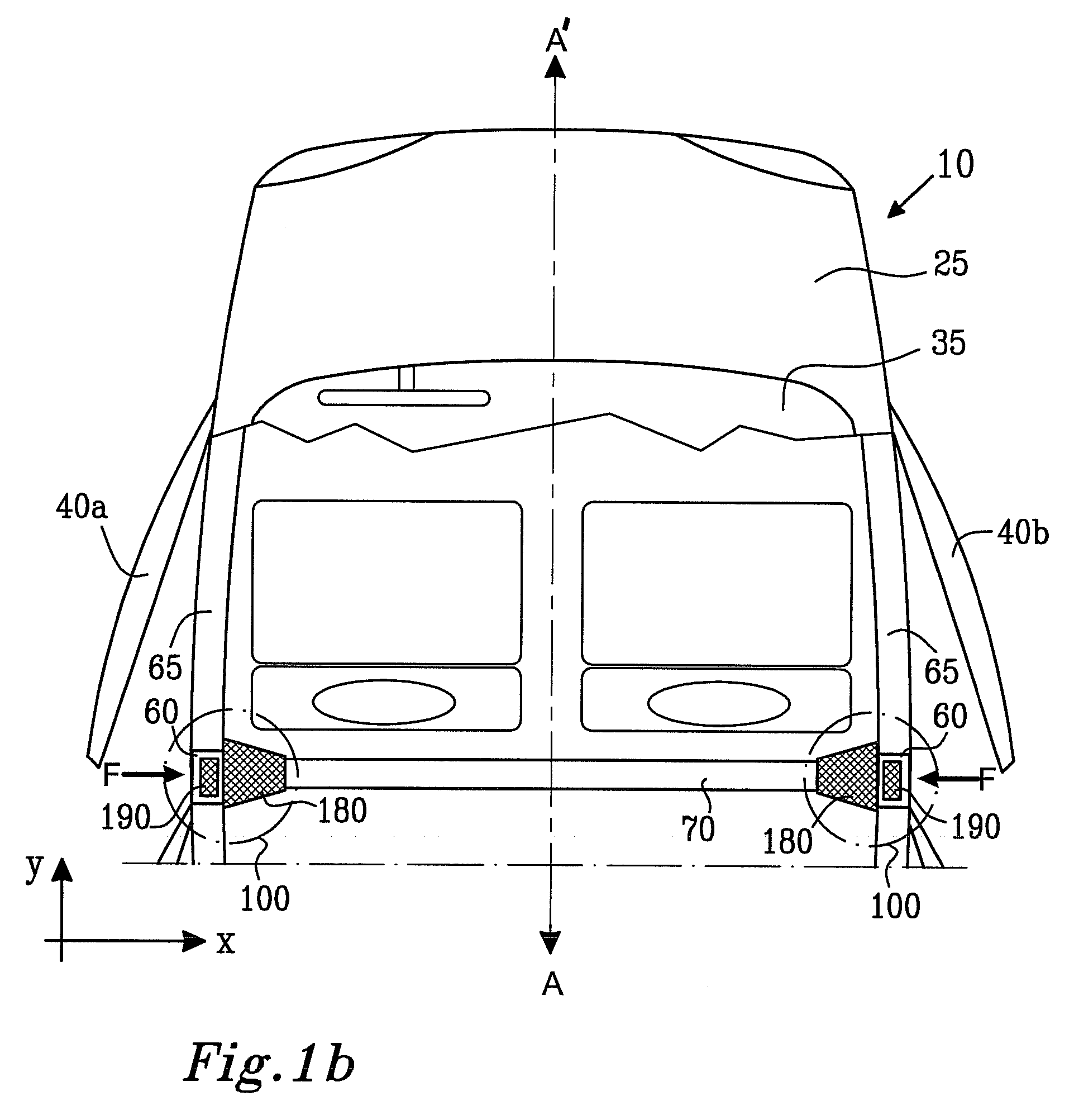
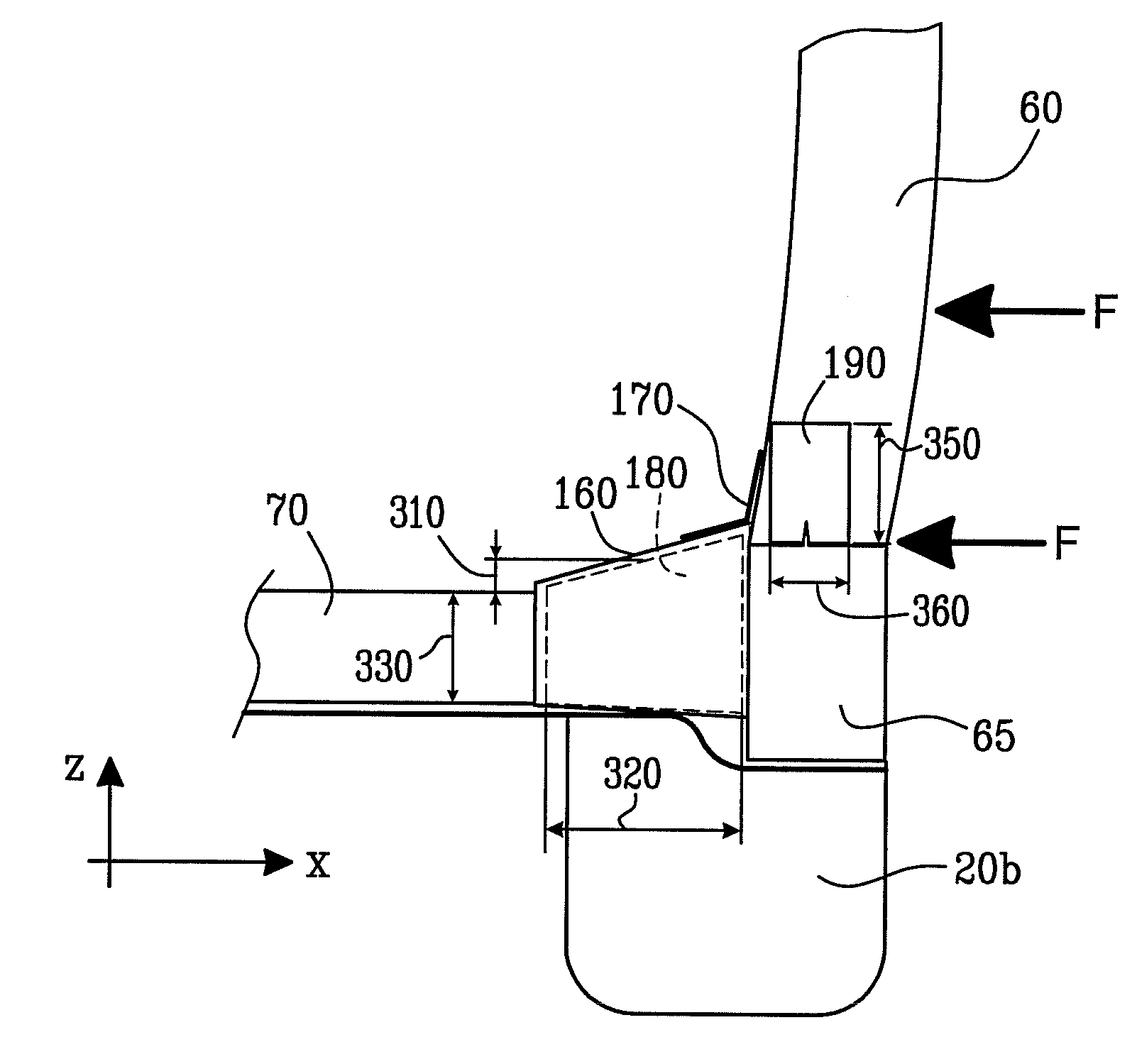
ActiveUS20070052260A1Effective absorptionReduce harmVehicle seatsUnderstructuresPlastic materialsEngineering
There is provided a vehicular impact energy absorption block arrangement adapted to provide impact energy absorption at a region substantially between a first strengthening member and a second strengthening member of a road vehicle. The energy absorption block arrangement comprises one or more energy absorber blocks operable to suffer deformation, for example substantially non-elastic deformation, when subject to forces arising from an impact or crash of the vehicle, thereby at least partially absorbing the impact energy. The one or more energy absorber blocks are fabricated from expanded plastics material foam, for example expanded polypropylene plastics material foam including pores therein. The pores may be substantially opened or closed.
Owner:VOLVO CAR CORP
Impact energy absorption block arrangement
ActiveUS7488017B2Effective absorptionReduce harmVehicle seatsUnderstructuresPlastic materialsEngineering
Owner:VOLVO CAR CORP
Container with sliding lid
InactiveUS20060037484A1Optimize allocationImprove gripMeat processingKitchen equipmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
A container for breath mints and the like includes a tray and lid. The lid may be retracted to define a dispensing slot of limited width for controlled dispensing. An internal shelf may be provided to facilitate dispensing. The lid and tray are configured to resist inelastic deformation during normal use.
Owner:WM WRIGLEY JR CO
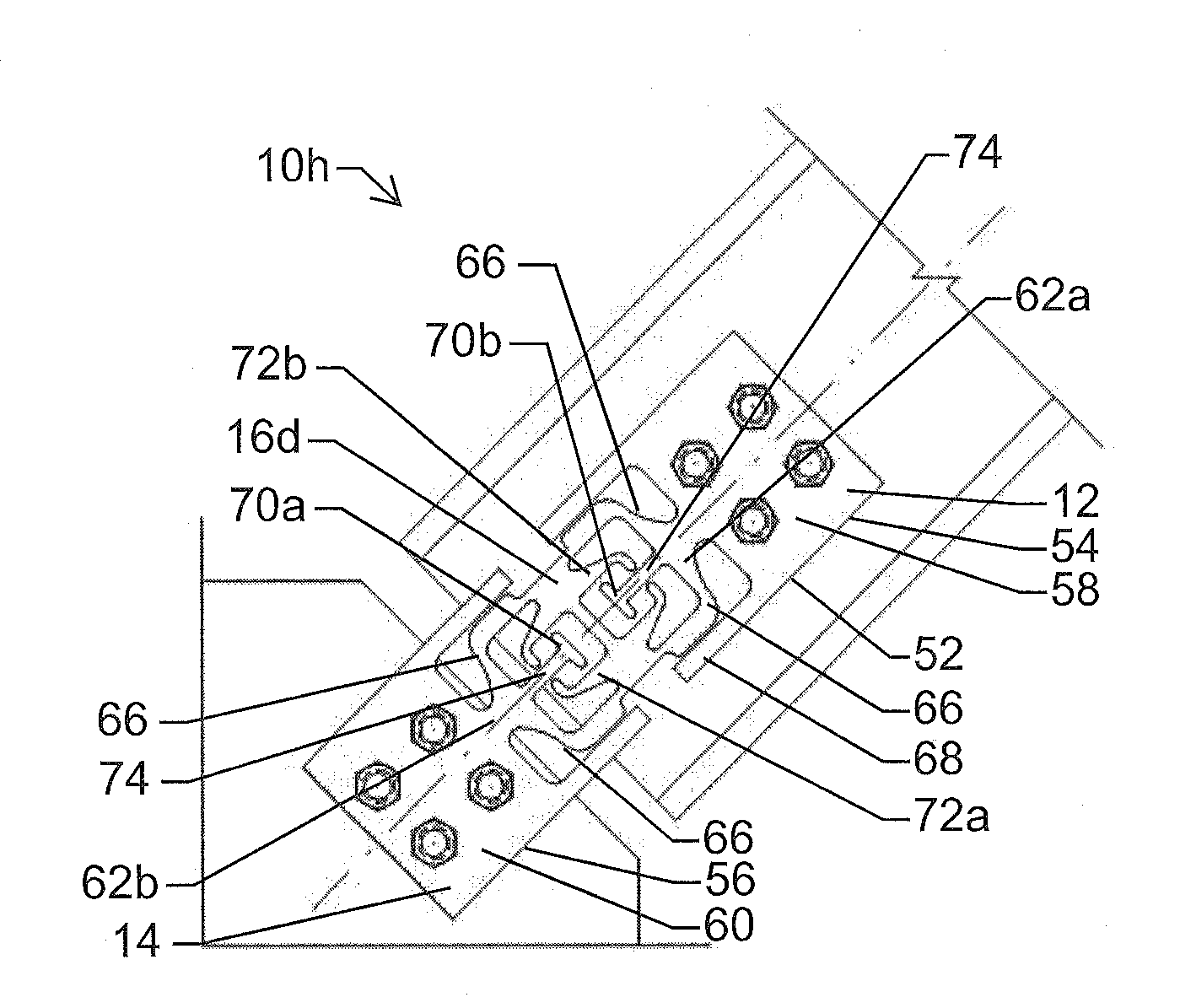
Member-to-Member Fuse Connection
ActiveUS20140062648A1Increased stiffness inelastic stiffnessIncrease dampingBuilding constructionsProtective buildings/sheltersEngineeringInelastic deformation
A member-to-member connection bracket comprising a first connection member for coupling the connection bracket to a first structural member, a second connection member for coupling the connection bracket to a second structural member; and a fuse member disposed between the first connection member and the second connection member, the fuse member comprising at least one of hinge locations. The at least one hinge location provides inelastic deformation at a pre-determined load and the pre-determined load is less than the elastic yield load of a first structural member and a second structural member. The hinge locations may have a reduced thickness. The fuse member may have a tubular cross-section. A connection utilizing the member-to-member connection bracket is also included.
Owner:SIMPSON STRONG TIE
Method and system for printing onto a deformable cast polymer article
ActiveUS20060201349A1High quality printingTransfer printingDuplicating/marking methodsImage transferEngineering
A printing system configured to print an image onto a deformable cast polymer article comprising: (a) means for supporting a deformable cast polymer article in preparation for printing thereon, the means for supporting comprising a pressure platen, the deformable cast polymer comprising a finished surface to be printed on and a secondary surface; (b) an image transfer medium located contiguous with the finished surface, the image transfer medium configured to produce the image on the finished surface upon transfer of an ink image, comprising one or more inks, supported by the image transfer medium; (c) means for applying pressure to the deformable cast polymer article in the form of a deformable pressure applicator, such as a flexible membrane, the means for applying being flexible and configured to deform and conform to a surface of the deformable cast polymer article, and to cause an opposing surface of the deformable cast polymer article, under heat, to inelastically deform and conform to the pressure platen, the means for applying also being configured to cause the image transfer medium to conform to the finished surface such that substantially all of the ink image is caused to be in contact with the finished surface; and (d) means for heating at least a portion of the cast polymer to a pre-determined temperature for a pre-determined time sufficient to achieve the inelastic deformation of at least a portion of the cast polymer article, and to effectuate the transfer of the ink image to the finished surface.
Owner:TRUSTONE PROD
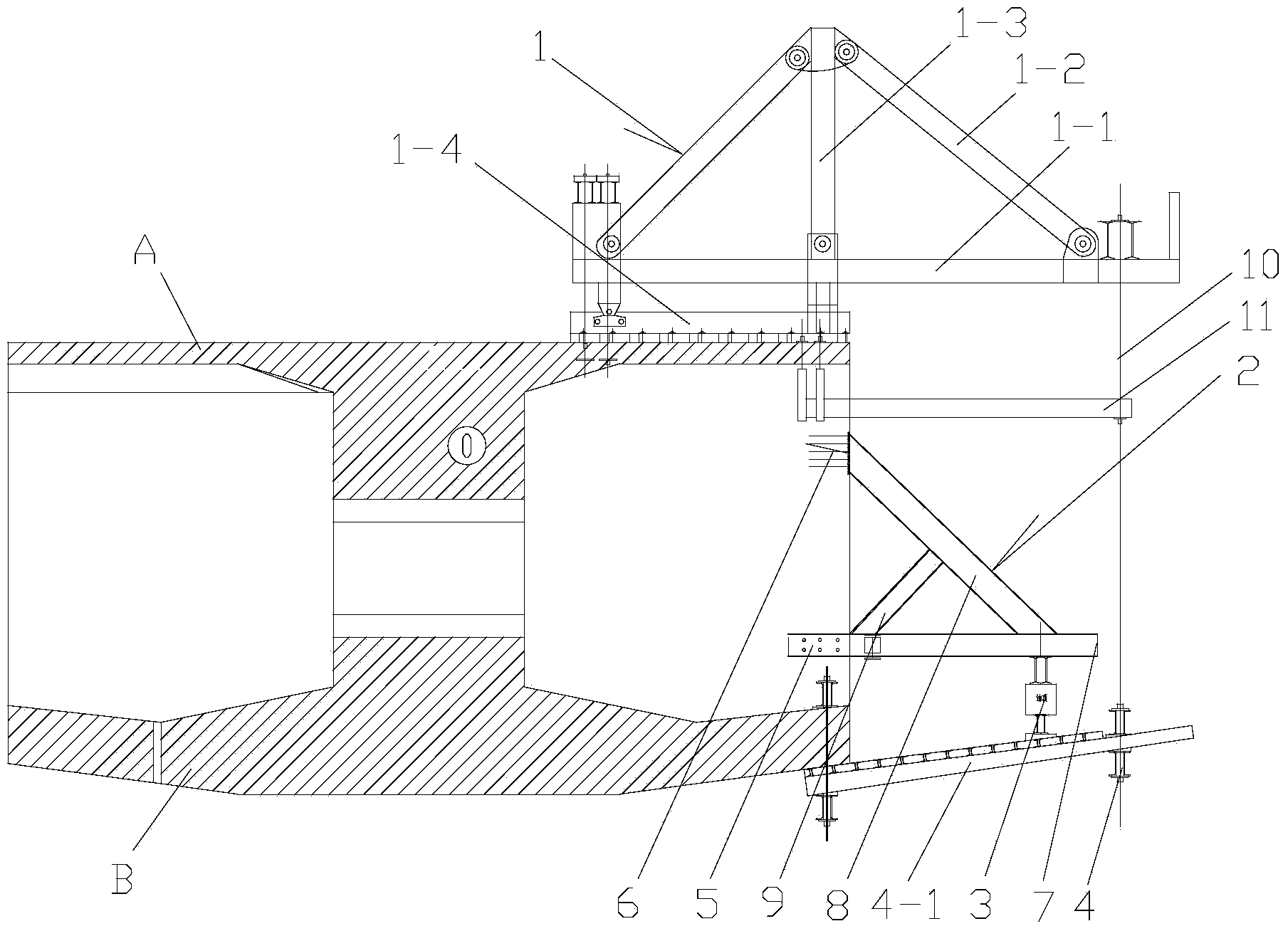
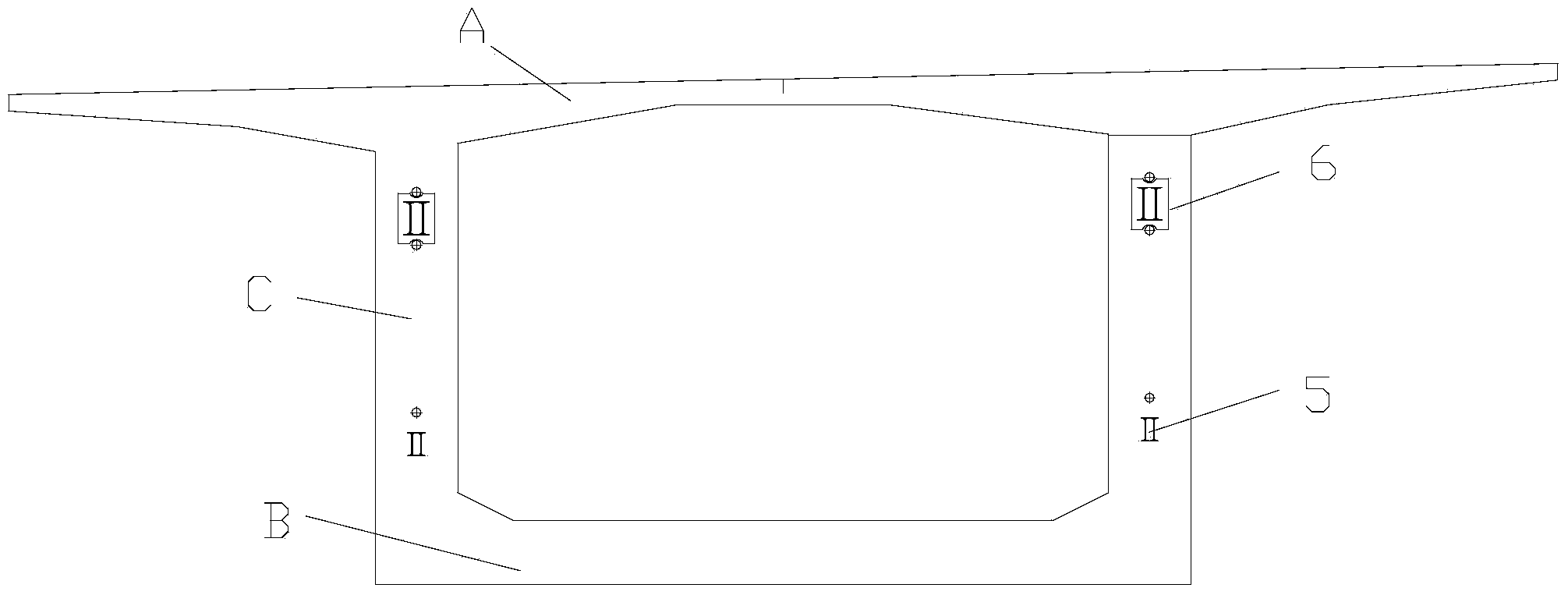
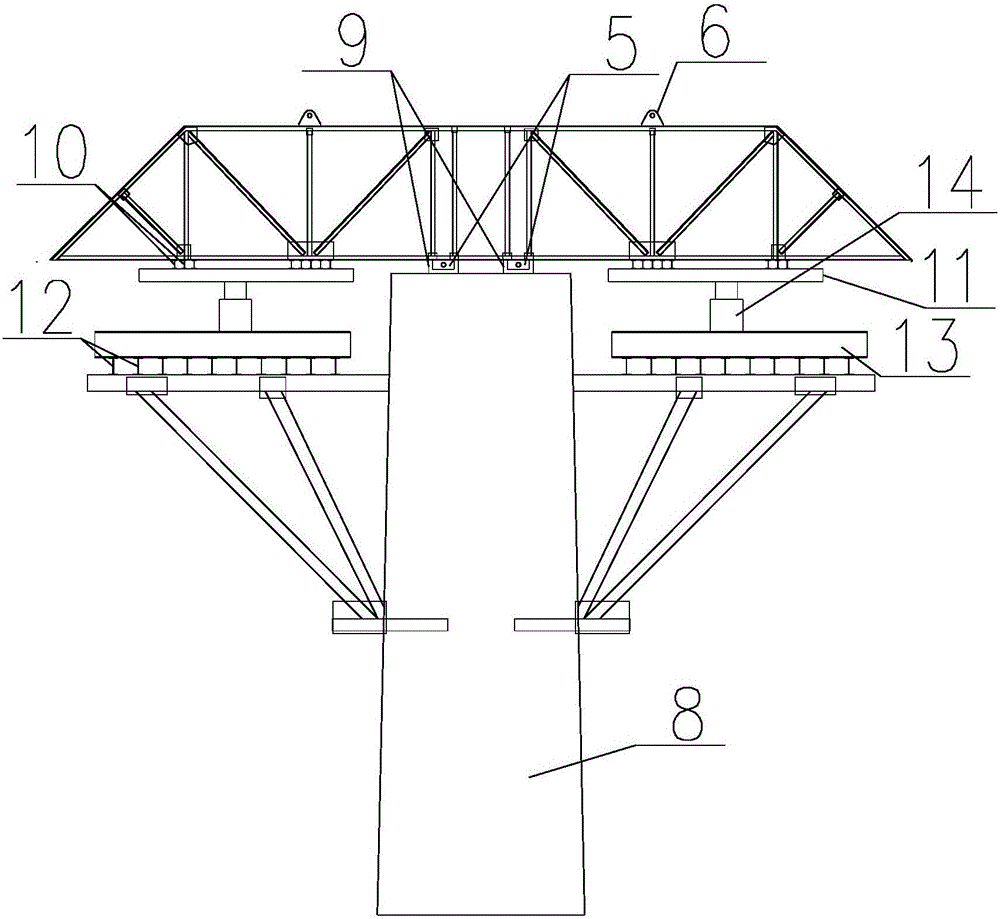
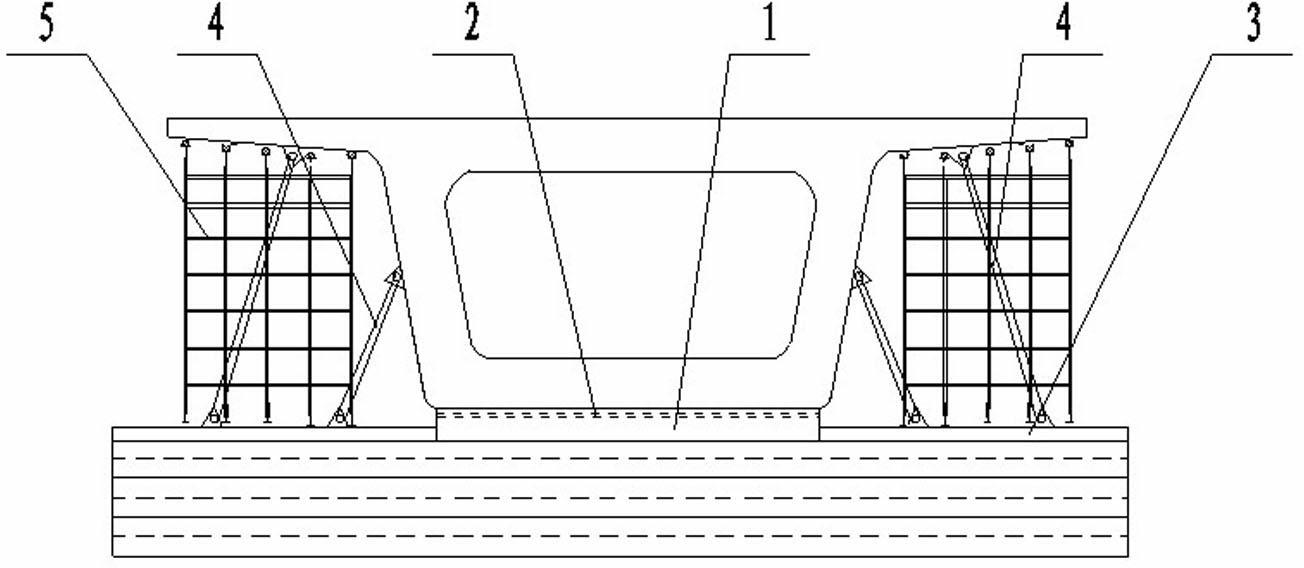
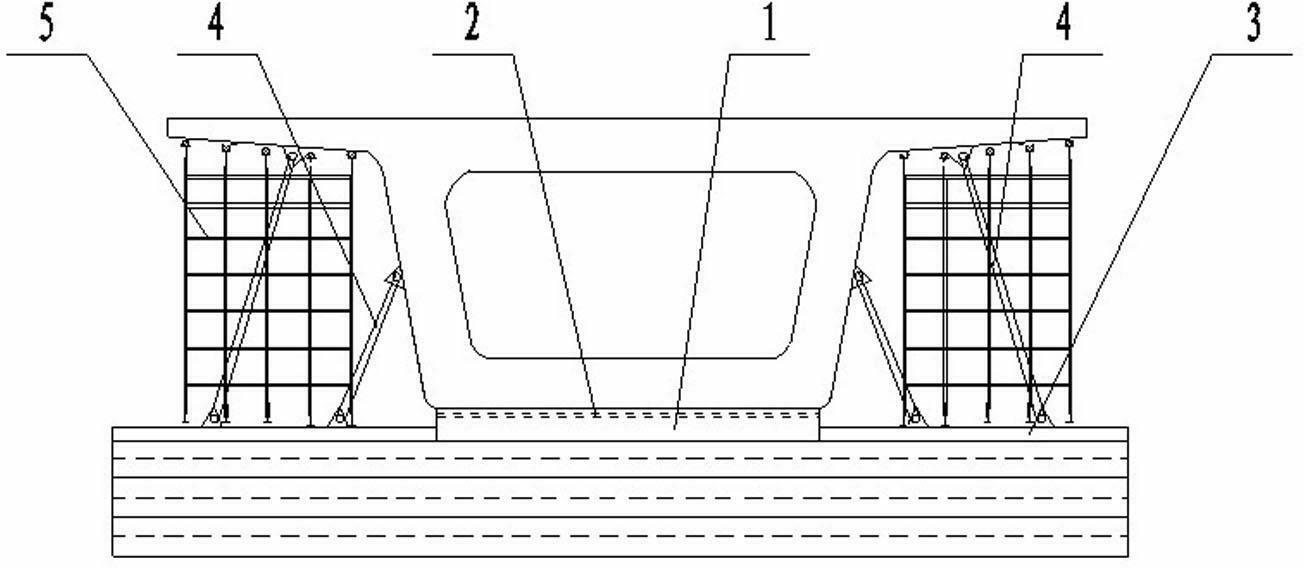
Bridge cast-in-cantilever method cradle counter-pressure construction method
The invention relates to a bridge cast-in-cantilever method cradle counter-pressure construction method, and belongs to the technical field of building construction. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a bridge foundation section, mounting cradles and a casting bottom die, manufacturing a counter-pressure mechanism, mounting the counter-pressure mechanism, placing a pressing device, regulating pressure and performing loading and detecting, and finally, realizing the actual working state of the cradle casting. The method is characterized in that by controlling the pressure of a hydraulic oil jacking device, the base die is downwards pressed, a hanging rod is upwards pulled, the actual stress of the cradles is simulated, and the deformation parameters of each part of each cradle are measured, so that the reliability of the cradles is verified, the non-elastic deformation of the cradles is eliminated, and the formwork erection elevation is convenient to correct. The method disclosed by the invention overcomes the defects of a traditional preloading method and can be used for accurately simulating the actual stress situation of the cradle construction in the cast-in-cantilever method, and the method has the advantages of easy control of preloading, high safety, good stabilization, time conservation, labor conservation and lower cost. The method can satisfy the requirements of various kinds of cast-in-cantilever construction.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINGIAL TRANSPORTATION ENG GRP
Ion optics with shallow dished grids
InactiveUS6864485B2Big ratioTotal current dropThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersClassical mechanicsInelastic deformation
In accordance with one specific embodiment of the present invention, the ion optics for use with an ion source have a plurality of electrically conductive grids that are mutually spaced apart and have mutually aligned respective pluralities of apertures through which ions may be accelerated and wherein each grid has an integral peripheral portion. A plurality of moment means are applied to a circumferentially distributed plurality of locations on the peripheral portion of each grid, which is initially flat, thereby establishing an annular segment of a cone as the approximate shape for that peripheral portion and a segment of a sphere as the approximate dished shape for the grid as a whole. The plurality of grids have conformal shapes in that the direction of deformation and the approximate spherical radii are the same. This elastic deformation during installation avoids any need for any permanent or inelastic deformation during fabrication, as well as controlling the excessive thermal displacements and accompanying performance changes to which flat grids are prone.
Owner:KAUFMAN & ROBINSON
Non-in-situ prepressing method of self-anchored type support frame and self-anchored type support frame thereof
ActiveCN101824801AHigh technical contentShorten construction timeForms/shuttering/falseworksBridge erection/assemblyEconomic benefitsJackscrew
The invention discloses a non-in-situ prepressing method of a self-anchored type support frame and the self-anchored type support frame thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out design of the self-anchored type support frame according to the self gravity of a structural object; processing and producing the self-anchored type support frame in a factory; distributing equipment such as the support frame, jacks and the like according to a non-in-situ prepressing distribution drawing of the self-anchored type support frame for carrying out non-in-situ prepressing in the factory; sequentially and progressively applying loads for carrying out prepressing; and observing the deformation quantity of the self-anchored type support frame and determining the pre-bulge degree of the support frame: determining the elasticity deformation quantity and the non-elasticity deformation of the self-anchored type support frame, simultaneously combining the support frame mechanics for calculating the obtained flexibility, and carrying out integral analysis to determine the pre-bulge degree of the self-anchored type support frame. The invention can effectively solve the prepresing problem in the high-pier large-tonnage structural object support frame construction, can also save the construction cost to a large degree on the premise of ensuring the engineering construction quality, can simultaneously shorten the structural object construction period, and can create good economic benefits.
Owner:THE 5TH ENG MBEC
Method for making a non-driving vehicle axle beam
InactiveUS20070283562A1Increase pressureVehicle componentsMetal working apparatusRegioselectivityEngineering
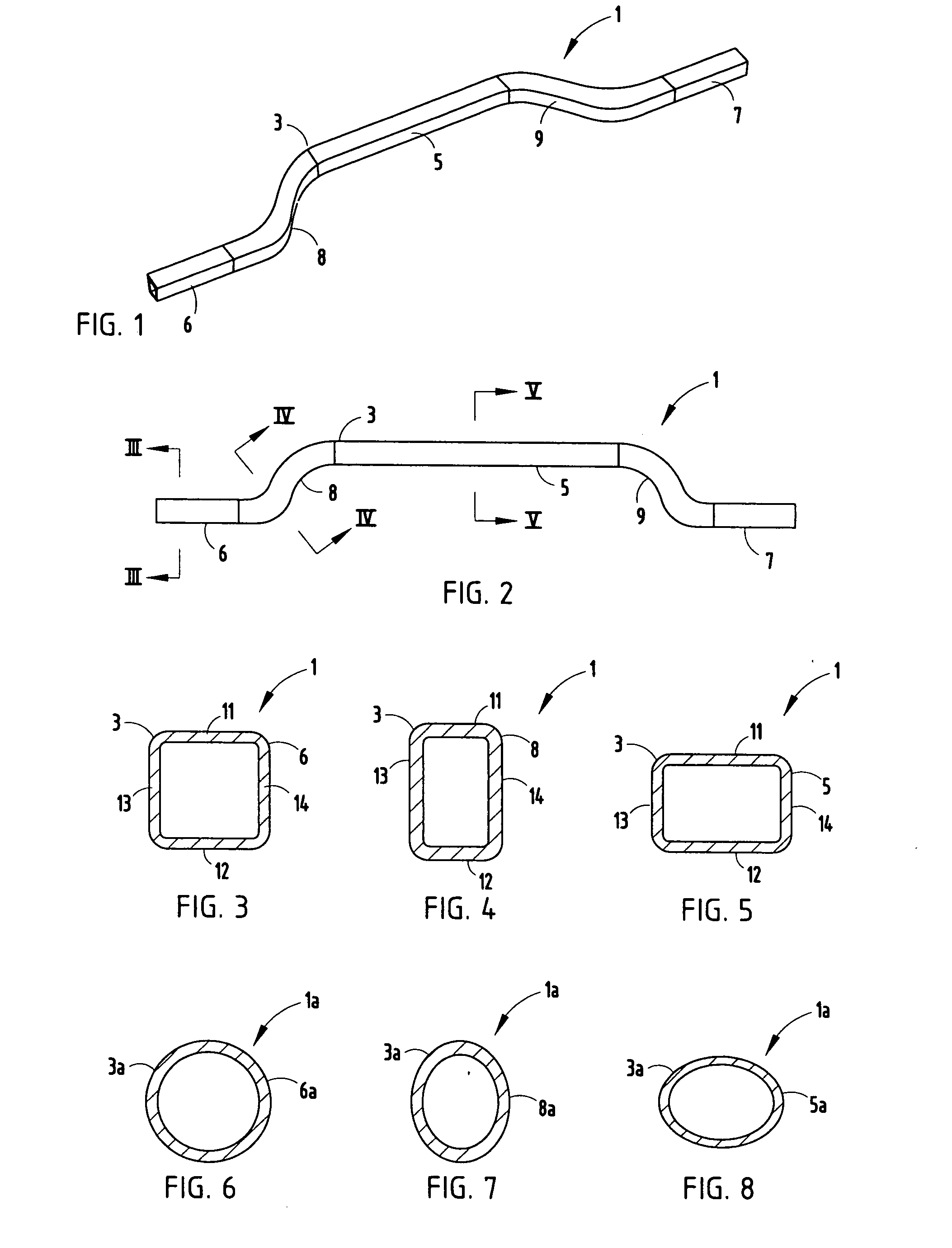
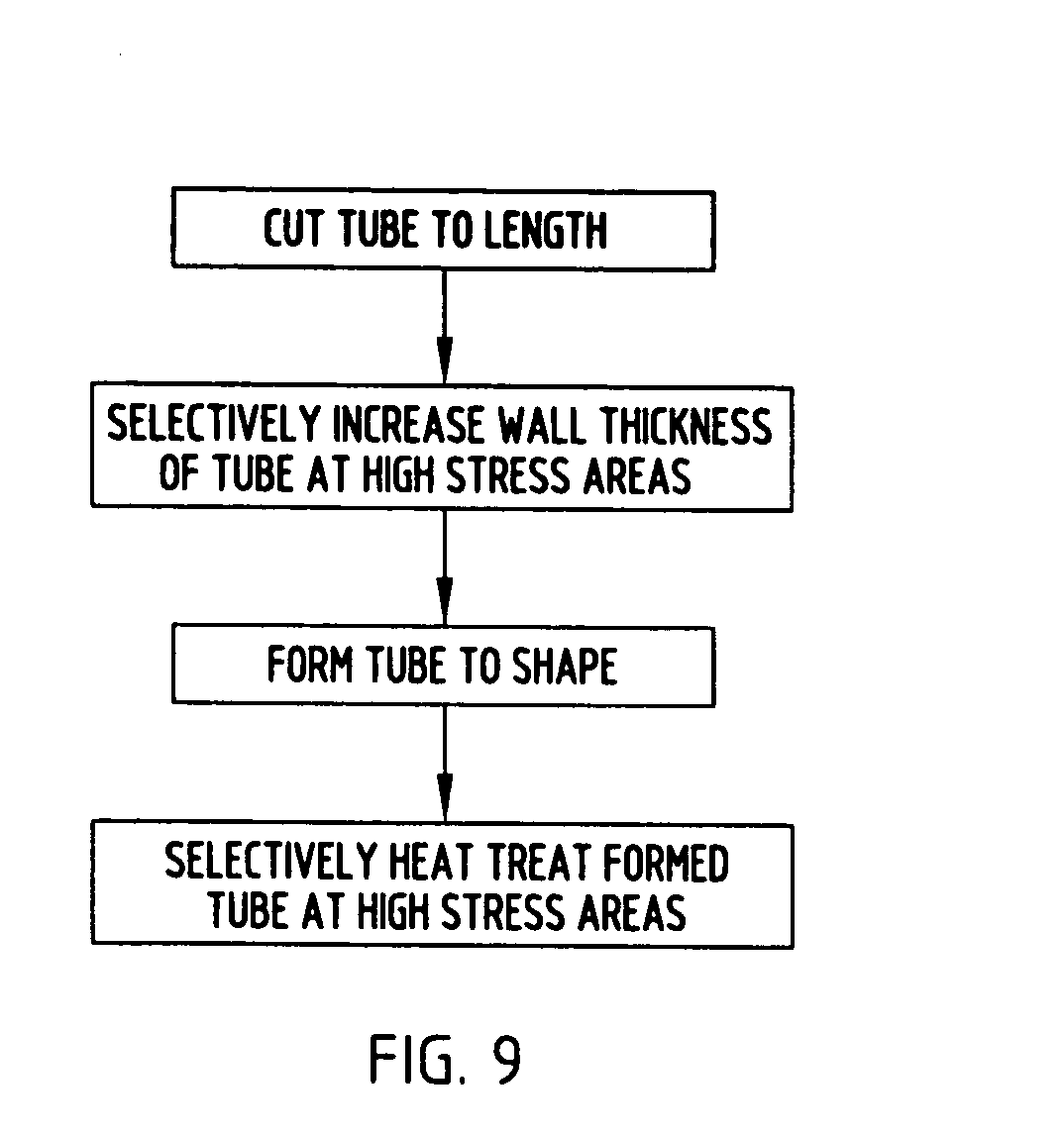
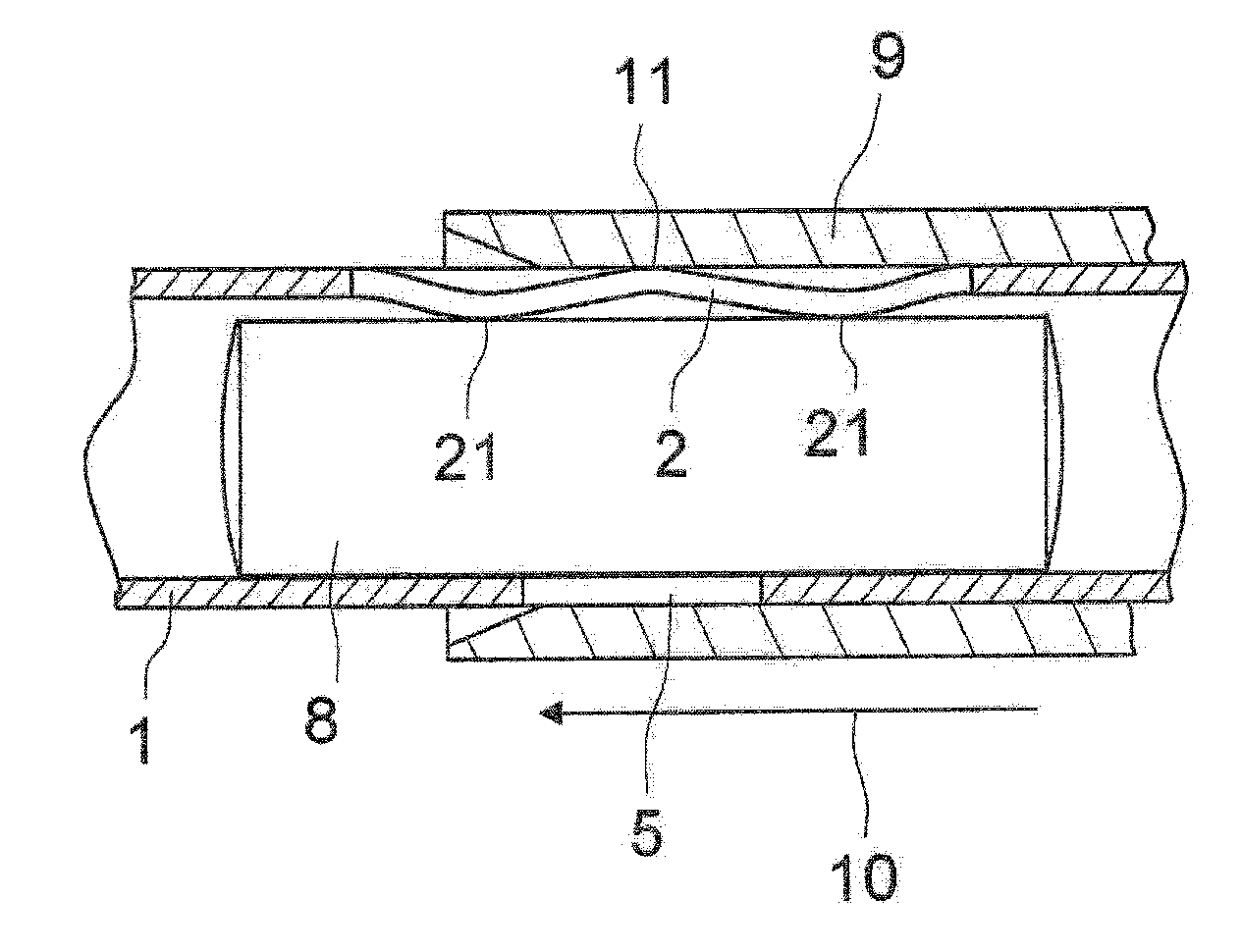
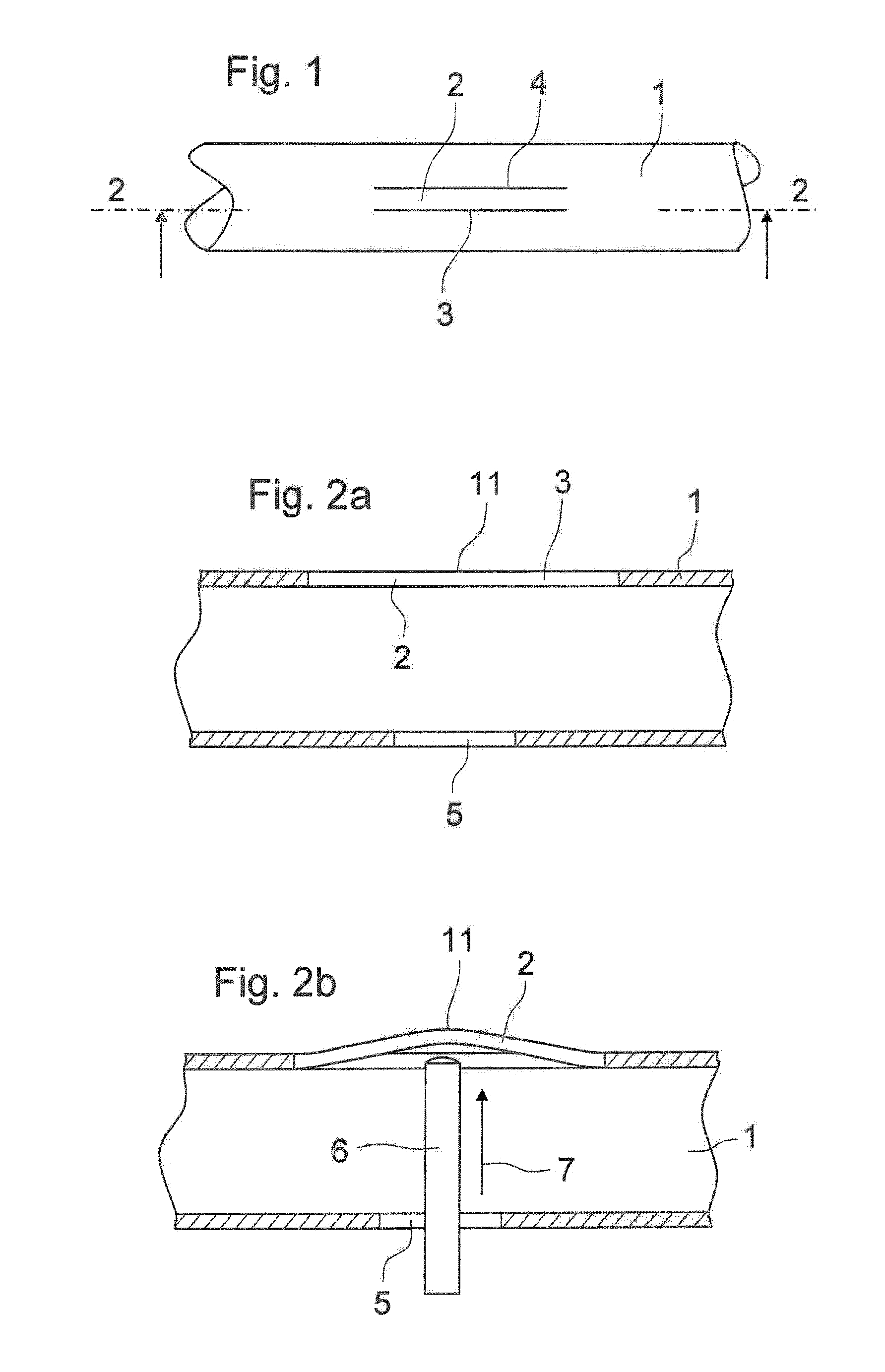
A method for making a non-driving vehicle axle beam includes selecting a straight section of elongate tube of hardenable steel. The tube is cut to length, and positioned in a die cavity which corresponds to the shape of the finished axle beam. Pressurized fluid is communicated with the interior of the tube to inelastically deform the same into conformance with the shape of the die cavity. The formed tube is removed from the die and selectively heat treated at the areas of high stress during use to define the finished axle beam.
Owner:BENTELER AUTOMOTIVE CORP
System tube and process for supporting cylindrical elements of an endoscope optical system
InactiveUS20120176669A1Easy to disassembleEasy to adjustEndoscopesTelescopesInelastic deformationEndoscope
A system tube of an endoscope optical system, designed to contain cylindrical elements of an image guide provided with lenses and to support the elements by tongues cut out of the wall of the system tube and deformed nonelastically. Wherein the tongues are deformed toward the outside and are bent elastically by a holder toward the inside to below the level of the outer surface of the system tube. In a system tube of an endoscope optical system, designed to contain cylindrical elements of an image guide provided with lenses and to support the elements by means of nonelastically deformed tongues cut out of the wall of the system tube, the tongues are deformed toward the outside and are elastically bent by a holder toward the inside to below the level of the outer surface of the system tube.
Owner:OLYMPUS WINTER & IBE
Member-to-member fuse connection
ActiveUS9514907B2Little strengthImprove elastic stiffnessBuilding constructionsProtective buildings/sheltersEngineeringInelastic deformation
A member-to-member connection bracket comprising a first connection member for coupling the connection bracket to a first structural member, a second connection member for coupling the connection bracket to a second structural member; and a fuse member disposed between the first connection member and the second connection member, the fuse member comprising at least one of hinge locations. The at least one hinge location provides inelastic deformation at a pre-determined load and the pre-determined load is less than the elastic yield load of a first structural member and a second structural member. The hinge locations may have a reduced thickness. The fuse member may have a tubular cross-section. A connection utilizing the member-to-member connection bracket is also included.
Owner:SIMPSON STRONG TIE
Method for manufacturing high strength and large specification wire rope sling
ActiveCN101608429ALow costSave materialBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblyBridge engineeringEngineering
The invention relates to a manufacturing method in the technical field of bridge engineering, in particular to a method for manufacturing a high strength and large specification wire rope sling. The method comprises the following steps: (1) checking raw materials, and ensuring that a wire rope has no broken wire, no rust and the like; (2) according to the length of a workshop tensioning groove, performing optimal length matching on a long cable and a short cable to be matched into a certain length; (3) manufacturing a temporary anchorage device to ensure performing pretension; (4) performing pretension to control the inelastic deformation of the wire rope; (5) resisting corrosion; (6) cutting off a mark; (7) performing anchor manufacturing on the wire rope, and passing the wire rope into a buffer before anchor manufacturing; (8) casting an ingot by using a special conical ingot mould, and preheating the mould; and (9) performing tensioning retest on the sling according to a length matching table. The method can be applied to bridges; and according to the length of the workshop tensioning groove, the long cable and the short cable are matched to perform optimal length matching to be matched into a certain length, so that the method is favorable for performing pretension, saving materials simultaneously and reducing the bridge cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUJIANG CABLE +1
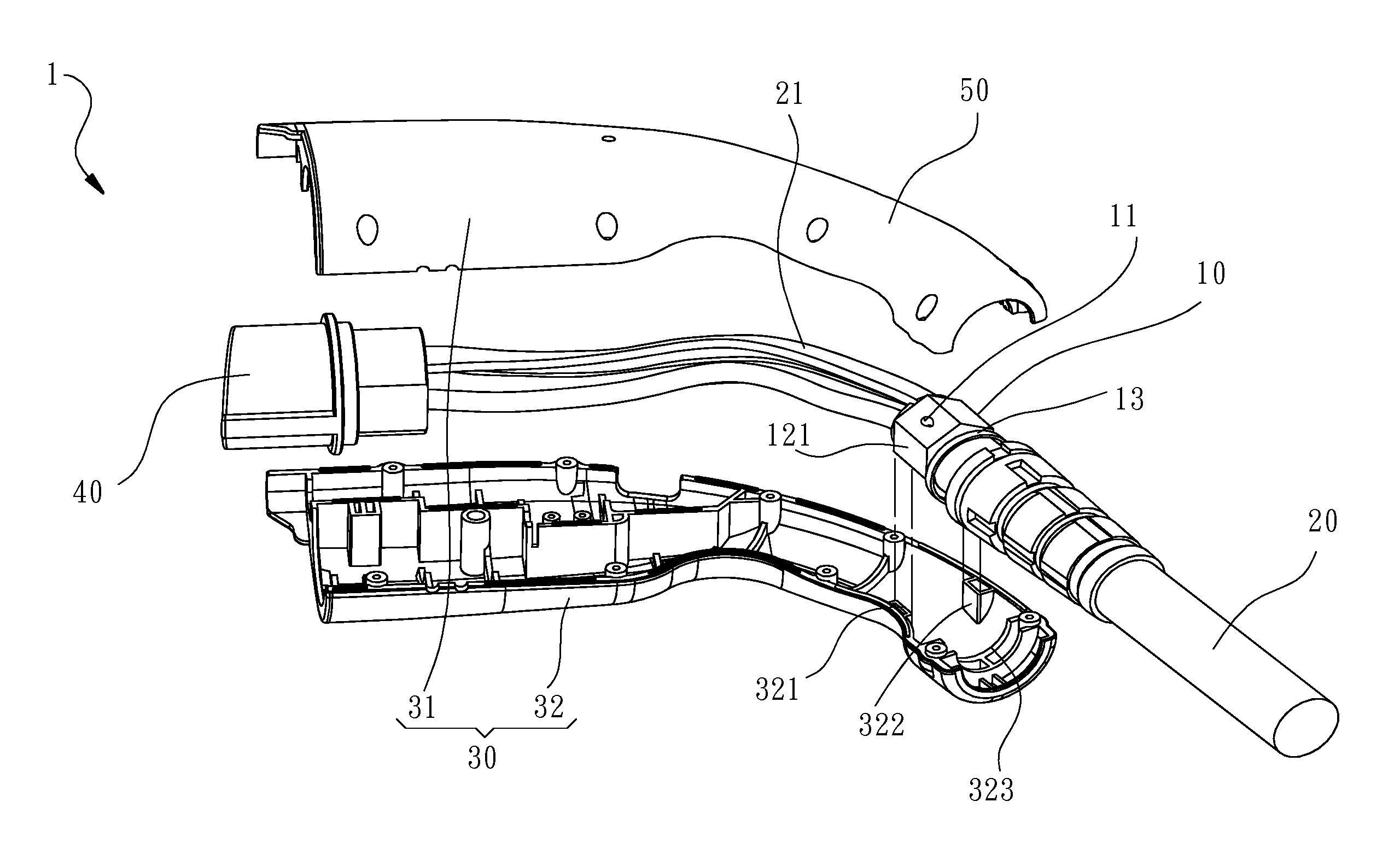
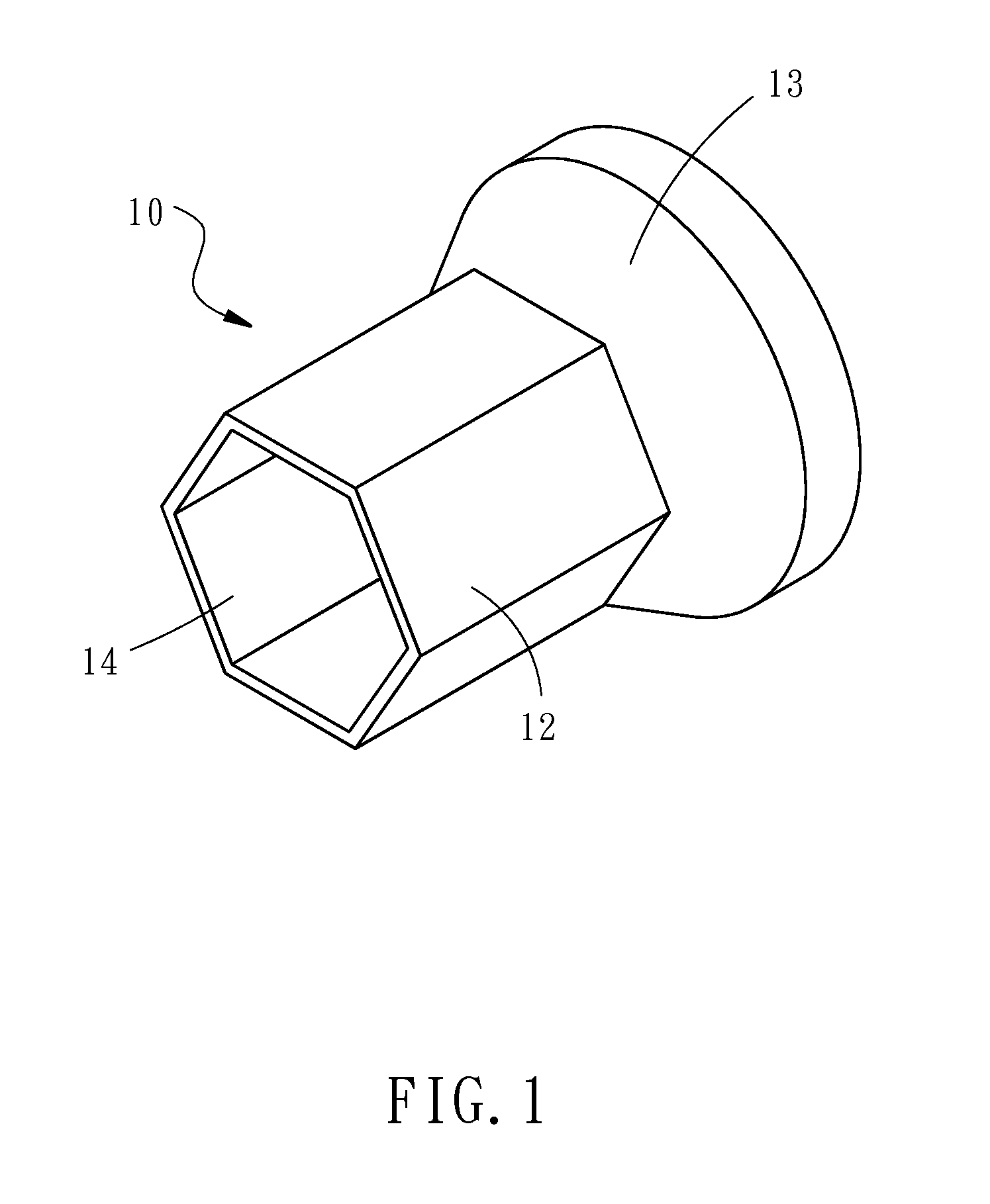
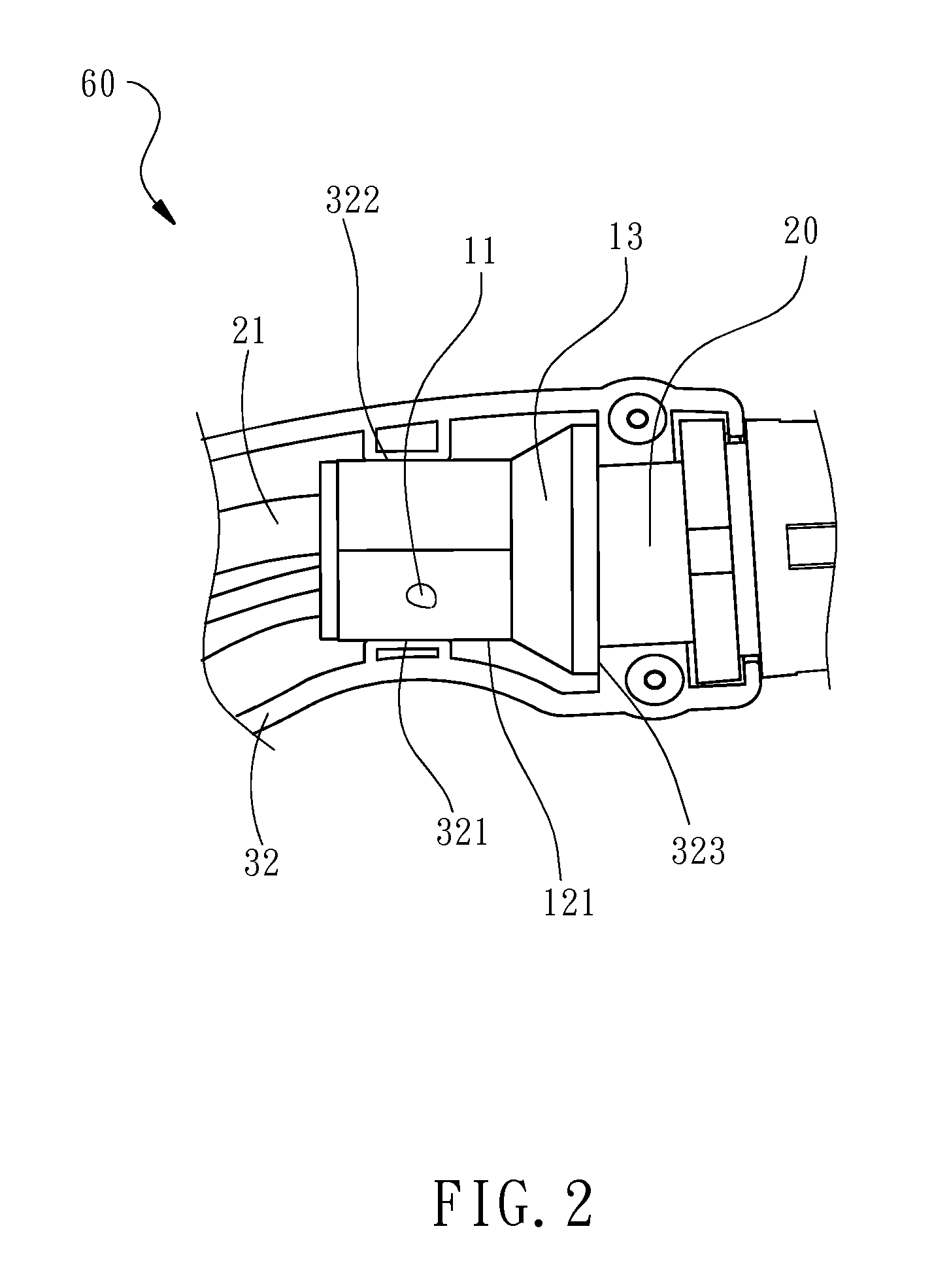
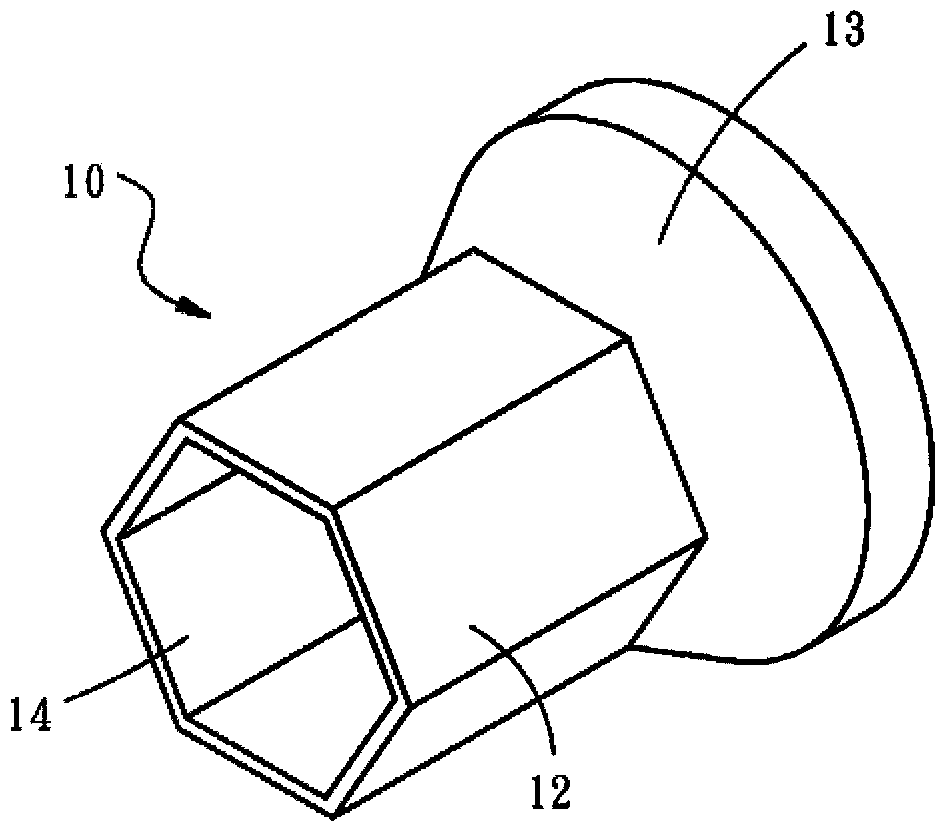
Cable positioning device and charger using same
ActiveUS20140354216A1Avoid disconnectionImprove installation efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsInelastic deformationElectric wire
A cable positioning device and a charger using the cable positioning device is disclosed to include a cable positioning device mounted in a mounting structure inside the charger to secure a cable. The cable positioning device includes a polygonal column that can be forced by an external pressure to deform non-elastically and to further tightly fit the cable, having at least one surface thereof abutted against an inner wall of the mounting structure in the axial direction of the cable to prevent displacement of the cable positioning device and the internal electric wires of the cable due to accidental twisting of the external part of the cable, improving the cable installation efficiency.
Owner:KS TERMINALS INC
Cable positioning element and charging gun using same
InactiveCN104242179AAvoid Axial MisalignmentPrevent rotationBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerSection planeEngineering
The invention relates to a cable positioning element and a charging gun using the cable positioning element. The cable positioning element is suitable for mounting a cable in a mounting base. The cable positioning element includes a column of which the cross section is polygonal, and a hollow channel is formed in the column and allows penetration of the cable. The column can be stressed to produce inelastic deformation to press against the cable, and at least one side face of the column can abut against one inner wall face of the mounting base. Accordingly, the situation that due to the distortion and rotation of the cable, the cable positioning element and wires in the cable positioning element rotate can be avoided, and the assembly efficiency of the cable is improved.
Owner:KS TERMINALS INC
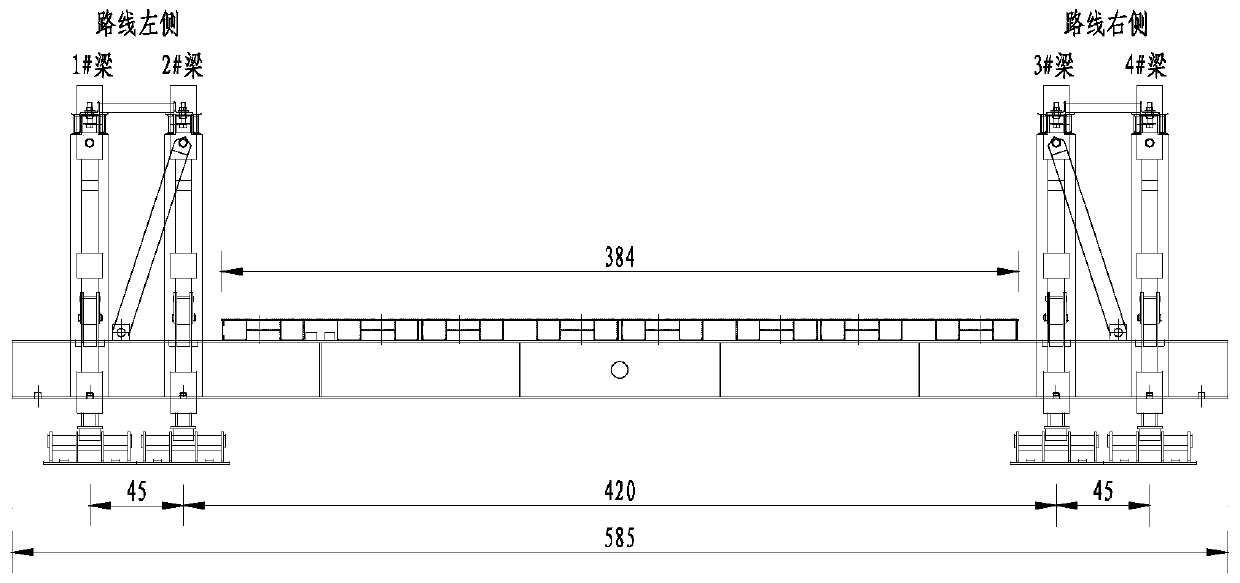
Fabricated prestressing device and method for high pier scaffoldings
ActiveCN106400694AEasy to installEasy to useBridge erection/assemblyStress distributionStructural engineering
The invention discloses a fabricated prestressing device and method for high pier scaffoldings. The fabricated prestressing device includes piers on which the scaffoldings are positioned, and a spatial truss. The spatial truss is hinged to the top of the piers. The base of the spatial truss is fixedly connected to a first stress distribution allocation girder group for prestressing. The upper end of the scaffoldings is provided with the second allocation girder group for prestressing. A hydraulic jack is arranged between the first and the second allocation girder group for prestressing. The fabricated prestressing device has a simple structure and is easily assembled and disassembled. Not only can the device actualize the prestressing test for piers and scaffoldings quickly and effectively but the device can also remove the inelastic deformation of scaffoldings in the process of prestressing. The device can obtain an accurate deformation value of every pier and scaffolding under the corresponding load effect.
Owner:CCCC SECOND HARBOR ENG
Steel trestle static load test evaluation method considering non-elastic deformation
ActiveCN110095274AThe calibration factor is accurateReduce misjudgmentMachine part testingElasticity measurementEngineeringInelastic deformation
Owner:GUANGXI TRANSPORTATION SCI & TECH GRP CO LTD
Prefabrication and construction method of box girder in-situ pedestal
InactiveCN102605718AImprove mechanical performanceReduce the number of erectionsBridge erection/assemblyFalseworkPre stress
The invention particularly relates to a prefabrication and construction method of a box girder in-situ pedestal, which solves the problems that cast-in-place box girders are high in cost and slow in progress and engineering construction is affected. The prefabrication and construction method includes: a, surveying lofting, performing replacement and layered compaction, and backfilling and tampering the area around an abutment; b, erecting a formwork to concrete a concrete pedestal serving as a bottom form, reserving pull bar holes on the top of the pedestal, and casting a concrete foundation around the pedestal; c, tying tie bars to fasten the bottoms of the lateral forms, using support bars to adjust the top elevation of the lateral forms, using a cup-lock scaffold to reinforce the lateral forms, and placing adjustable jacks and square timber on the top of the scaffold; d, pre-stressing the lateral forms to eliminate non-elastic deformation of a foundation and the scaffold, and correcting elevation of the foundation and the lateral forms again according to pre-stressing results; and e, sequentially installing bottom web reinforcement, inner membrane forms, top plate reinforcement and embedded parts, and pouring body concrete of the box girder. By the method, the stress effect of the forms can be improved greatly, and the prefabrication and construction method has the advantages of simple structure, reasonable design, simplicity in operation and effectiveness in use.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY 12TH BUREAU GRP +1
Pad of vehicle seat and method of manufacturing the pad
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
Cable positioning device and charger using same
ActiveUS9257857B2Avoid disconnectionImprove installation efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsRelieving strain on wire connectionInelastic deformationElectric wire
A cable positioning device and a charger using the cable positioning device is disclosed to include a cable positioning device mounted in a mounting structure inside the charger to secure a cable. The cable positioning device includes a polygonal column that can be forced by an external pressure to deform non-elastically and to further tightly fit the cable, having at least one surface thereof abutted against an inner wall of the mounting structure in the axial direction of the cable to prevent displacement of the cable positioning device and the internal electric wires of the cable due to accidental twisting of the external part of the cable, improving the cable installation efficiency.
Owner:KS TERMINALS INC
Adhesive backed decorative article, method of making, and method of use
InactiveUS20180281506A1Susceptible to effectEasy to operateFilm/foil adhesivesDecorative surface effectsAdhesiveInelastic deformation
A decorative article comprising a main body portion that can be deformed based on the shape of an adhering surface, and can be fixed to the adhering surface via an adhesive layer, without substantially stretching during adhesion. The main body portion will not inelastically deform, even if an operator pulls on the main body portion, when adhering to the adhering surface. The main body portion is deformed based on the shape of the adhering surface. Therefore, when the operator deforms the main body portion based on the shape of the adhering surface and adheres the adhesive-backed decorative article to the adhering surface, it is not necessary to perform a position adjustment by pulling and stretching the main body portion. Furthermore, an adhesive-backed decorative article can be adhered to the adhering surface regardless of the shape of the adhering surface.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Suspended cast beam No. 0 block bracket opposite-fulcrum prepressing construction method
InactiveCN102518049AOutstanding FeaturesHighlight significant progressBridge erection/assemblySocial benefitsEngineering
The invention relates to a suspended cast beam No. 0 block bracket opposite-fulcrum prepressing construction method which comprises the following steps of: respectively embedding more than one steel strand connectors along the longitudinal direction on the left side and the right side inside a bearing platform, wherein each row of steel strand connectors is provided with a plurality of steel strand connectors, the quantity of the steel strand connectors in all rows of steel strand connectors are equal, each steel strand connector is fixedly connected with the bottom end of one steel strand respectively, and each steel strand extends along the vertical direction to penetrate out the top end of the bearing platform; arranging a bracket above the constructed bearing platform; laying a bracket load distribution beam on the top of the bracket along the horizontal direction, and connecting the bracket load distribution beam with the upper parts of all the steel strands by using tool anchors and clamping pieces. The invention aims at providing a suspended cast beam No. 0 block bracket opposite-fulcrum prepressing construction method which can effectively eliminate the non-elastic deformation of the bracket and reduce the construction period, the elastic deformation value of the bracket can be accurately obtained, accurate parameters can be provided for elevations of bottom dies and vertical dies for No. 0 block construction, and the method has good economic and social benefits.
Owner:CCCC FOURTH HIGHWAY ENG +1
System and method for providing a downhole mechanical energy absorber
InactiveUS8256516B2Maximizes limit loadReduce noisePortable framesDrilling rodsMechanical energyEngineering
A system and a method provide a downhole mechanical energy absorber that protects downhole tools from impact loads and shock loads that occur during run-in contacts, tool drops, perforating blasts, and other impact events. A continuous localized inelastic deformation of a tube is a primary energy absorber in a load limiting design of the downhole mechanical energy absorber.
Owner:STARBOARD INNOVATIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com