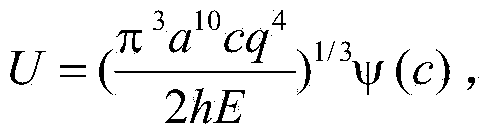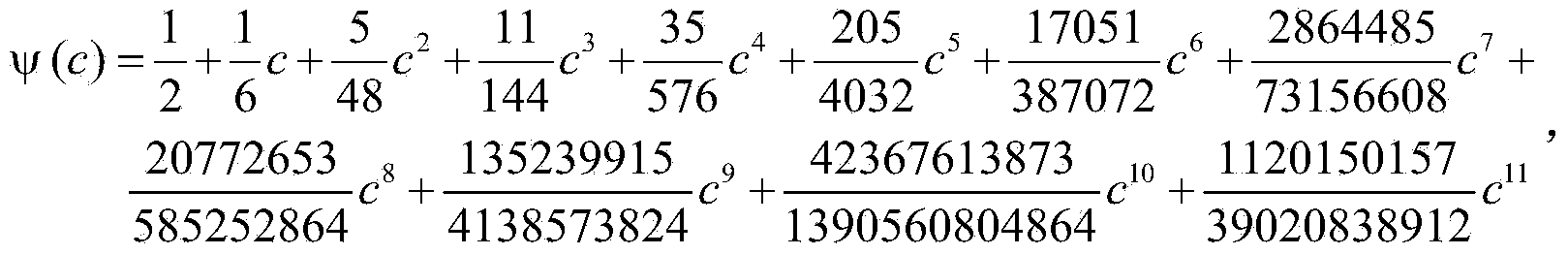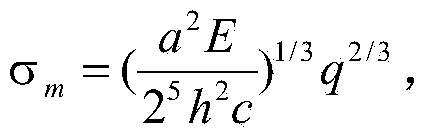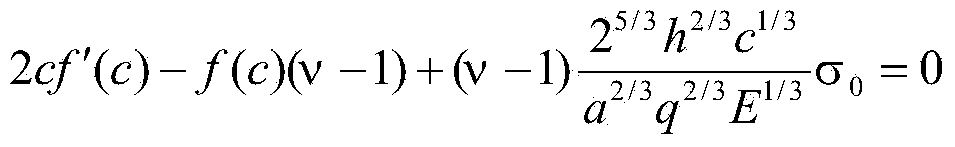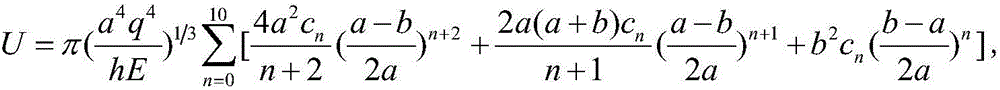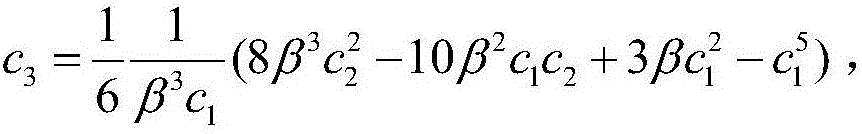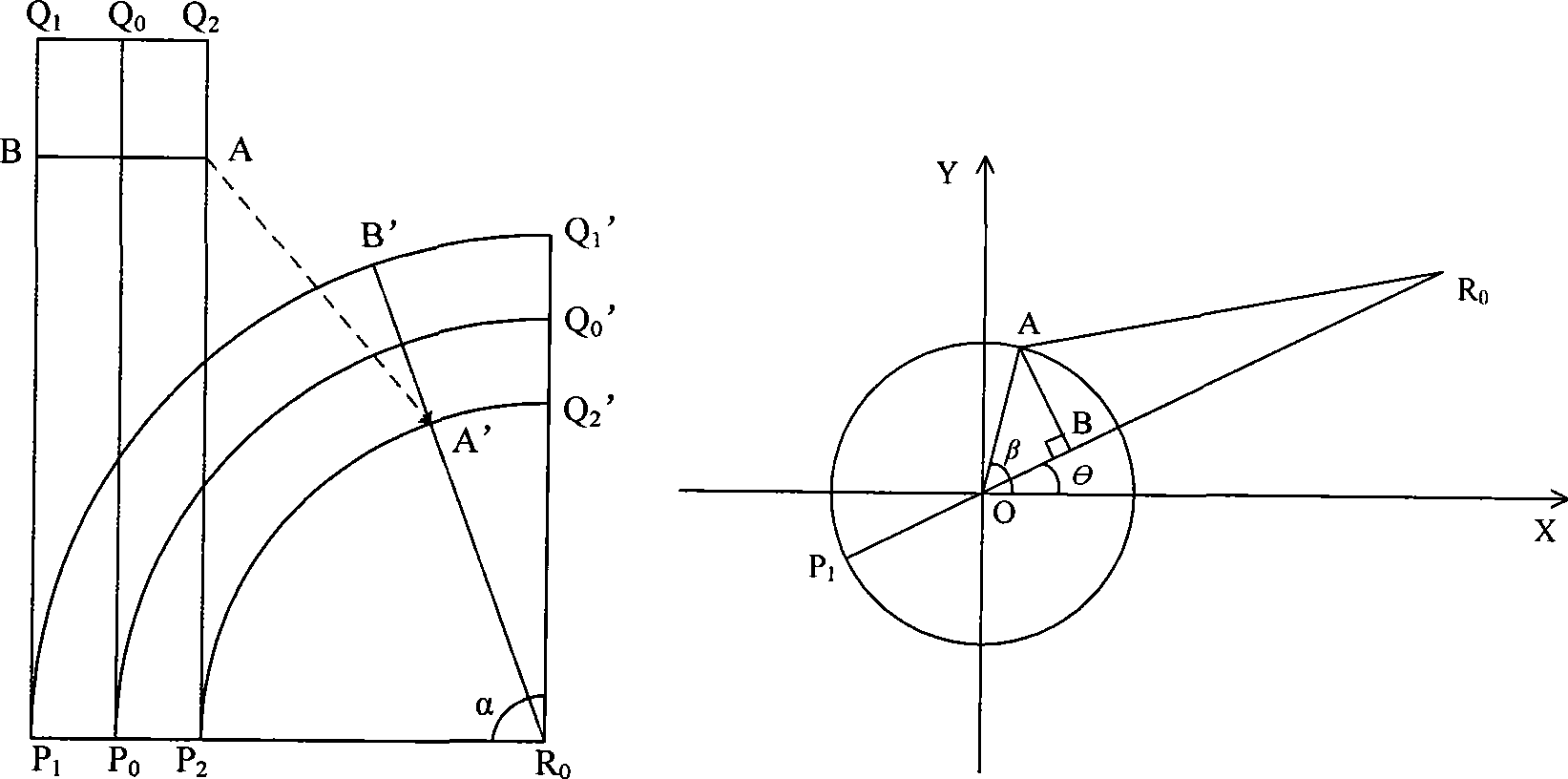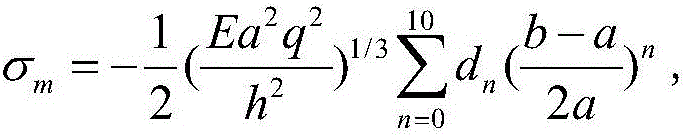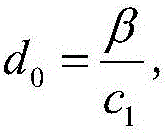Patents
Literature
509 results about "Deformation Problem" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
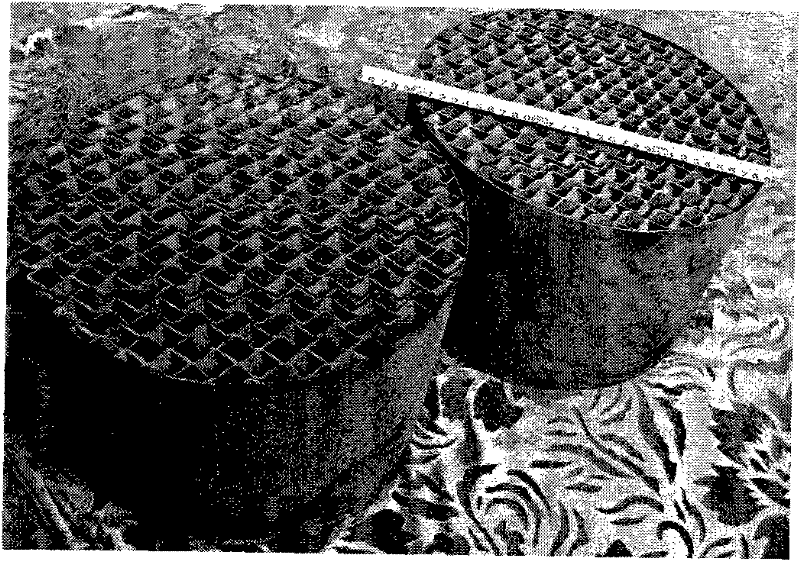
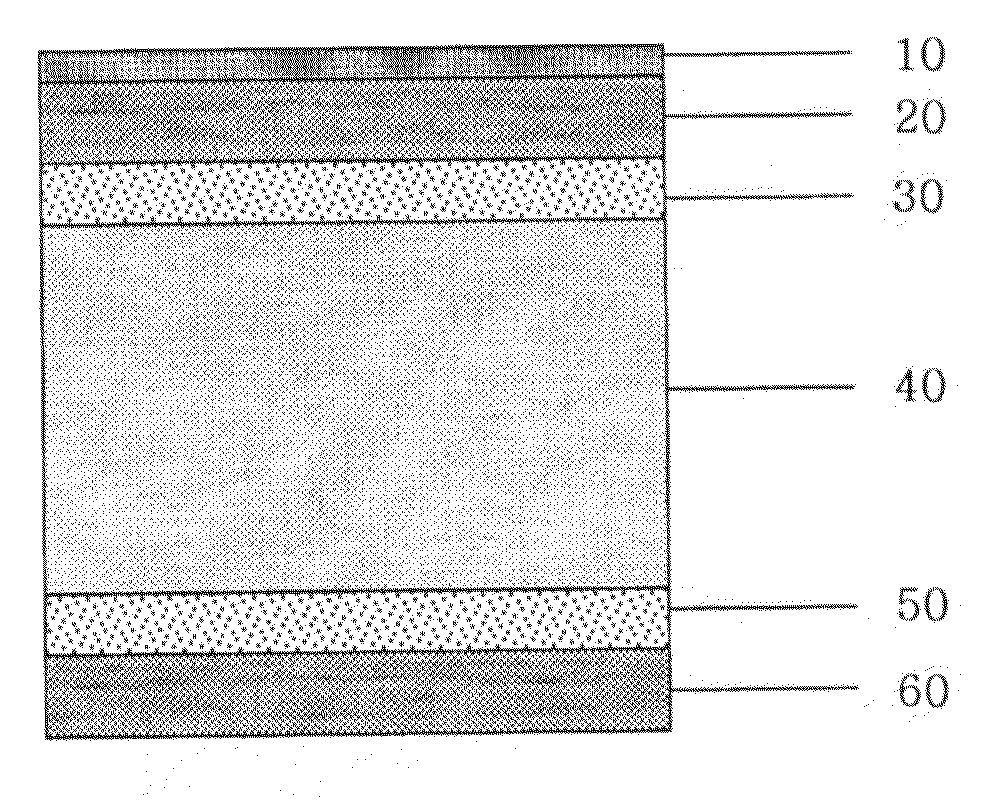
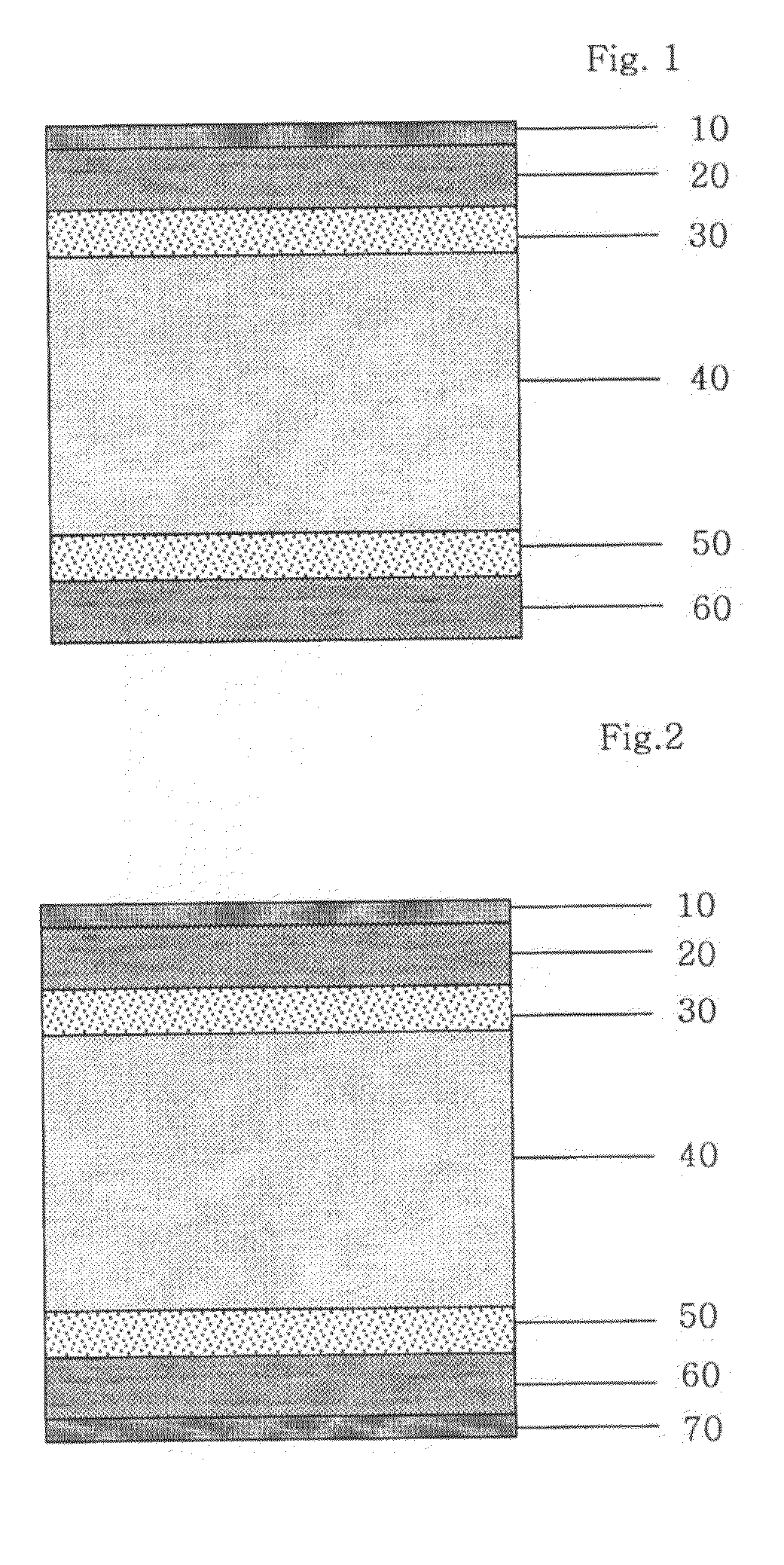
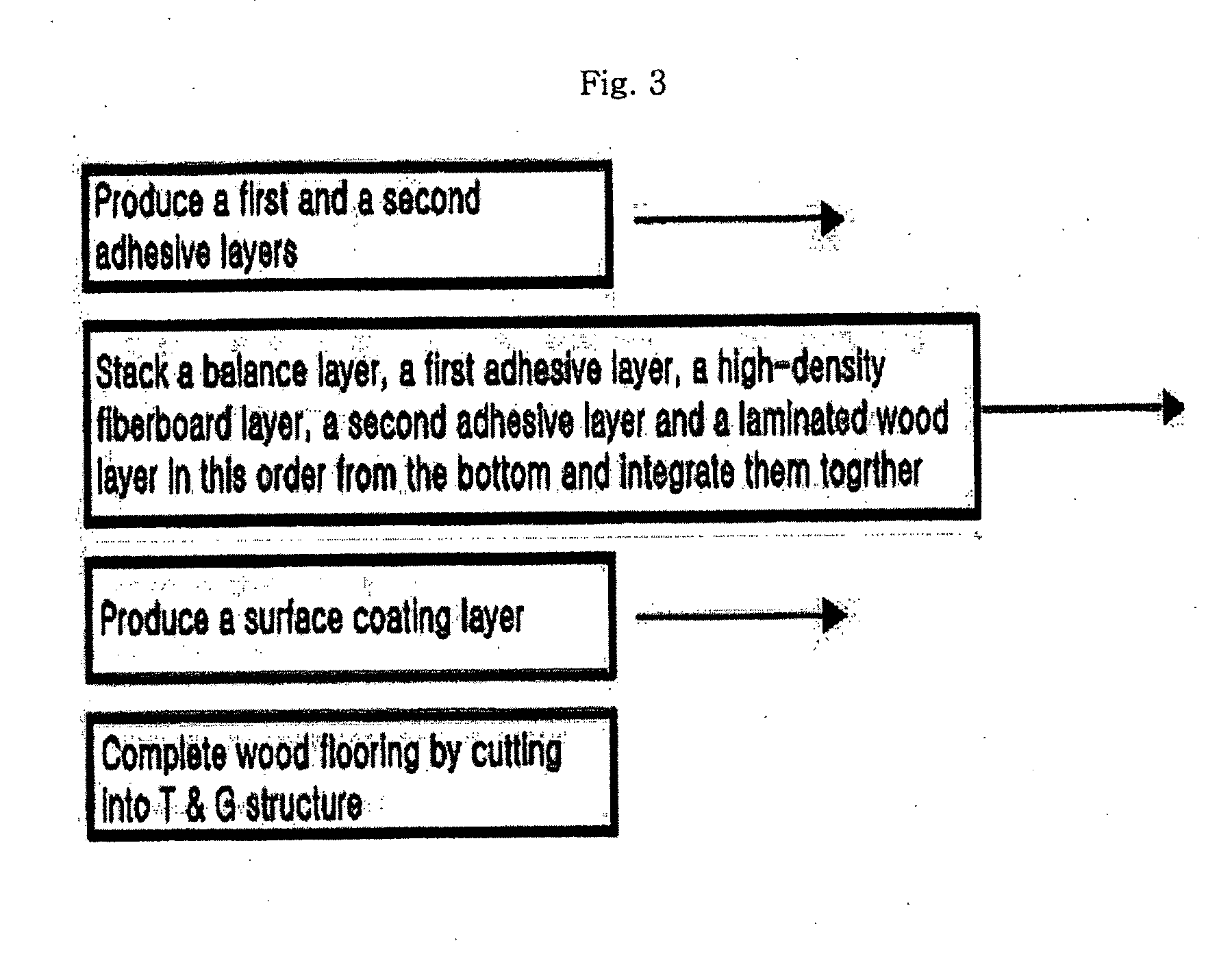
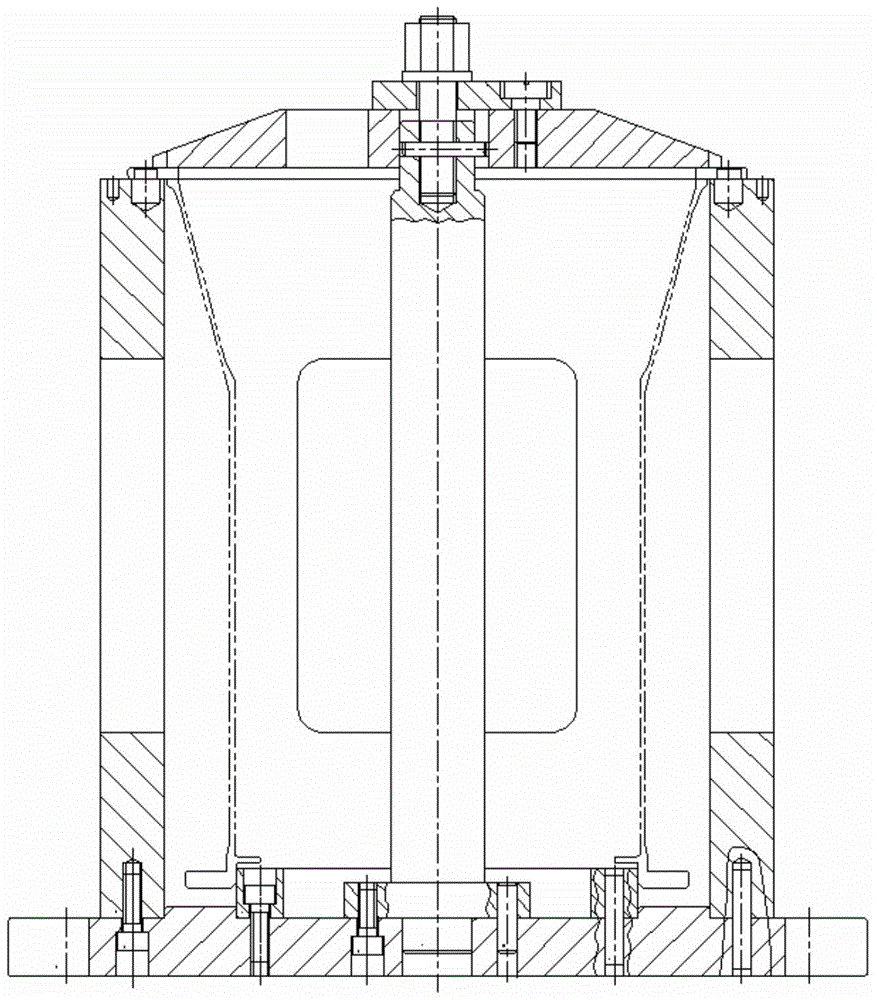
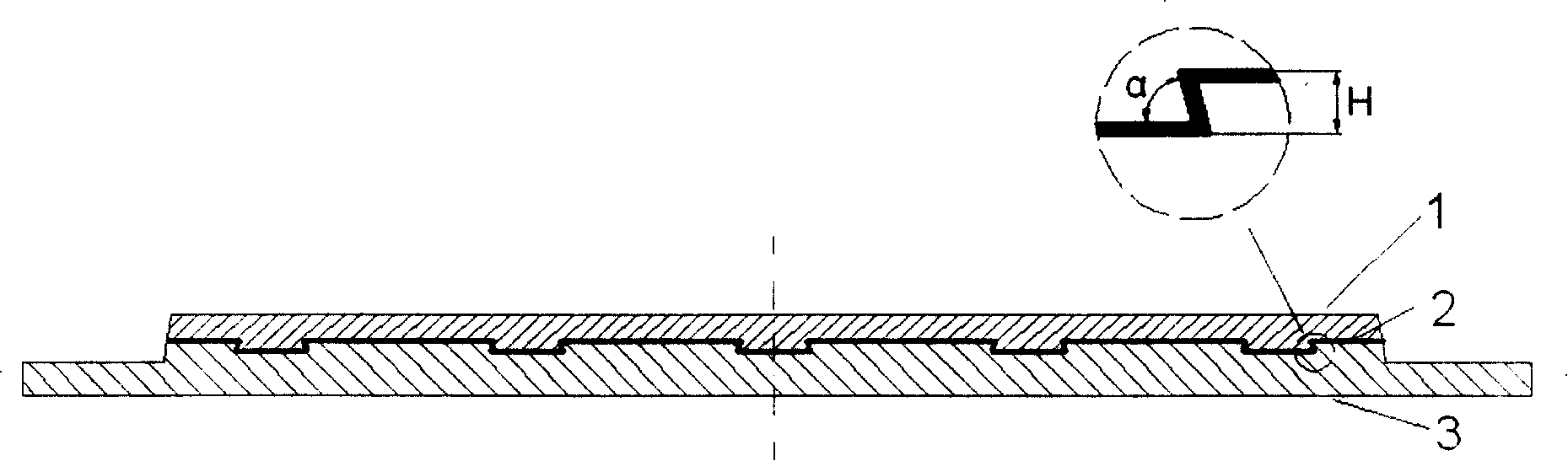
Wood Flooring With Laminated Wood And HDF Using Symmetric Structure And Process For Manufacturing The Same
InactiveUS20090197036A1Stable structureEliminate the problemLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsHigh densityVolumetric Mass Density
Disclosed is a wood flooring containing laminated wood and high-density fiberboard using a symmetric structure and a process for manufacturing the same. The wood flooring includes a high-density fiberboard core layer and an upper laminated wood layer and lower laminated wood or veneer layer symmetrically stacked about the high-density fiberboard core layer to achieve a stable structure, and the lower laminated wood or veneer layer has a density of 100±30% of that of the upper laminated wood layer to keep the balance therebetween. With this configuration it is possible to completely eliminate deformation problems caused by variation of environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, etc., and to impart the natural texture of raw lumber and high durability to the flooring surface.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Friction stir welding additive manufacture method of bar material
ActiveCN105397276ADoes not involve formingDoes not involve coagulationNon-electric welding apparatusManufacturing technologyShielding gas
A friction stir welding additive manufacture method of a bar material relates to a method for manufacturing a bar material. The objective of the invention is to solve the air hole, crack and large deformation problems of the material manufactured by the existing high-energy beam additive manufacture method. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing cylindrical parent metal; step 2, preparing an additive manufacture die; step 3, preparing an additive manufacture base plate; step 4, welding the die with the base plate; step 5, positioning the die and the base plate; step 6, determining additive manufacture parameters; and step 7, conducting the forming process of additive manufacture. The method is simple in manufacture technology, does not require protection gas or vacuum environment, solves air hole, crack and deformation problems easily occurring in the high-energy beam additive manufacture process, and can obtain a high-performance structural material. The method is suitable for the additive manufacture of various materials.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Silicon carbide foamed ceramics corrugated structured packing and preparation method and applications thereof
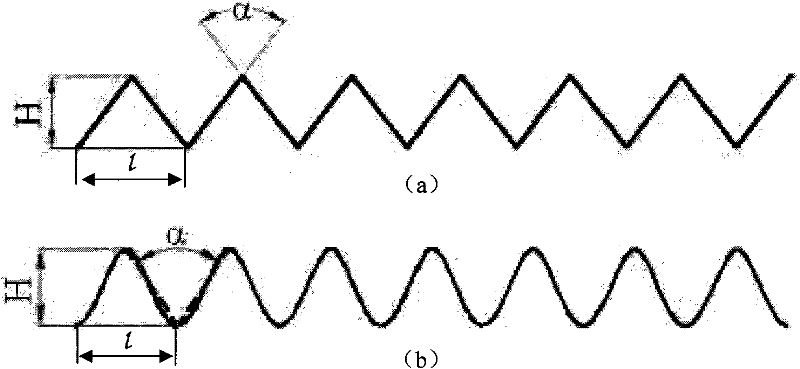
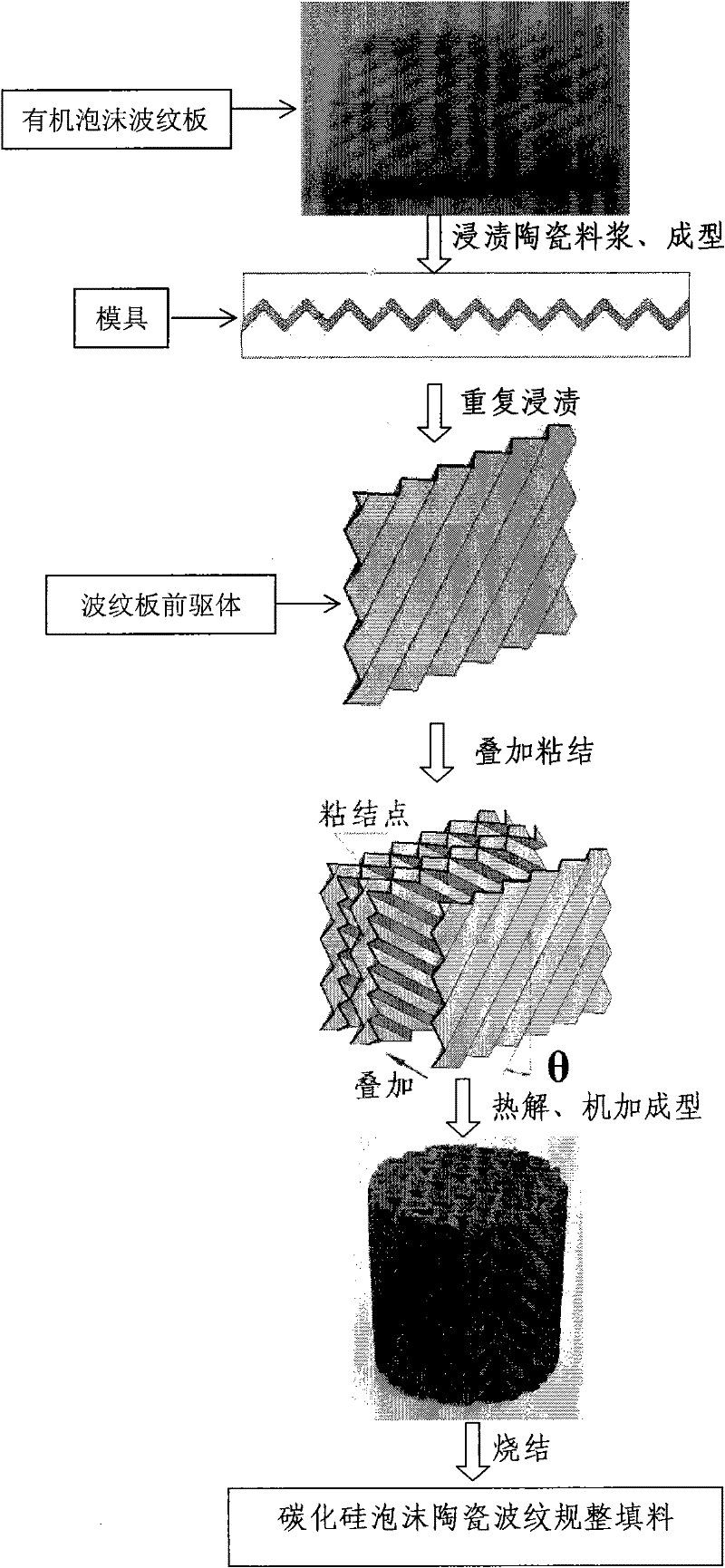
InactiveCN102218293AResolve compressionSolve the problem of elongation deformationPress rollersDistillation separationNetwork structureDeformation Problem
The invention relates to the field of structured packing, and in particular relates to silicon carbide foamed ceramics corrugated structured packing and a preparation method and applications thereof. The packing is formed by the stacking and combining silicon carbide foamed ceramics packing units of corrugated geometrical shapes; the packing unit plates are silicon carbide foamed ceramics of three-dimensional communicated network structures; the foam pore size is between 10PPi and 80PPi; the volume fraction can be controlled between 10% and 70%; and the corrugated shape of the packing units are triangles or smooth waves. The organic foam is cut into required corrugated shapes in advance, and then is subjected to press molding or double-roll extrusion molding, the deformation problem of compression and elongation of foam holes in the molding process is solved well, the shape of the foam holes of the obtained packing units is regular, and the original three-dimensional communicating structure of the organic foamed templates is maintained preferably; and the structured packing and the preparation method provided by the invention are suitable for a plurality of operation processes, especially are suitable for the separation process of systems difficult to be separated, adapt to the requirements of high efficiency and low energy consumption, and are especially suitable for the separation process of various high-corrosion systems.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Machining method for deformation control of high-precision thin-wall cylinder shaft
InactiveCN106425286AHigh precision requirementsHigh hardnessWork clamping meansPositioning apparatusDeformation controlSuperalloy
The invention discloses a machining method for deformation control of a high-precision thin-wall cylinder shaft. A process scheme is determined: because a workpiece belongs to a thin-wall piece, the deformation control needs to be considered at the beginning of formulating a process route, the influence on deformation of the workpiece by machining stress in finish turning is controlled; an anti-deformation fixture structure is determined: a workpiece clamping mode is researched; a fixture clamping scheme is improved; a special anti-deformation fixture is used for finely turning inner and outer molded surfaces and machining a large end surface hole groove and a small end surface hole groove to solve the deformation problem caused in workpiece machining; the large end surface is axial reference of the whole workpiece to reach high precision requirement; and the small end surface is higher in technical condition requirement on the large end surface. The machining method has the following advantages: the technical difficulty of deformation of a high-temperature alloy thin-wall cylinder shaft is solved, a qualified workpiece is finally machined, the technical bottleneck of deformation of the high-temperature alloy thin-wall cylinder shaft is broken through, the workpiece design requirements are guaranteed, and the machining method can be popularized and applied in the same kind of workpieces to provide precious experiences for similar workpiece machining.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
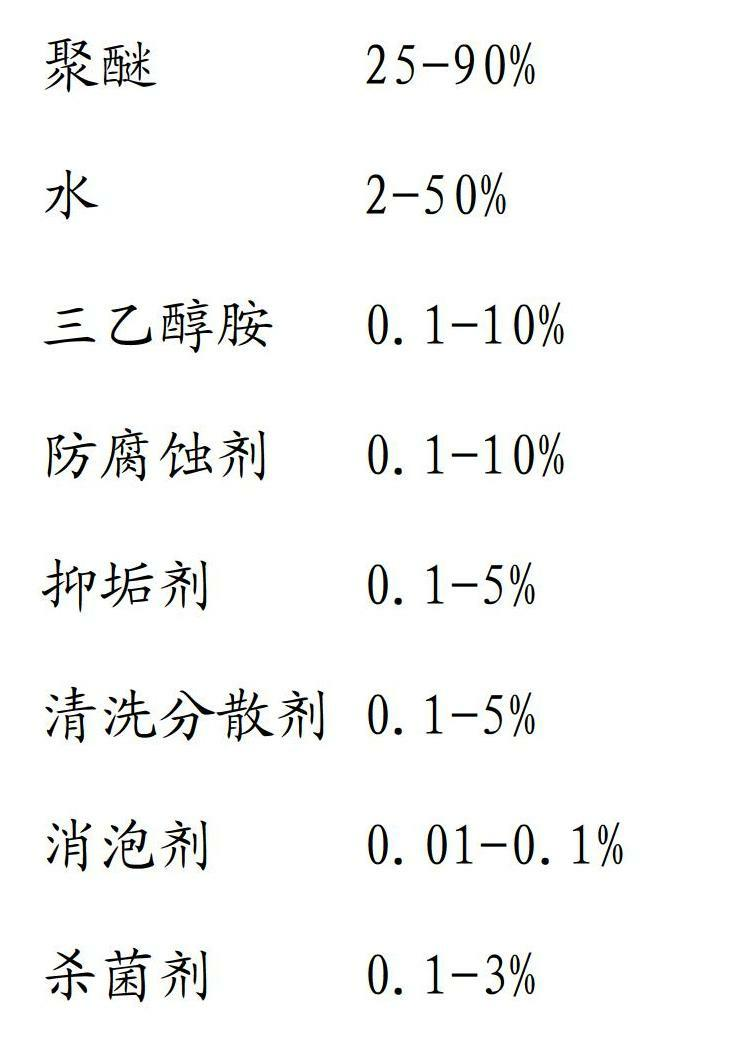
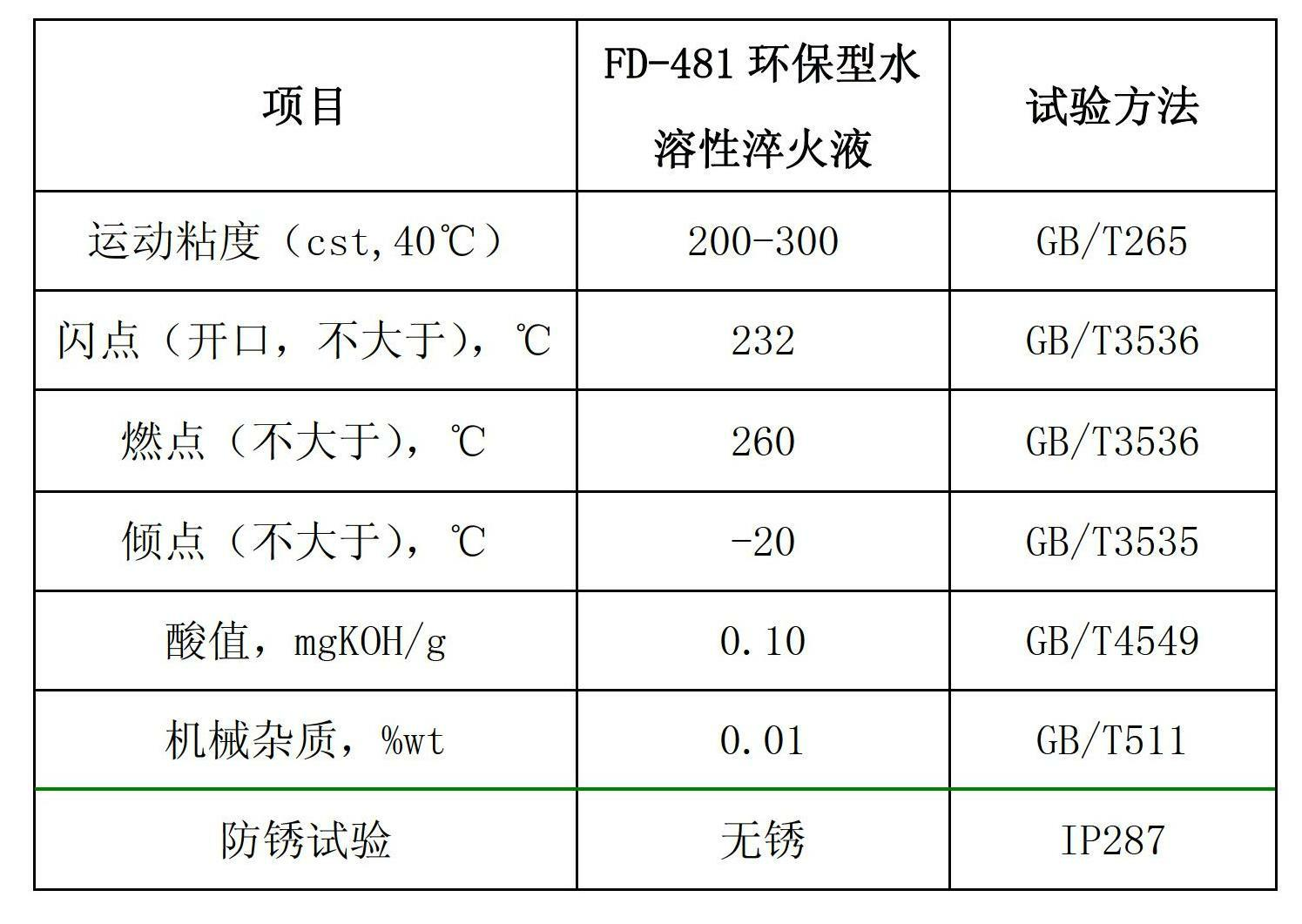
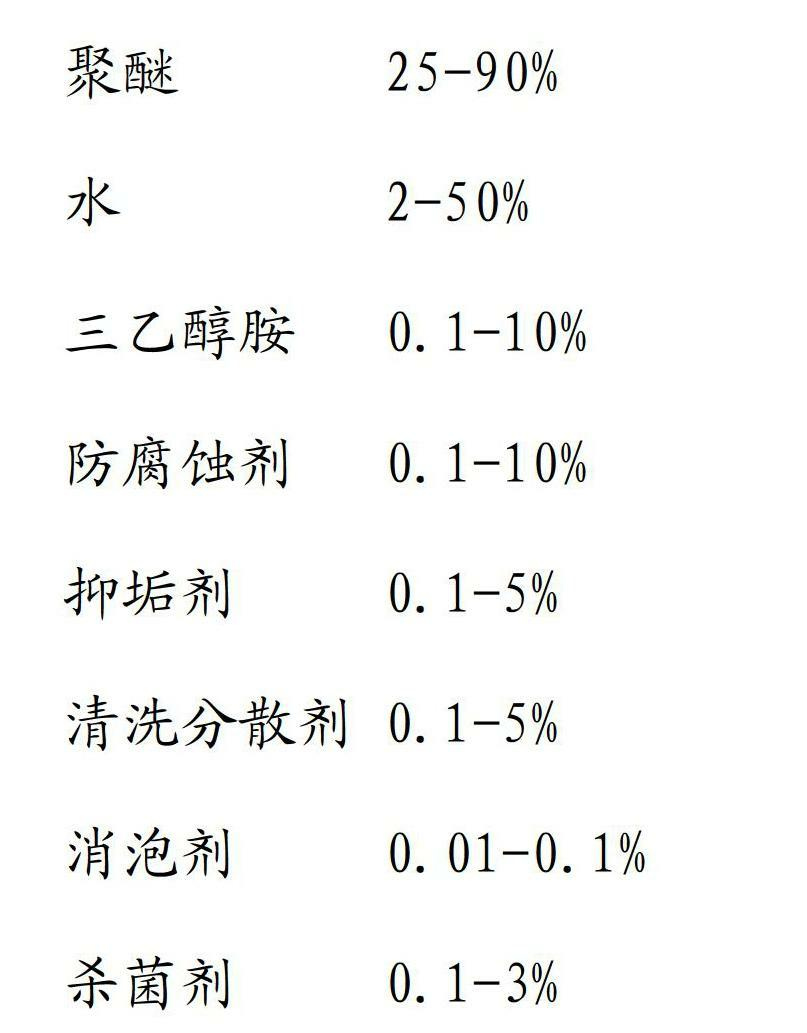
Environmental protection water-solubility quenching liquid
ActiveCN102643963AImprove final performanceImprove machining accuracyQuenching agentsSolubilitySurface cleaning
The invention discloses environmental protection water-solubility quenching liquid, which, by weight, comprises components of 25-90% of polyether, 2-50% of water, 0.1-10% of triethanolamine, 0.1-10% of anticorrosive agent, 0.1-5% of dirty restrain agent, 0.1-5% of washing dispersing agent, 0.01-0.1% of antifoaming agent and 0.1-3% of fungicide. The polyether molecular weight is 30000-50000. The water-solubility quenching liquid is compounded with balanced rust-inhibiting additive and the washing dispersing agent, has great cooling speed in a high-temperature cooling stage, can refine grains, has moderate cooling speed in a low-temperature cooling stage, effectively solves cracking and deformation problems in a workpiece cooling process, and improves surface quality of a workpiece. Excellent rust-proof performance effectively protects the quenched workpiece, and rust-proof requirements between working procedures are completely met. The environmental protection water-solubility quenching liquid has prominent surface cleaning performance, scale cinder is avoided, output quantity is small, production efficiency is improved, and production cost is saved.
Owner:上海福岛新材料科技有限公司
Thermal treatment technology of high-nitrogen stainless bearing steel
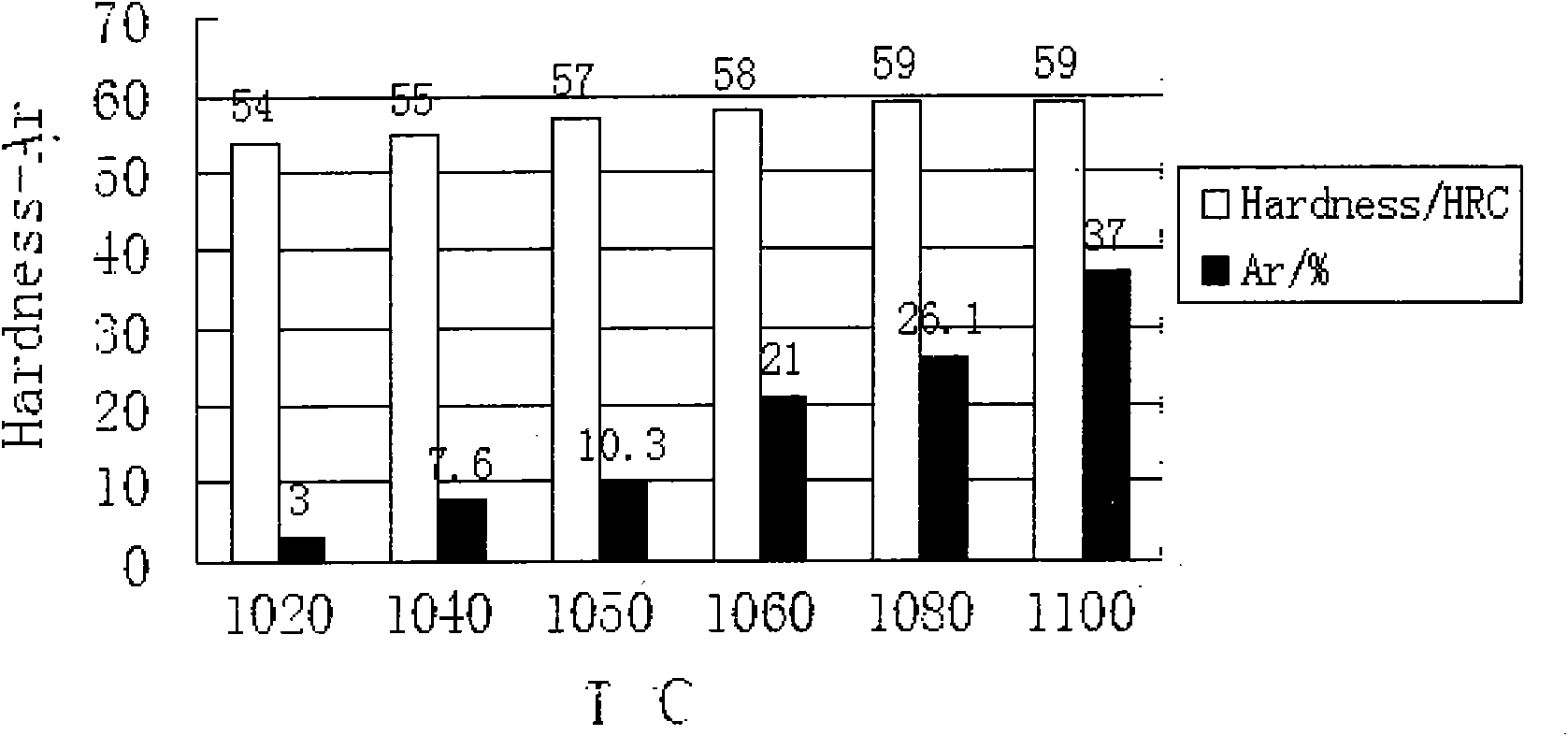
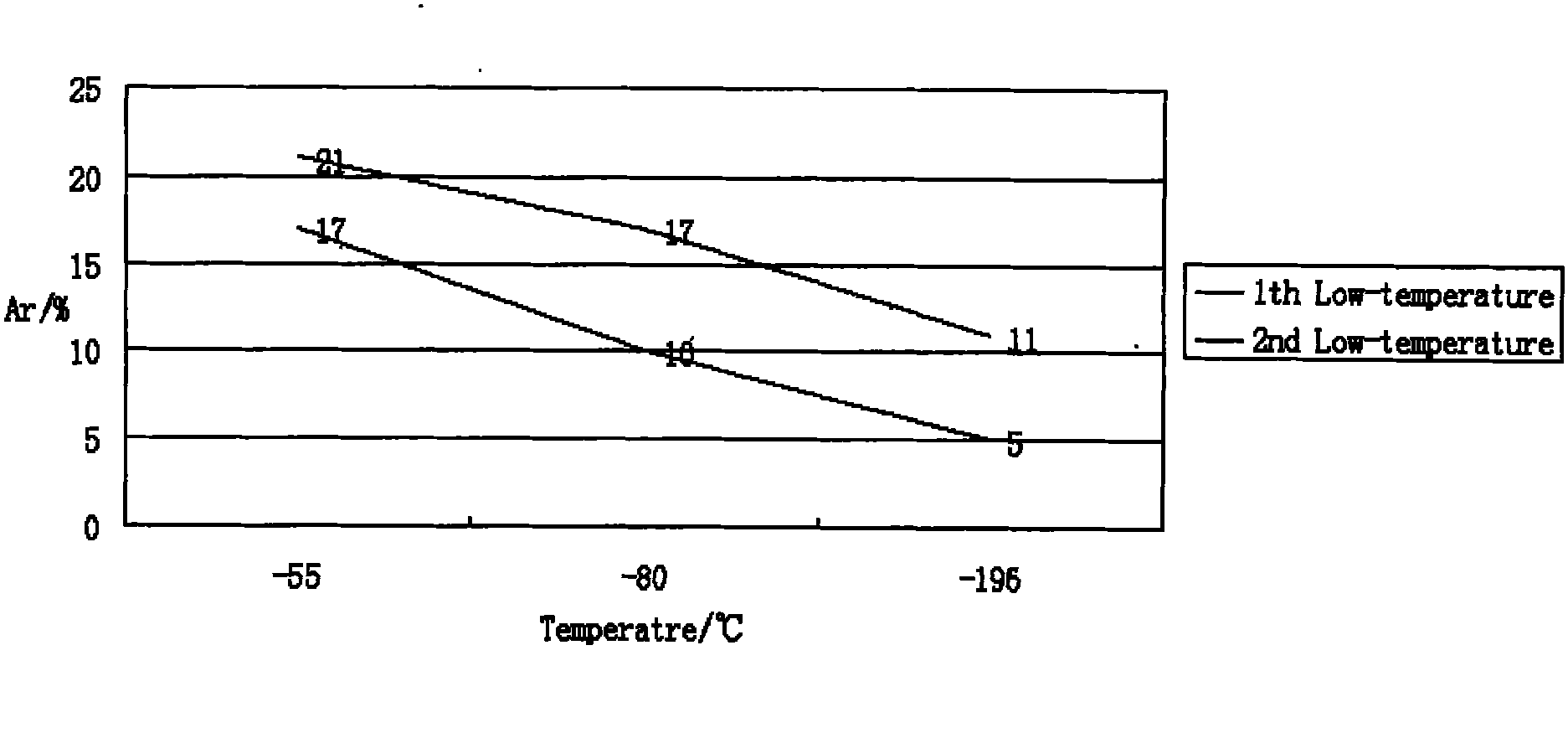
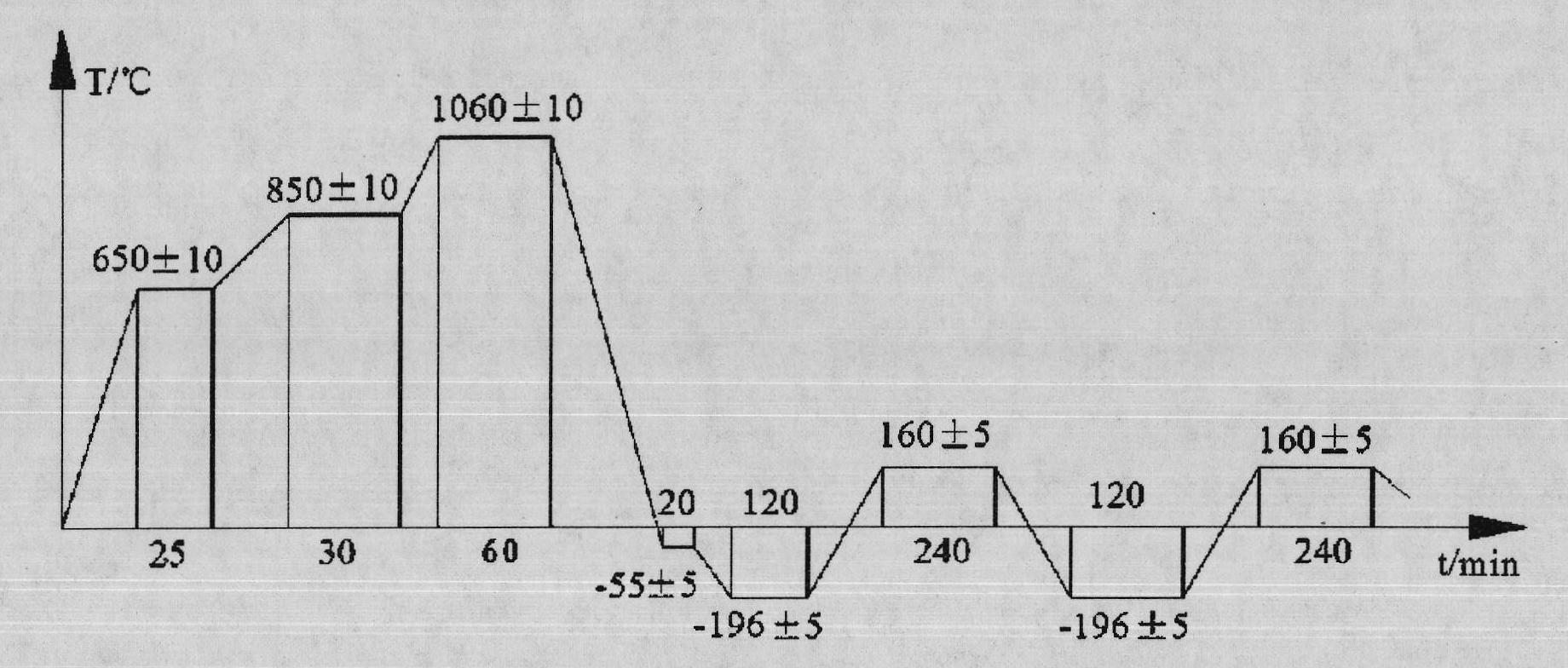
InactiveCN101935752AControl contentGuaranteed dimensional stabilityHeat treatment process controlCold treatmentRoom temperature
The invention discloses a thermal treatment technology of high-nitrogen stainless bearing steel, comprising the following steps of: primarily preheating at a temperature of 650+ / -10 DEG C and preserving the temperature for 25-35 min; secondarily preheating at a temperature of 850+ / -10 DEG C and preserving the temperature for 20-45 min; quenching at a temperature of 1060+ / -10 DEG C and preserving the temperature for 50-60 min; cooling to the room temperature after the quenching and performing cold treatment in half an hour at a temperature of -196+ / -5 DEG C for 2-3 h for twice; and warming to the room temperature after the cold treatment and performing tempering immediately at a temperature of 160+ / -5 DEG C for 4-4.5 h for twice. The best thermal treatment technology of 40Crl5Mo2VN high-nitrogen stainless bearing steel of the invention, which is finally determined on the basis of numerous experiments, not only effectively controls the content of the remained austenite to guarantee the size stability problem of the 40Crl5Mo2VN steel workpiece, but also solves the deformation problem and crack problem of the thermal treatment.
Owner:LUOYANG LYC BEARING
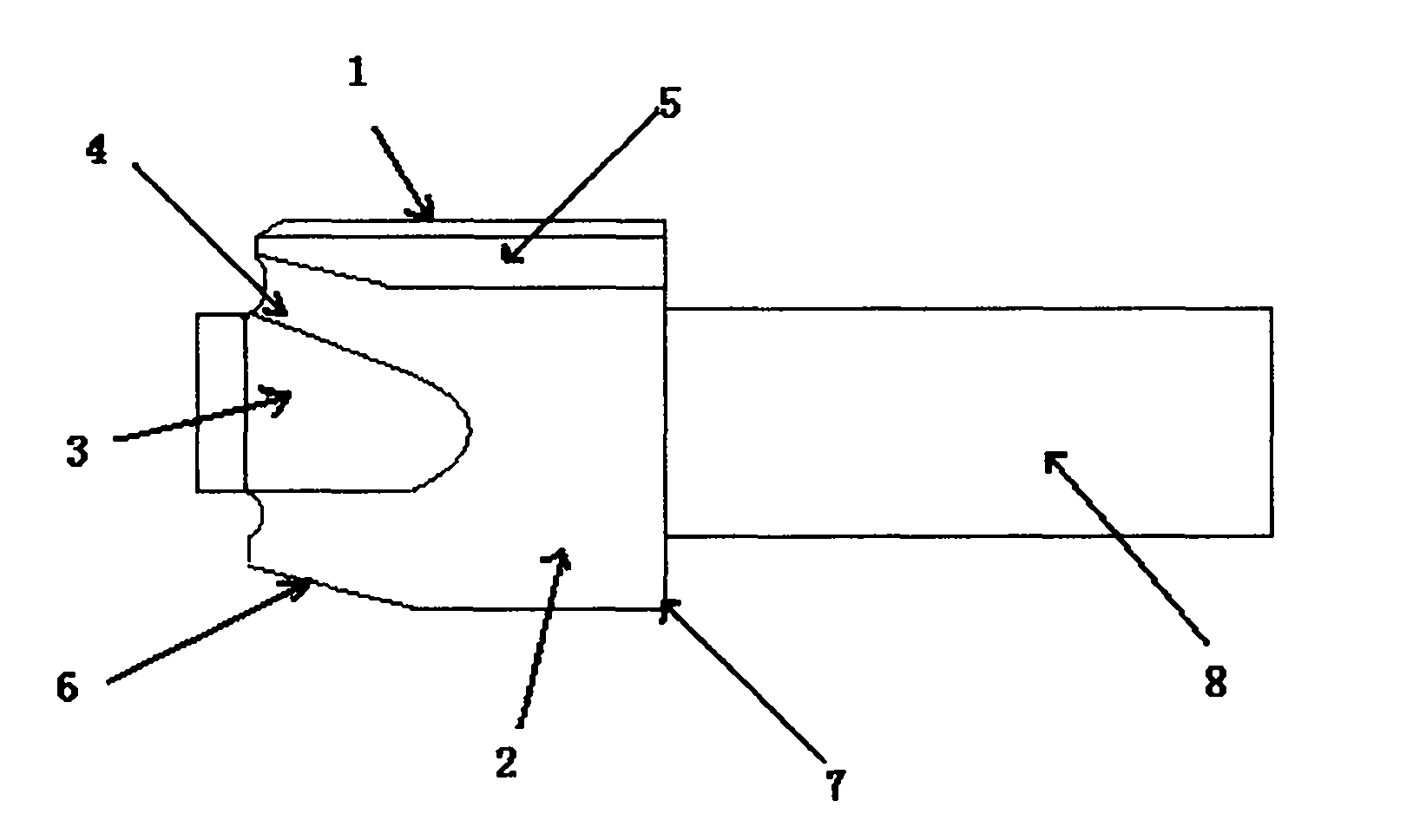
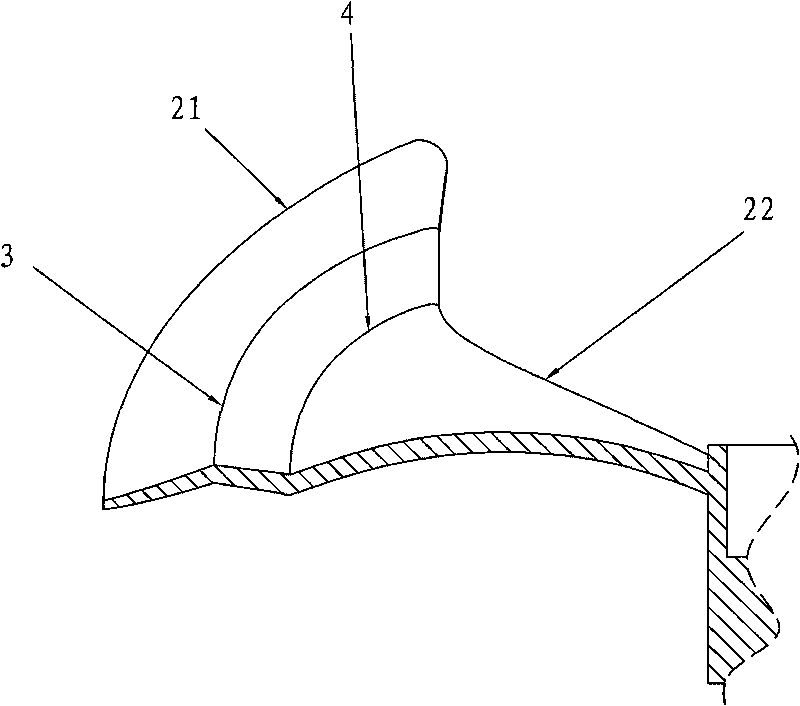
NC (numerical control) processing method for special-shaped joint part
InactiveCN101767264ASolve processing deformationMeet the design requirementsNumerical controlMachining process
The invention provides an NC (numerical control) processing method for a special-shaped joint part. The profile surface of a tee joint is divided into the following parts: a side wall 1, an upper-lower profile 2, an upper-part circular arc 3, a through-connection circular arc 4, a profiled groove 5, a spigot outer wall 6, a root part 7 and a technical chuck 8. The NC processing method is characterized in that: a part blank is adopted to reserve the technical chuck, so as to solve the problem of clamping deformation of the part; the outer profile surface is first processed through NC milling and then the inner profile surface is processed through NC linear cutting. The NC processing method overcomes the disadvantage that the part is difficult to meet the requirement of the special-shaped profile surface for the wall thickness due to having extremely poor rigidity during the processing. The NC processing method in the invention can be applied for manufacturing the special-shaped joint part of a stress application main pipe of a certain machine, and can solve the deformation problem without stress processing.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
Method for strengthening process rigidity of thin-wall blade based on non-uniform allowance
InactiveCN103084639ASolve the deformation problem caused by insufficient rigidity in CNC milling finishingControl processing deformationAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusNumerical controlPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a method for strengthening the process rigidity of a thin-wall blade based on non-uniform allowance; from the perspective of adjusting the process rigidity of a blank in ahead of finely processing the thin-wall blade, the milling is carried out according to the method, so that the processing deformation of a thin-wall blade machine can be effectively controlled, and the processing error is reduced; because the deformation of the blade generated under the action of milling force is mainly in the normal direction of the blade, the rigidity of various points of the blade under the milling conditions and the rigidity variation tendency of the whole blade are researched and found out by analyzing the deformation of the various points of the blade under the same cutting force; on the basis, a method for distributing the fine processing allowance of the blade is optimized; and the cutting deformation of the thin-wall blade in the fine processing is reduced. The stability in the cutting process is improved from two aspects comprising the optimization of processing and cutting force and the optimization of the rigidity of work-pieces; and therefore, the deformation problem caused by insufficient numerical control milling and fine-processing rigidity of the thin-wall blade is solved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
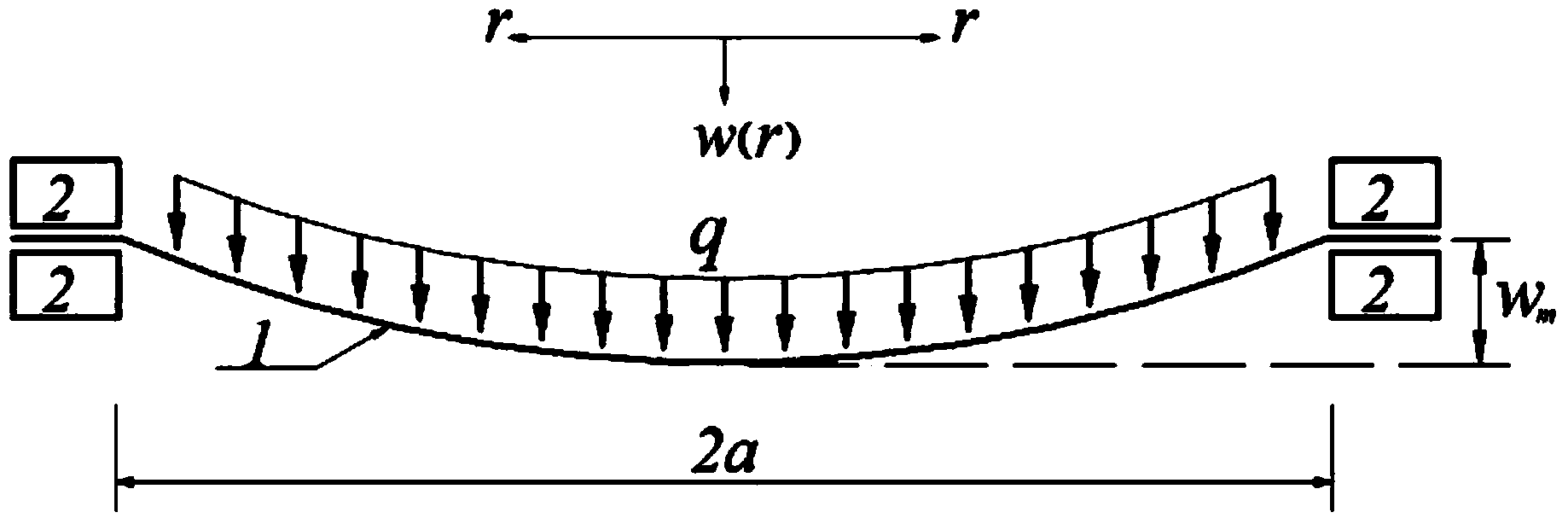
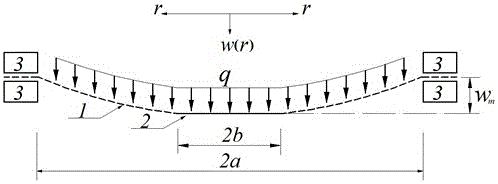
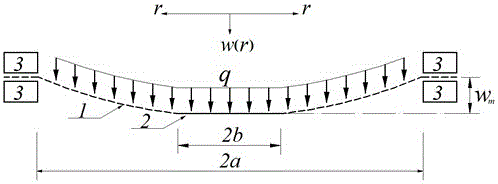
Method for determining resilience of prestressed circular film under uniformly-distributed load
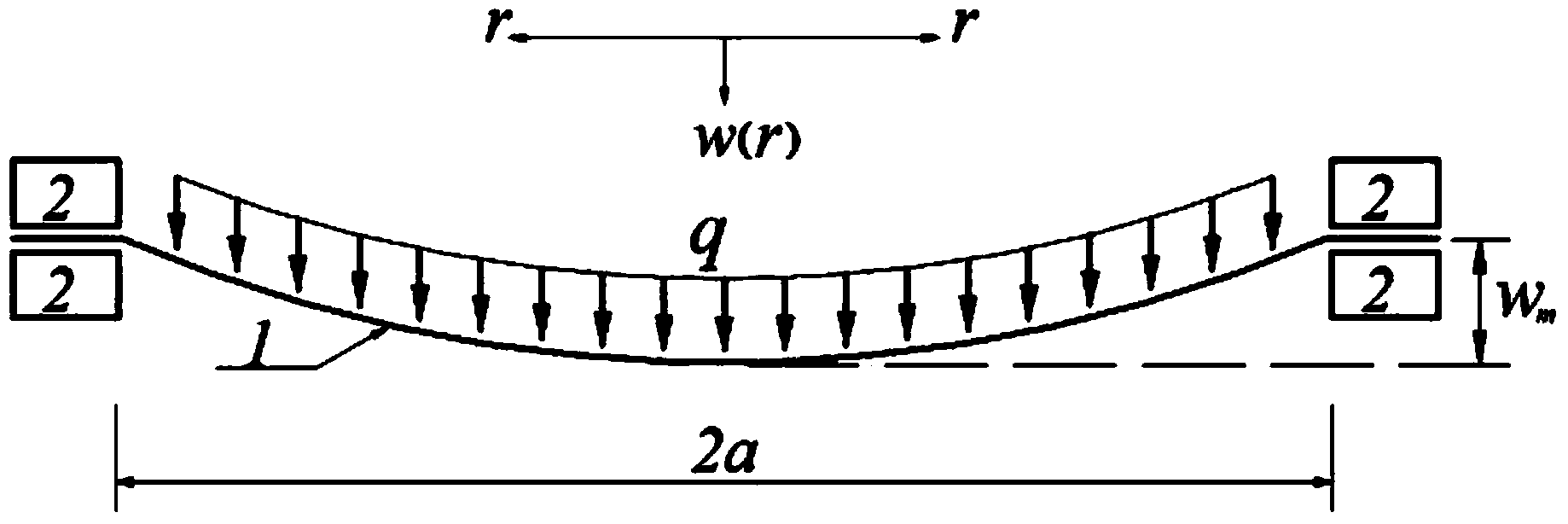
The invention discloses a method for determining resilience of a prestressed circular film under a uniformly-distributed load. The method comprises the following steps: fixedly clamping the periphery of a circular film with radius of a, thickness of h, Young modulus of elasticity of E, poisson ratio of v and prestress of sigma O, applying a transverse uniformly-distributed load q on the circular film. On the basis of the static balance analysis on the axisymmetric deformation problem of the circular film, by utilizing a load measuring value q, the elastic energy U of the film after being deformed can be accurately determined.
Owner:YANGZHOU PULAOSHI TECH DEV CO LTD
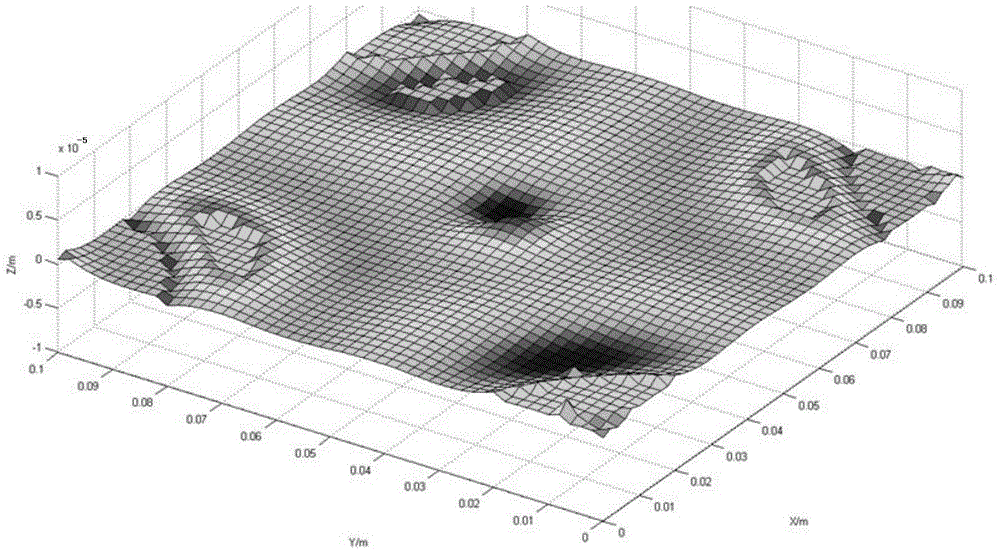
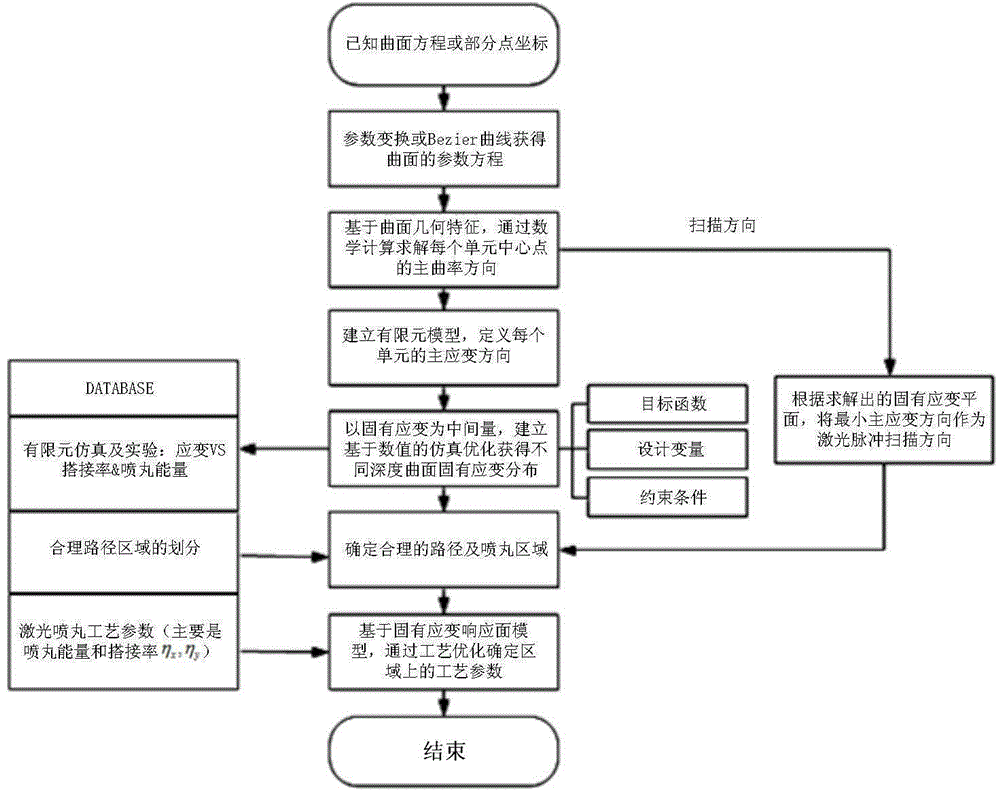
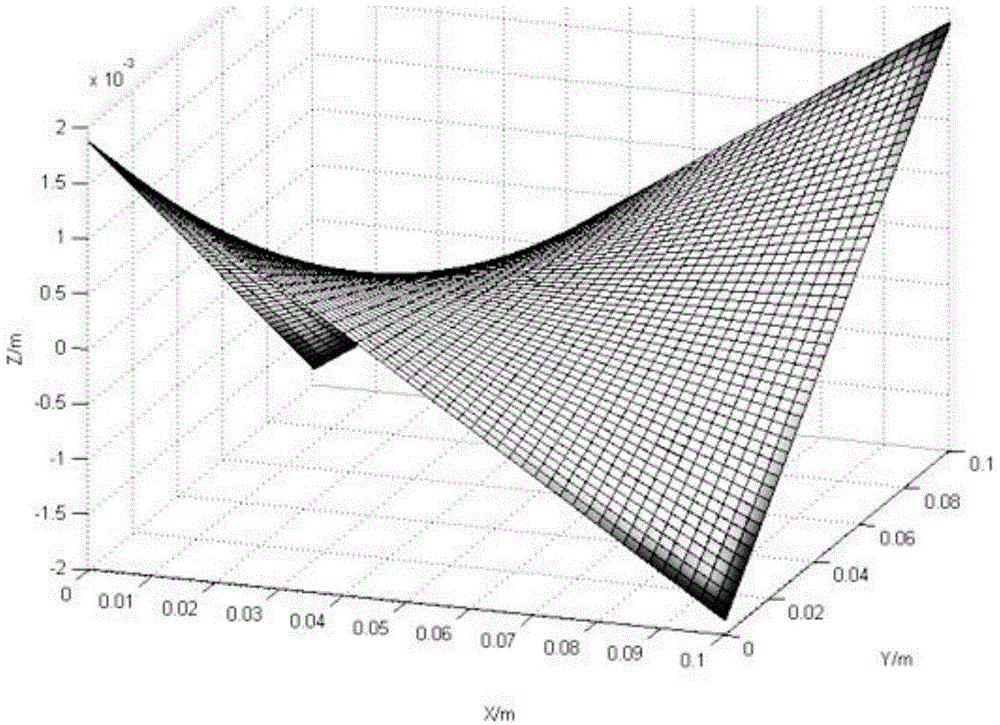
Method for determining laser peening forming process parameter of complex curved-surface-shaped workpiece
ActiveCN104899345AImprove fatigue resistanceAccelerated corrosionSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelStrain response
The invention provides a method for determining a laser peening forming process parameter of a complex curved-surface-shaped workpiece. The method comprises the following steps: according to a curved surface parameter equation of the workpiece, carrying out geometrical characteristic analysis on the curved surface of the workpiece to calculate a main strain direction so as to obtain a laser pulse scanning direction in laser peening forming; establishing a workpiece bending deformation finite element model which takes depth-direction inherent strain distribution as a deformation source, and optimizing an inherent strain field to obtain the inherent strain distribution of different positions of the workpiece along the depth direction, wherein an inherent strain direction is the main strain direction; and according to inherent strain response surface models under different laser peening forming process parameters and the inherent strain of different positions of the workpiece along the depth direction, optimizing the laser peening forming process parameters, and obtaining an optimal laser peening forming process parameter corresponding to different inherent strain fields on the surface of the workpiece. A non-elastic deformation problem can be converted into an elastic deformation problem to improve the efficiency and the precision of finite element simulation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
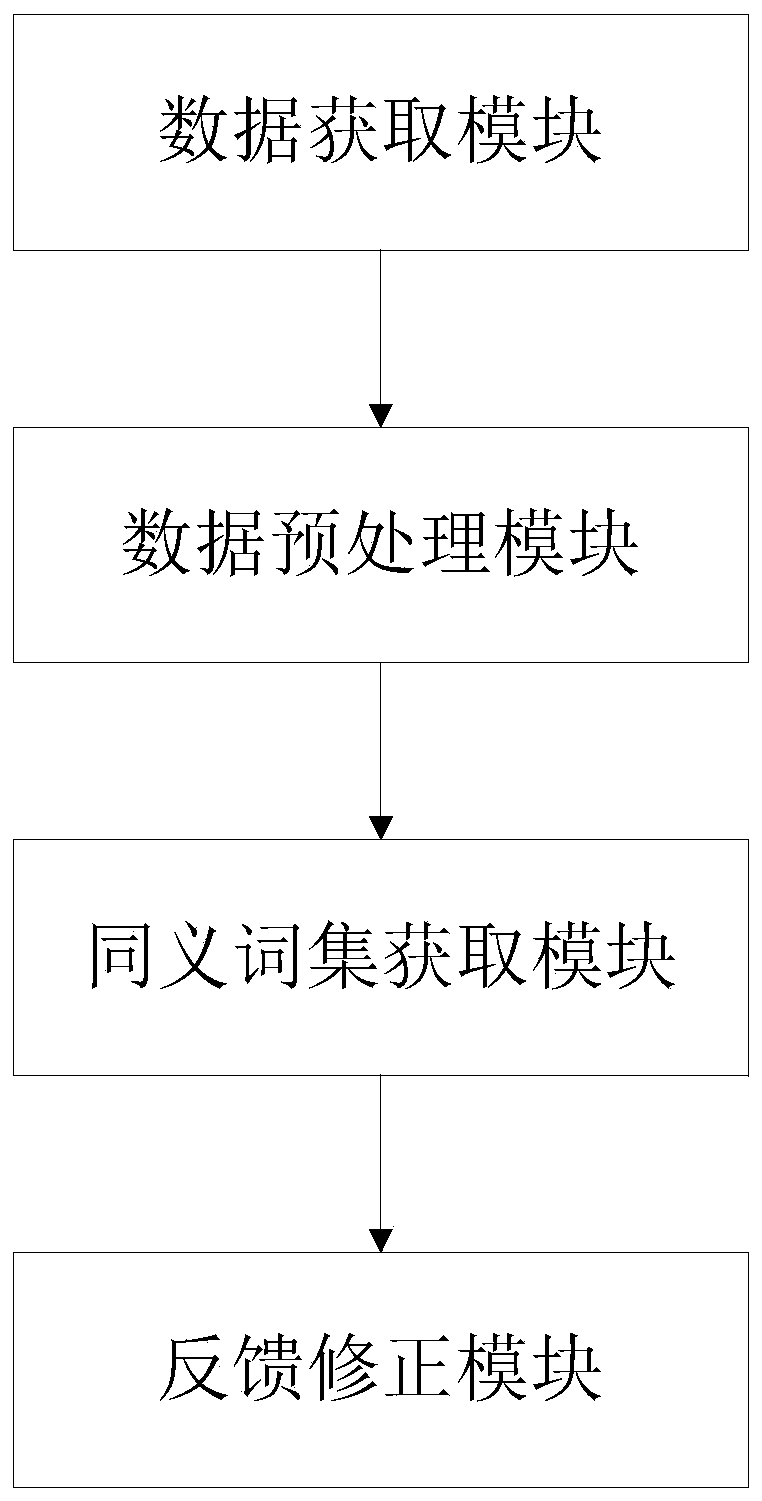
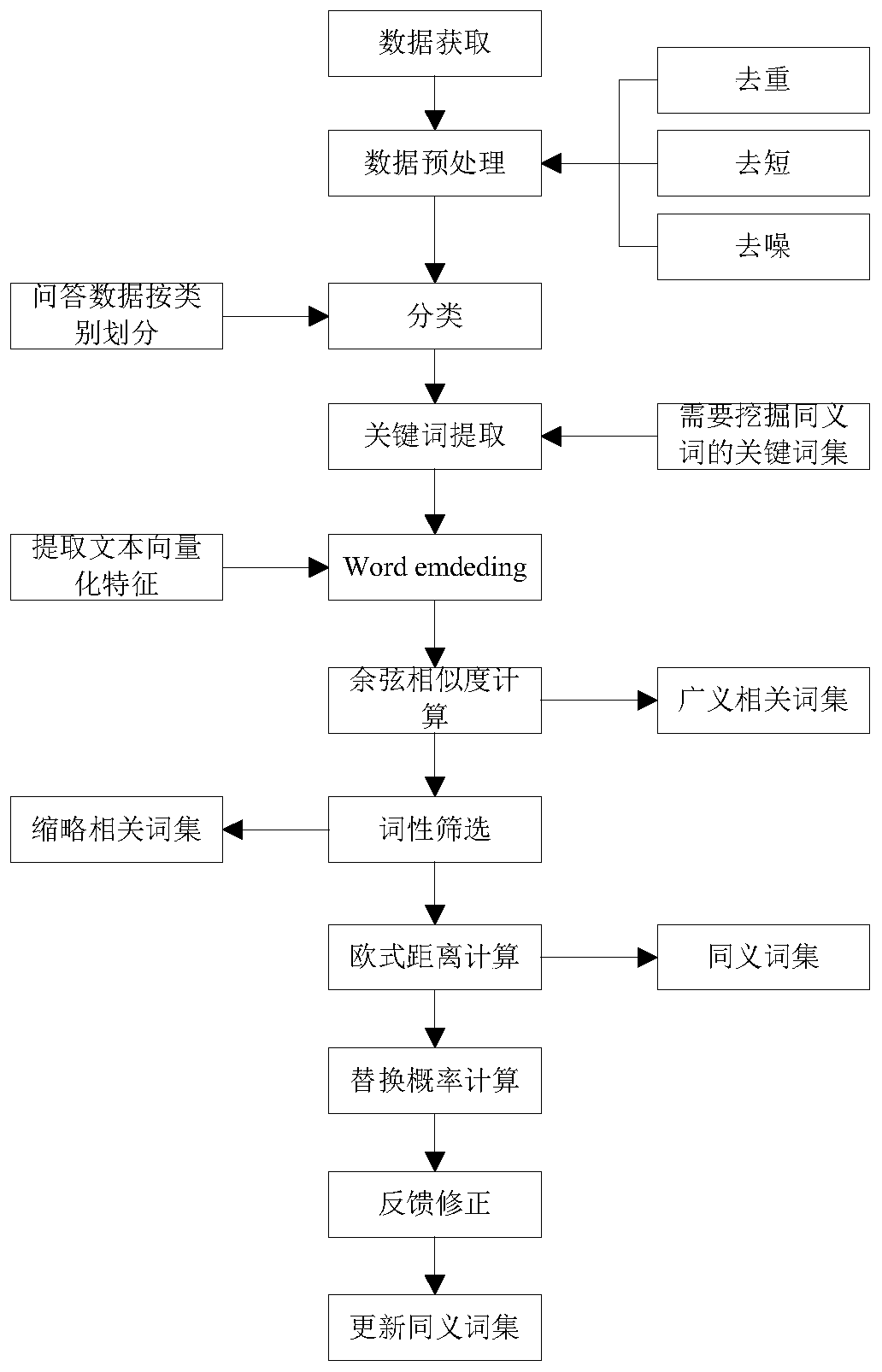
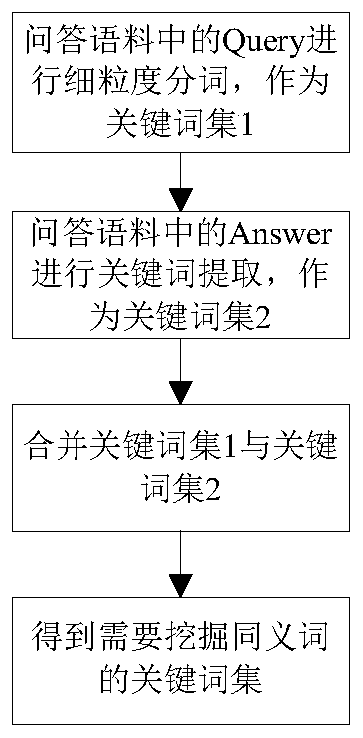
Synonym mining method and device for question and answer retrieval system
ActiveCN110442760AEasy to digImprove digging efficiencyWeb data indexingOther databases clustering/classificationCo-occurrenceThumbnail
The invention relates to a synonym mining method and device for a question and answer retrieval system. According to the invention, question and answer corpora are classified; keyword extraction is carried out by category to obtain a set of keywords to be processed, meanwhile, word vector training is carried out on large corpora in the vertical field; cosine similarity of the word vectors is calculated to obtain a generalized related word set of the keywords of the current category; part-of-speech screening is performed to obtain a set of thumbnail-related words, an Euclidean distance is calculated in the thumbnail related word set; synonym pairs are obtained, the co-occurrence frequency of the synonym pairs is counted; the replacement probability of the synonyms is calculated, finally, feedback correction is conducted on the synonym pairs which do not meet the retrieval recall threshold value according to the retrieval recall result obtained after replacement of the synonyms, the semantic deformation problem obtained after replacement of the synonyms is well solved, and the accuracy of synonym mining and the accuracy of question and answer pair retrieval results are improved.
Owner:ENJOYOR COMPANY LIMITED
Test method for simulating long-term deformation of rockfill
InactiveCN102621009AEasy extractionAccurately obtainMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesParticle flowTriaxial shear test
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for determining maximum stress value of prestress circular thin film under uniformly-distributed loads
The invention discloses a method for determining the maximum stress value of a prestress circular thin film under uniformly-distributed loads. The method comprises the steps that the periphery of the circular thin film is fixedly clamped, wherein the radius of the circular thin film is a, the thickness of the circular thin film is h, the Yang elasticity modulus of the circular thin film is E, the Poisson ratio is nu, and the prestress of the circular thin film is sigma 0; one transverse uniformly-distributed load is applied to the circular thin film, and the maximum stress value sigma m of the thin film can be accurately determined on the basis of static balance analysis of the axial symmetric deformation problem of the circular thin film by means of the load measurement value q.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Treatment method for deformation of massive lost foam
The invention relates to a treatment method for deformation of massive lost foam. The method comprises the following steps of: correcting a deformed white die, recovering the corrected white die, making a shelf in accordance with the shape of the white die by using square steel, making anti-deformation radian, fixing the white die on the shelf, hanging the white die together with the fixing shelf, filling rugged dead angles on the white die subjected to shakeout vibration by using resin sand, spreading bottom sand in a sand box, flatly placing the white die on the bottom sand in the sand box,fixing the easily deformed part of the white die by using a refractory brick, and starting uniform shakeout, wherein the front and back, left and right height fall does not exceed 15 centimeters; compacting for 45 seconds; and finally discharging the top sand, and performing compaction after the top sand is flush with the upper opening of the sand box. By the method, the deformation problem of the massive lost foam is effectively solved, human-made defects and waste products are reduced, and the produced product has high precision and high surface finishment.
Owner:翼城县福旺铸造实业有限公司
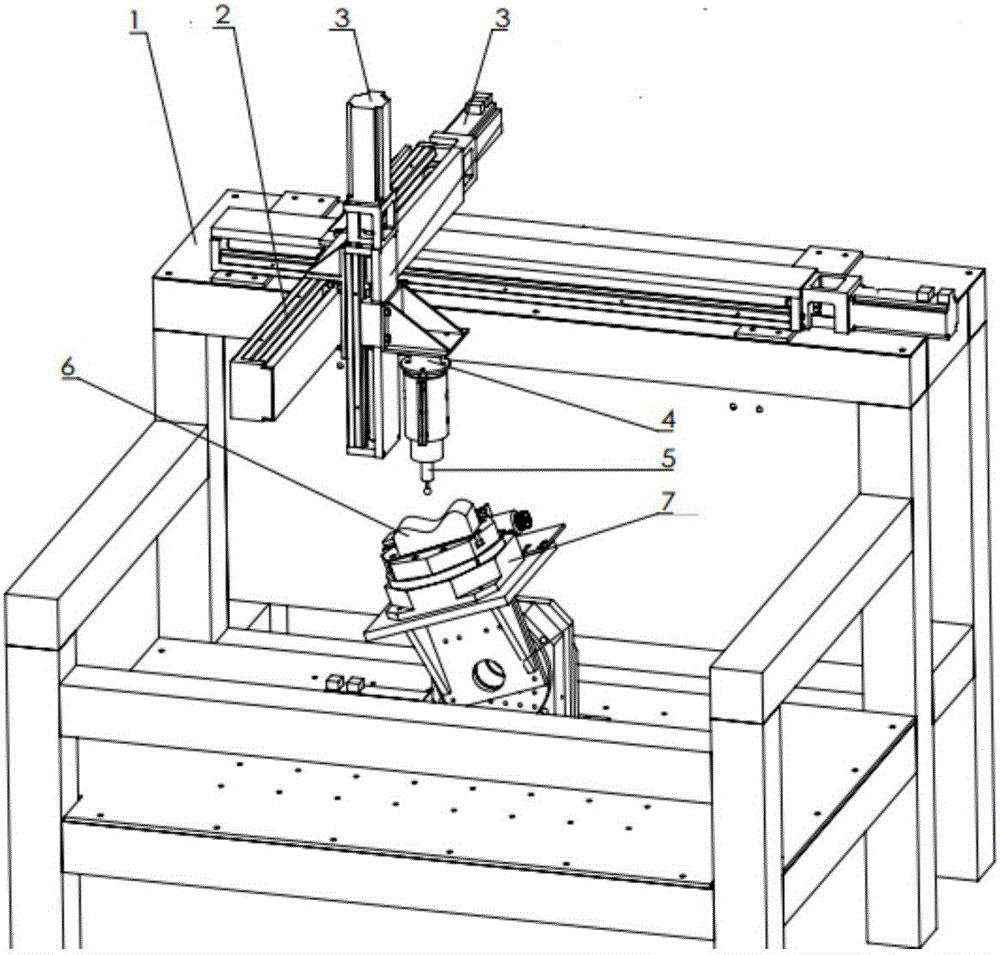
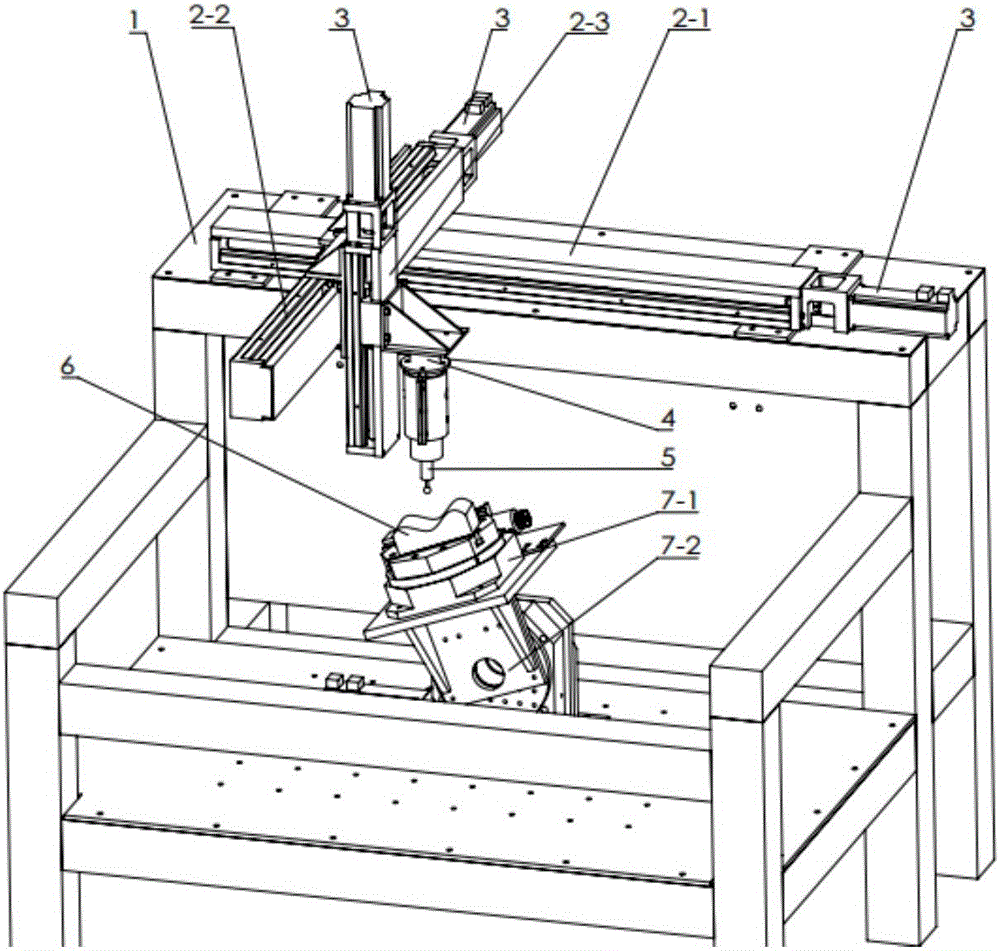
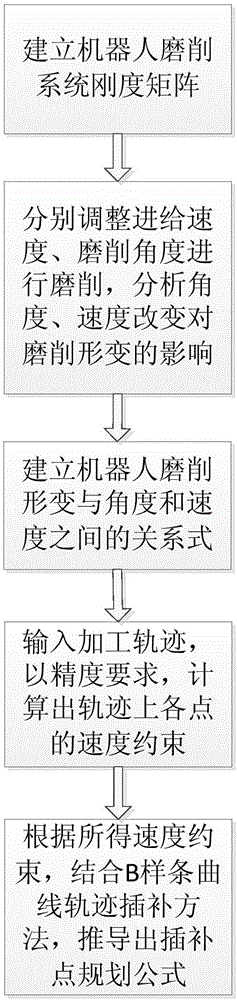
Robot grinding system for solving deformation problem and track planning method of robot grinding system
ActiveCN106426173AOptimize locationProgramme-controlled manipulatorGrinding drivesStress conditionsRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses a robot grinding system for solving the deformation problem and a track planning method of the robot grinding system. The system is a rectangular coordinate robot grinding system. The rectangular coordinate robot grinding system comprises a workbench rack, a guiding unit of a three-axis rectangular coordinate robot, a drive unit, a six-dimensional force sensor measuring unit, a grinding tool and a hook face workpiece. The rectangular coordinate robot grinding system further comprises a two-shaft rotation work platform installing the hook face workpiece, a deformation calculating module and an interpolation point optimizing module. According to the method, the deformation calculating module and the interpolation point optimizing module are used for conducting adjustment; according to the robot grinding system structure and stress conditions, the angle between the workpiece and the tool is changed through the two-shaft rotation platform, the deformation situation of a robot cutting system at different cutting angles and different feeding speeds is evaluated, the grinding feeding speed restraint formula based on grinding deformation is inferred according to the precision requirement, and finally the hook face grinding machining track is optimized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Vacuum adsorbing system for clamping and fixing thin plate during milling and use method thereof
InactiveCN102962700AImprove milling accuracyImprove processing qualityMilling equipment detailsPositioning apparatusEngineeringVacuum pump
A vacuum adsorbing system for clamping and fixing a thin plate during milling comprises a vacuum platform, a base, a rubber sealing strip, a pipeline, a digital display vacuum gauge and a vacuum pump, wherein the vacuum platform is positioned above the base; the rubber sealing strip is placed in a sealed groove both in the base and the vacuum platform; the pipeline comprises a threaded air faucet, a teflon pipe, a clamping sleeve, a three-way joint and a threaded connecting head; the base, the digital display vacuum gauge and the vacuum pump are connected with each other by the pipeline; and a use method of the vacuum adsorbing system for clamping and fixing the thin plate during milling comprises seven steps. According to the invention, by using a vacuum technology and through uniformly adsorbing and fixing a thin plate part on the vacuum platform, a clamping deformation problem of a workpiece is preferably solved, the milling accuracy of the part is enhanced and the machining quality of the part is improved. The vacuum adsorbing system has better practical values and broad application prospects in the technical field of mechanical machining.
Owner:INTELLIGENT AEROSPACE MFG TECH BEIJING CO LTD
Passive residual heat removal heat exchanger testing device
ActiveCN104952497AReduce water consumptionAvoid stress deformationNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringWater useEngineering
The invention relates to a passive residual heat removal heat exchanger testing device which comprises a heat transfer testing section, a voltage stabilizer, a shield pump, a heater, a circulation pump, a heat exchanger, a high-level water tank, a low-level water tank, a lifting pump, a water supplying pump and a spraying pump, wherein the heat transfer testing section, the voltage stabilizer, the shield pump, and the heater form a main loop system of the testing device; the heat transfer testing section comprises 3 C-shaped heat transfer pipes and a cooling water tank; the voltage stabilizer is connected with an outlet pipeline of the heat transfer testing section and an inlet pipeline of the shield pump; the shield pump is connected with the outlet pipeline of the heat transfer testing section; the flowing amount of a main loop is adjusted by adjusting a valve and a bypass valve in front of the shield pump; the heater is arranged between the shield pump and the heat transfer testing section. According to the device, the forms, sizes and materials of the heat transfer pipes are designed reasonably, so that the stress deformation problem can be reasonably avoided, the water use amount can also be greatly reduced, the heat transfer process can be simulated relatively accurately, and relatively accurate heat transfer data can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
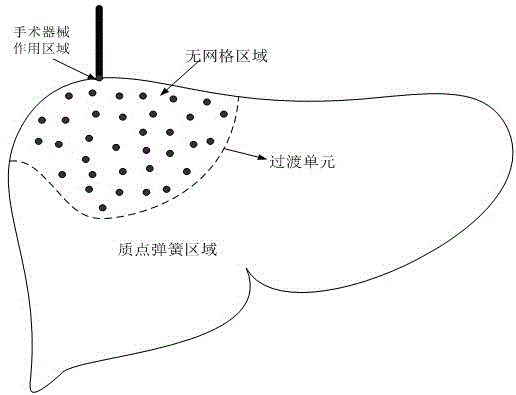
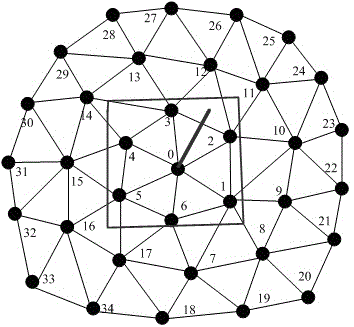
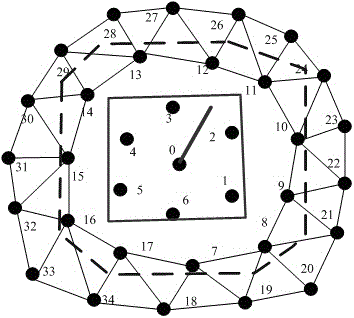
Soft tissue deformation method based on mixing of gridding method and non-gridding method
ActiveCN105513130AMedical simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSoft tissue deformationEngineering
The invention relates to a soft tissue deformation method based on mixing of a gridding method and a non-gridding method. The non-gridding method is adopted in a large-deformation region of an operation, and the gridding method is adopted in a non-operation region. By means of the non-gridding method in the operation region, the gridding deformation problem during large deformation can be avoided, deformation is in smooth transition so that deformation-simulated real sense can be achieved easily, meanwhile, the region model joint number is small while the operation region is small, and the real-time requirement can be met when the non-gridding method is adopted for the operation region; a particle-spring-based gridding deformation method is adopted in the non-operation region so that the defect that non-gridding calculation efficiency is low can be avoided, the advantages of a particle spring on real-time performance are given play to, meanwhile, because the non-operation region deformation is small, gridding deformation will not occur even a particle-spring method is adopted, and a deformation simulating effect is good. By means of the soft tissue deformation method, advantages of the gridding method and the non-gridding method in deformation simulation are given play to, the real sense and the real-time performance compromise, and the soft tissue deformation method is applicable to virtual deformation operation simulation.
Owner:FUQING BRANCH OF FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Connection method for metal target material and target holder
InactiveCN101177778ARealize tight and dense connectionAvoid pollutionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAtmospheric airHigh pressure
The invention relates to the connecting method of a metallic target and a target holder, essentially comprising the steps of connecting surface processing, brazing material coating and jointing, squeezing, bonding, etc. The target and the target holder are matched through corresponding boss and groove; when the target holder is heated to a temperature higher than the liquidus of the brazing material by 10 DEG C to 50 DEG C, the brazing material is coated at the combined face of the target and the target holder, and a pressure is forced at an axial direction, thus leading the target and the target holder to be matched closely; meanwhile, in the process of squeezing, all parts at the combined face are filled with the brazing material in a target holder groove, thus the rudimental air is exhausted. The steady connection between the target and the target holder can be realized in atmospheric environment by the method and the structure property and dimension of the target are not affected, thus the deformation problems in vacuum, high temperature, high pressure or other environments are avoided.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG +1
Method for determining elastic energy of circular membrane with rigid slab in center and under uniformly distributed load
The invention discloses a method for determining elastic energy of a circular membrane with a rigid slab in the center and under a uniformly distributed load. The method is characterized in that a clamping device with the internal radius of a is adopted to fixedly clamp a circular membrane with the thickness of h, the Young's elastic modulus of E and the Poisson's ratio of v, so as to form an axisymmetric circular membrane with the external radius of a and the internal radius of b, wherein a rigid slab with the radius of b is arranged in the center of the circular membrane, the periphery of the axisymmetric circular membrane is fixedly clamped, and the rigid slab is arranged in the center of the axisymmetric circular membrane; a uniformly distributed load q is transversely exerted on the axisymmetric circular membrane; based on static equilibrium analysis and energy equilibrium analysis of the axisymmetrical deformation problem, and by use of the measured value of the uniformly distributed load q, the elastic energy U of the circular membrane can be determined.
Owner:嘉善国宏环保科技有限公司
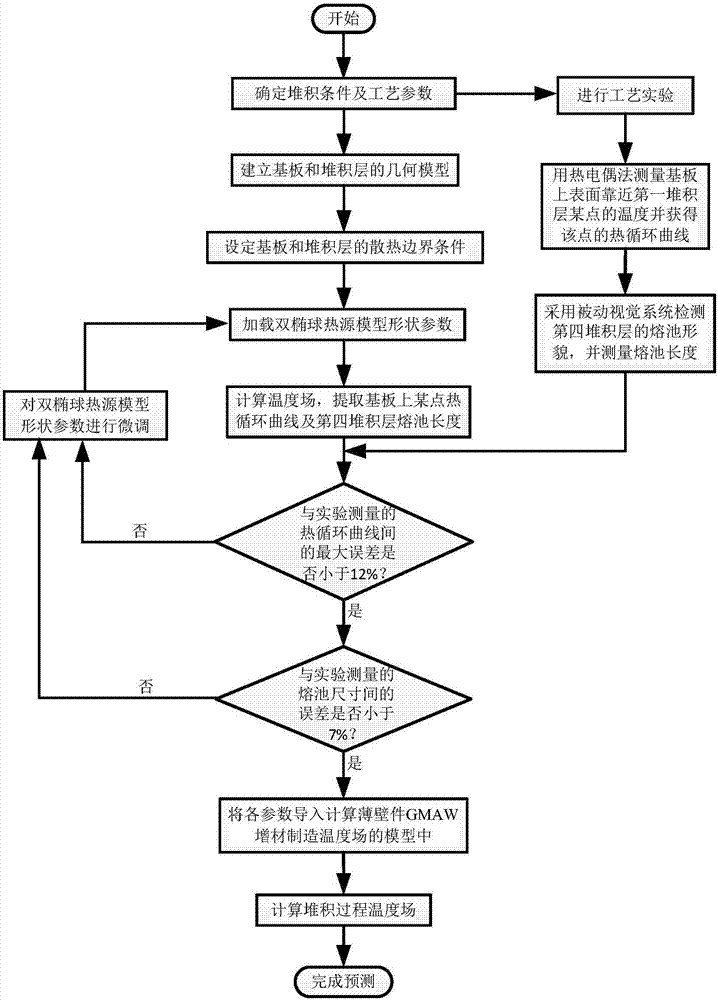
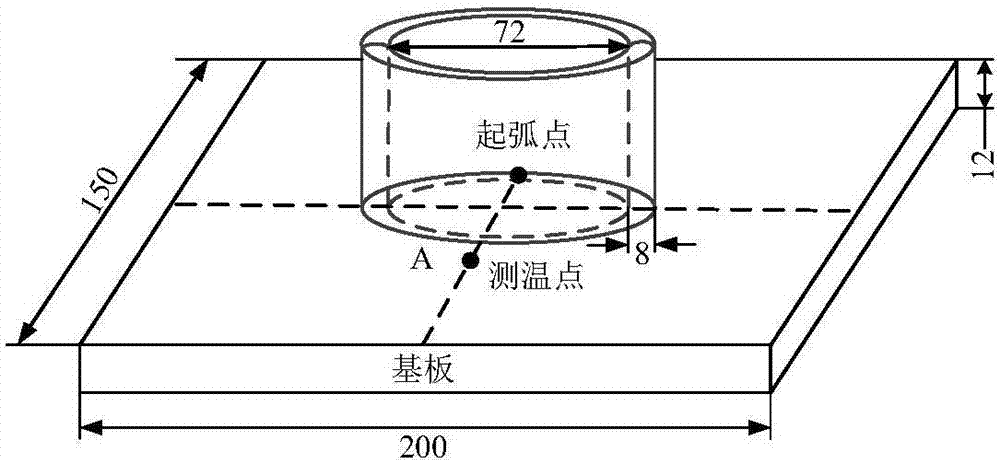
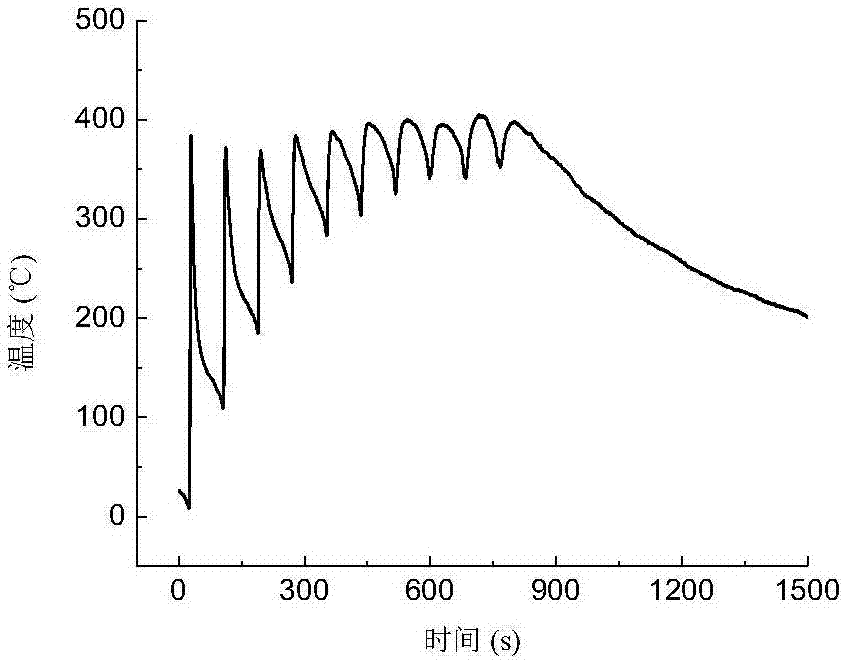
Thin-walled component arc wire filling additive manufacturing temperature field predicting method
ActiveCN106909714APredicted temperature fieldReliable methodGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMelting tankPredictive methods
The invention relates to a thin-walled component arc wire filling additive manufacturing temperature field predicting method. The method includes the steps that a stacking condition of a thin-walled component is determined; a thermal cycle curve is measured; the shape of any stacking layer molten pool above a second stacking layer is observed; a model is built and grids are divided; a heat dissipation boundary condition and a heat source parameter are loaded; a model temperature field is calculated, a thermal cycle parameter is extracted, the length of the stacking layer molten pools is measured, and compared with test data, the maximum error of thermal cycles and size errors of the molten pools are all smaller than preset values through a fine-tuning heat source model shape parameter; the fine-tuning model shape parameter is loaded in a numerical model of the thin-walled component, and arc wire filling additive manufacturing temperature field predicting is completed. The numerical calculation method is adopted, by comparing the thermal cycle parameters on a substrate with the sizes of the molten pools of the stacking layers, thin-walled component arc wire filling additive manufacturing temperature field predicting is accurately completed, and a theoretical basis is provided for solving residual stress and deformation problems caused in the thin-walled component arc wire filling additive manufacturing process.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Novel stainless steel side wall structure and mounting method of novel stainless steel side wall
InactiveCN107901932AReduce welding processGuarantee the appearance qualityAxle-box lubricationRailway bodiesStructural engineeringEngineering
The invention provides a novel stainless steel side wall structure and a mounting method of a novel stainless steel side wall. The novel stainless steel side wall structure comprises a side wall skeleton. The side wall skeleton is formed by connecting a plurality of cross beams and a plurality of vertical columns in a mutually-crossing mode, and the cross beams and the vertical columns are fixed through mutual inserting; end vertical columns are arranged on the left and right sides of the side wall skeleton correspondingly; door vertical columns are arranged on the left and right sides of doorframes correspondingly; a window upper cross beam is arranged on the upper portion of each window frame, and a window lower cross beam is arranged on the lower portion of each window frame; a waist cross beam is arranged below each window lower cross beam; three lower cross beams are arranged below each waist cross beam; a window upper vertical column is connected to each window upper cross beam;skeleton connecting plates are welded inside the connecting positions of the window upper cross beams and the window upper vertical columns in the side wall skeleton; window lower vertical columns are connected among each window lower cross beam, the corresponding waist cross beam and the three corresponding lower cross beams; and skeleton connecting plates are welded inside the connecting positions of the window lower cross beams and the window lower vertical columns in the side wall skeleton. The cross beams and the vertical columns of the novel stainless steel side wall structure are fixedthrough mutual inserting connection, the deformation problem caused by welding of a skeleton is solved, the production cost is saved, and the assembly production efficiency is improved.
Owner:CRRC NANJING PUZHEN CO LTD
Discrete floating type support method of large thin plate workpiece
InactiveCN102240913AGuaranteed flexible manufacturingAchieve supportWork holdersPositioning apparatusEngineeringLarge size
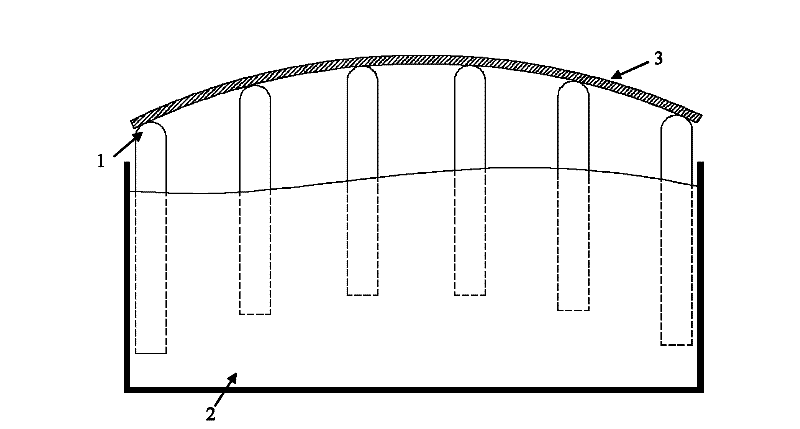
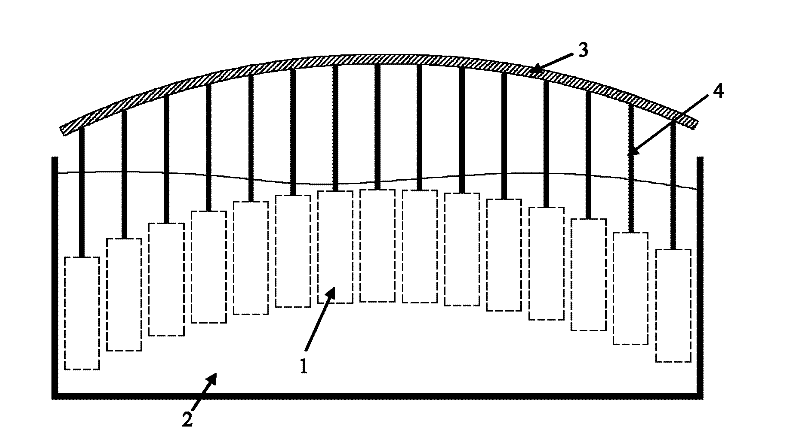
The invention discloses a discrete floating type support method of a large thin plate workpiece and relates to a support method used in detection and scribing or other manufacturing process steps of a large thin plate workpiece, belonging to the field of mechanical engineering. The method comprises the steps as follows: a plurality of discrete floating units (1) are placed in a liquid (2) for enabling the floating units (1) to float in the liquid (2), the depth of the liquid (2) is greater than the height of the floating units (1), and different regions of a large thin plate workpiece (3) are supported by means of the buoyancy of the floating units (1). The discrete floating type support method can provide a simple and practical flexible support method for detection or scribing and other manufacturing process steps of the large thin plate workpiece (3), thereby solving the deformation problem of the large thin plate workpiece (3) caused by self weight, and realizing the flexible manufacturing of the large-size or high-precision thin plate workpiece.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for processing part with thin wall and changed-angle curved surface appearance
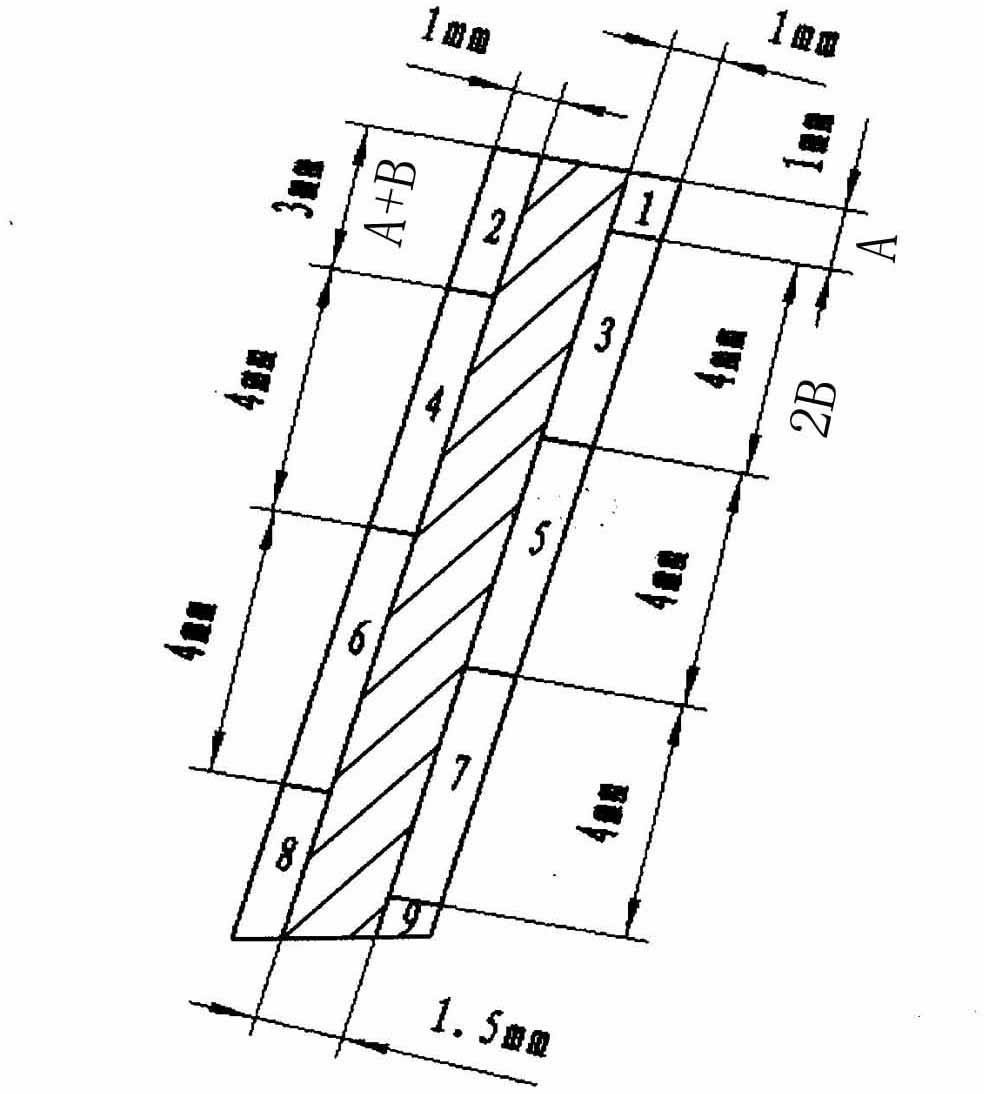
InactiveCN102581362AEven by forceControl deformationMilling equipment detailsEngineeringDeformation Problem
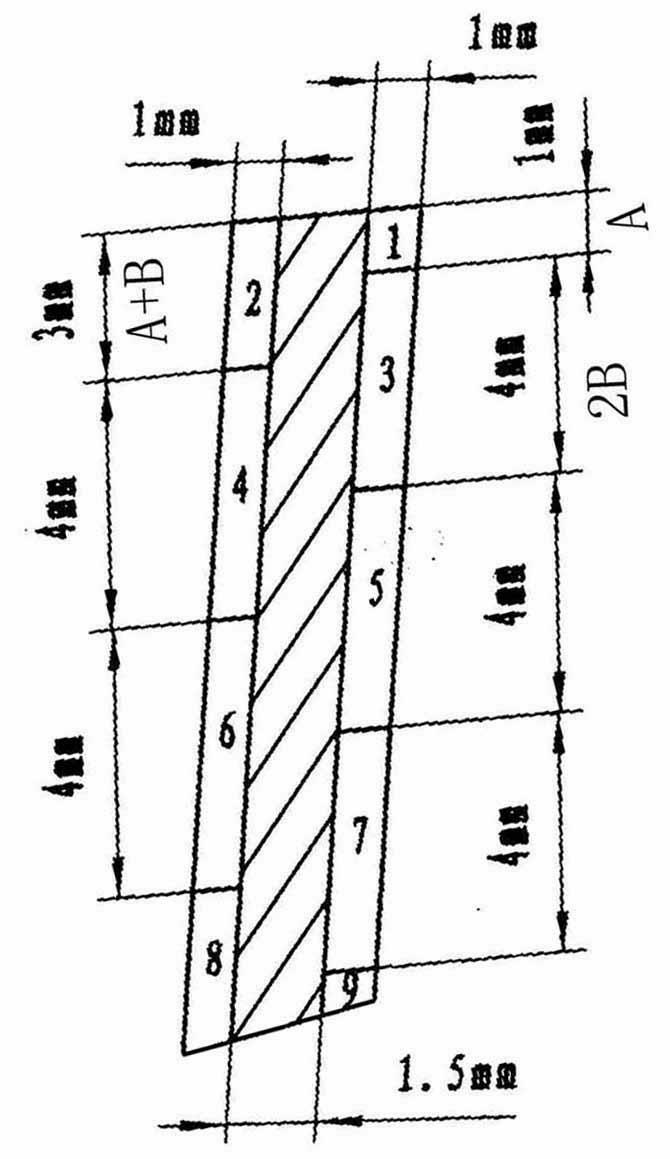
The invention relates to a method for processing a part with a thin wall and a changed-angle curved surface appearance, which comprises the basic step of conducting front face and reverse face alternate equal thickness feeding milling. The method is characterized by a firstly determining first axial cutting depth A and a milling bearing width B on the front face; secondly enabling an front face axial cutting depth to be A and enabling a reverse face axial cutting depth to be A+B after being turned over; thirdly enabling an axial cutting depth to be 2B after being repeatedly turned over until a surplus width of the front face and the reverse face to be less than 2B, and then directly conducting balance finish-milling and putting in place. The method adopts an axial unequal height circumferential cutting method, enables the part to be evenly stressed in a cutting process and enables stress release of a material to be even, thereby effectively controlling the deformation problem of the part with the thin wall and the changed-angle curved surface appearance.
Owner:SHENYANG AIRCRAFT CORP
3D grid deforming method based on surface area keeping
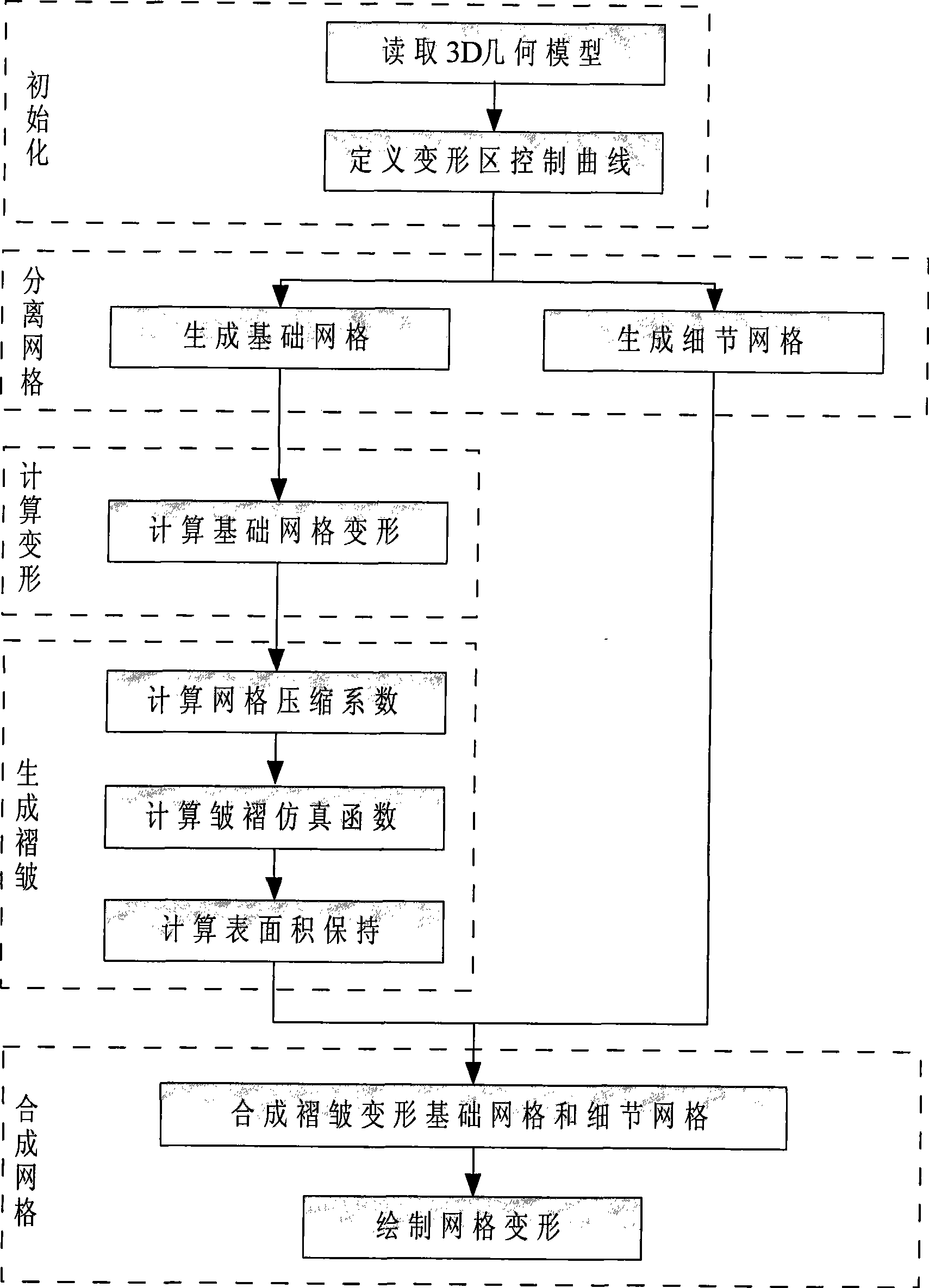
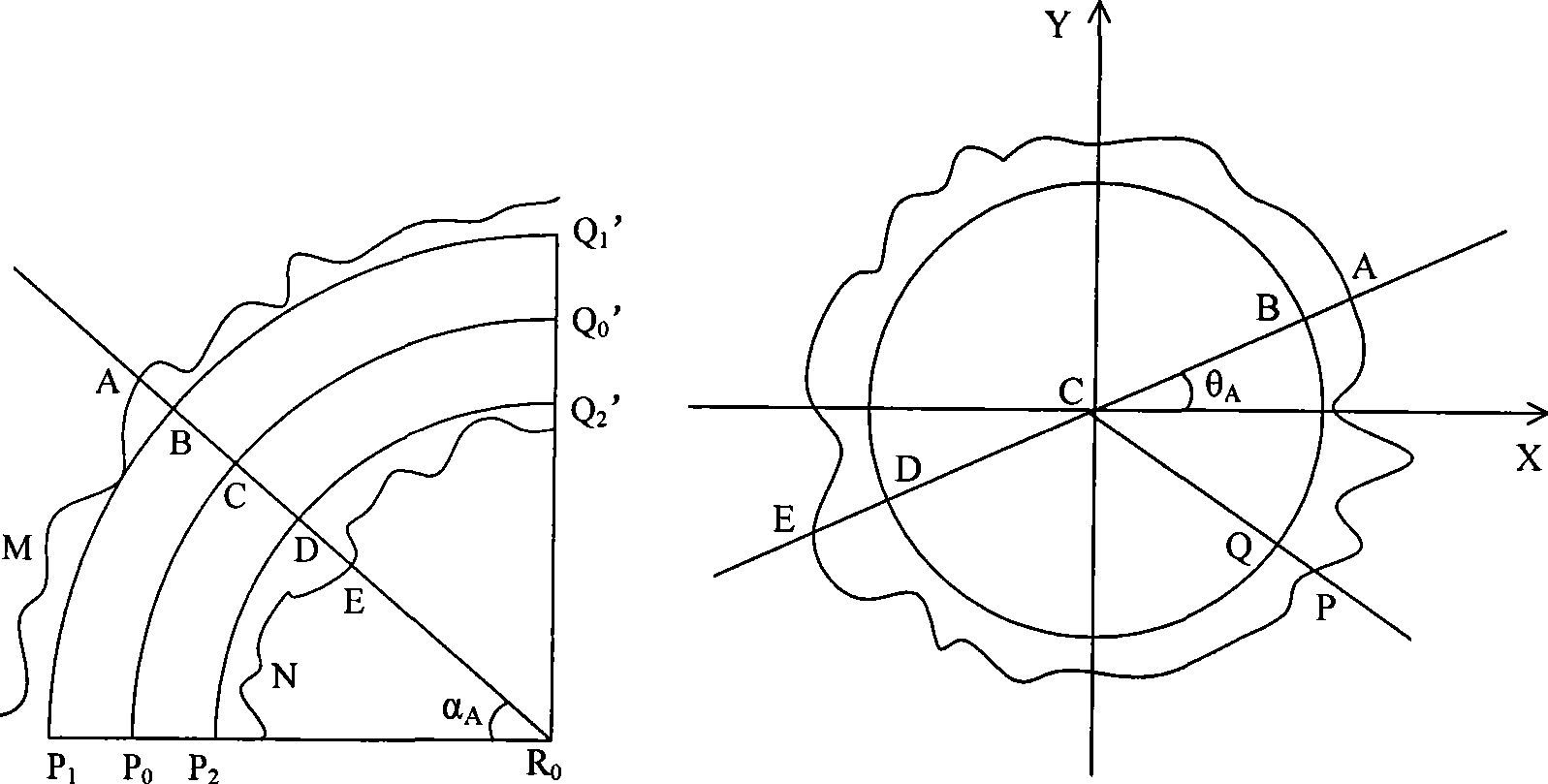
The invention relates to a three-dimensional grid deformation method based on surface area maintenance and provides an effective, fast and vivid deformation method for three-dimensional grid objects aiming at the deformation problem of a three-dimensional model of a soft object, which belongs to the field of computer application, in particular to the technical field of computer graphics and virtual reality. In the method, various forms of deformations are seen to be respectively composed of basic bending deformations, the local regions of the basic bending deformations are independently calculated, and a global deformation result is obtained through the joint of the regions; deformation regions are divided according to control curves, and a basic grid deformation algorithm irrelevant to an original grid model is proposed through separating and synthesizing basic deformation grids and detail grids; damped oscillation curves are used to simulate surface wrinkles at the bent and deformed inner sides of the soft object, and the vertex column length of a basic model is maintained to realize the surface area maintenance and improve the third dimension of grid deformation so as to realize the deformation of a three-dimensional grid model.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
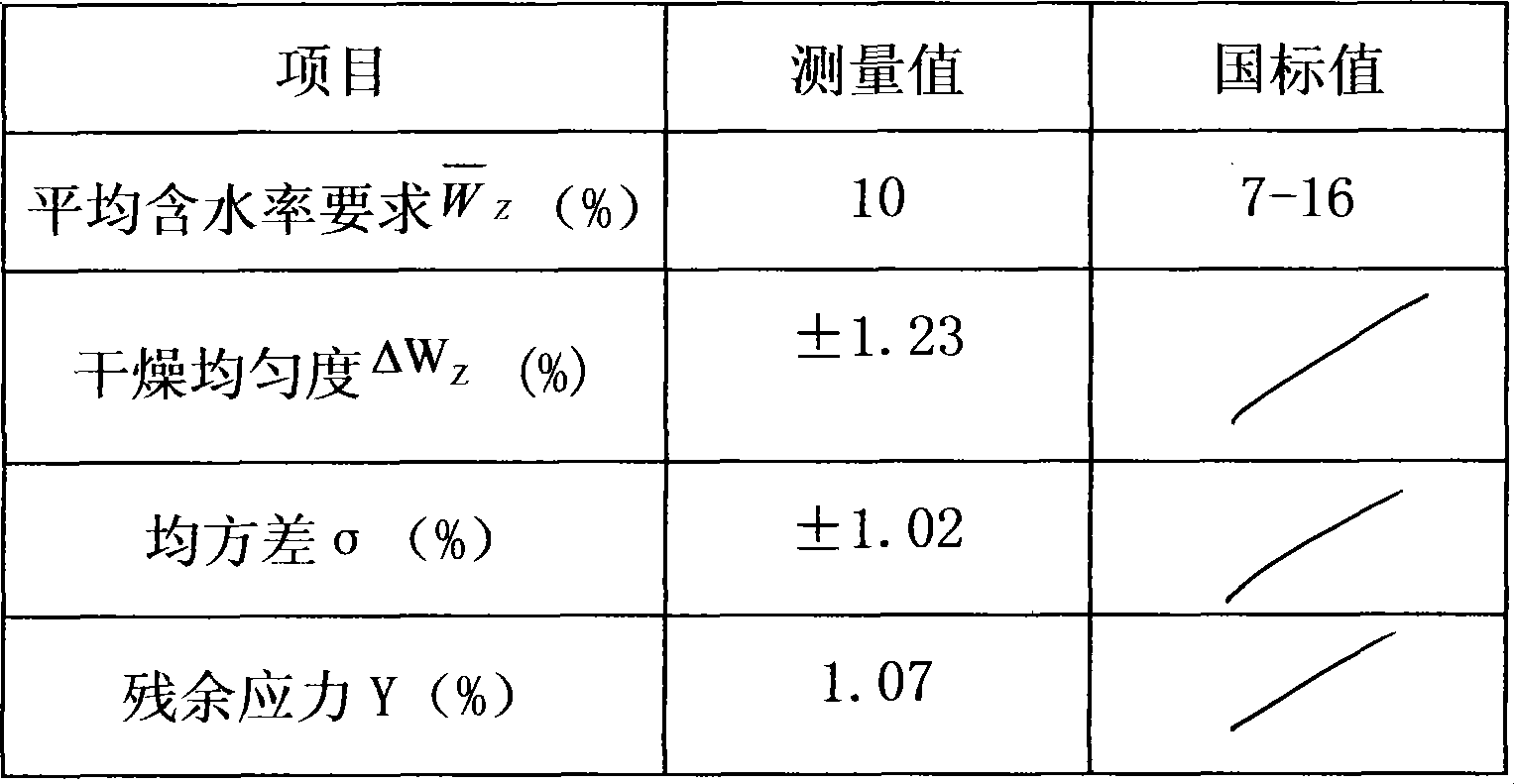
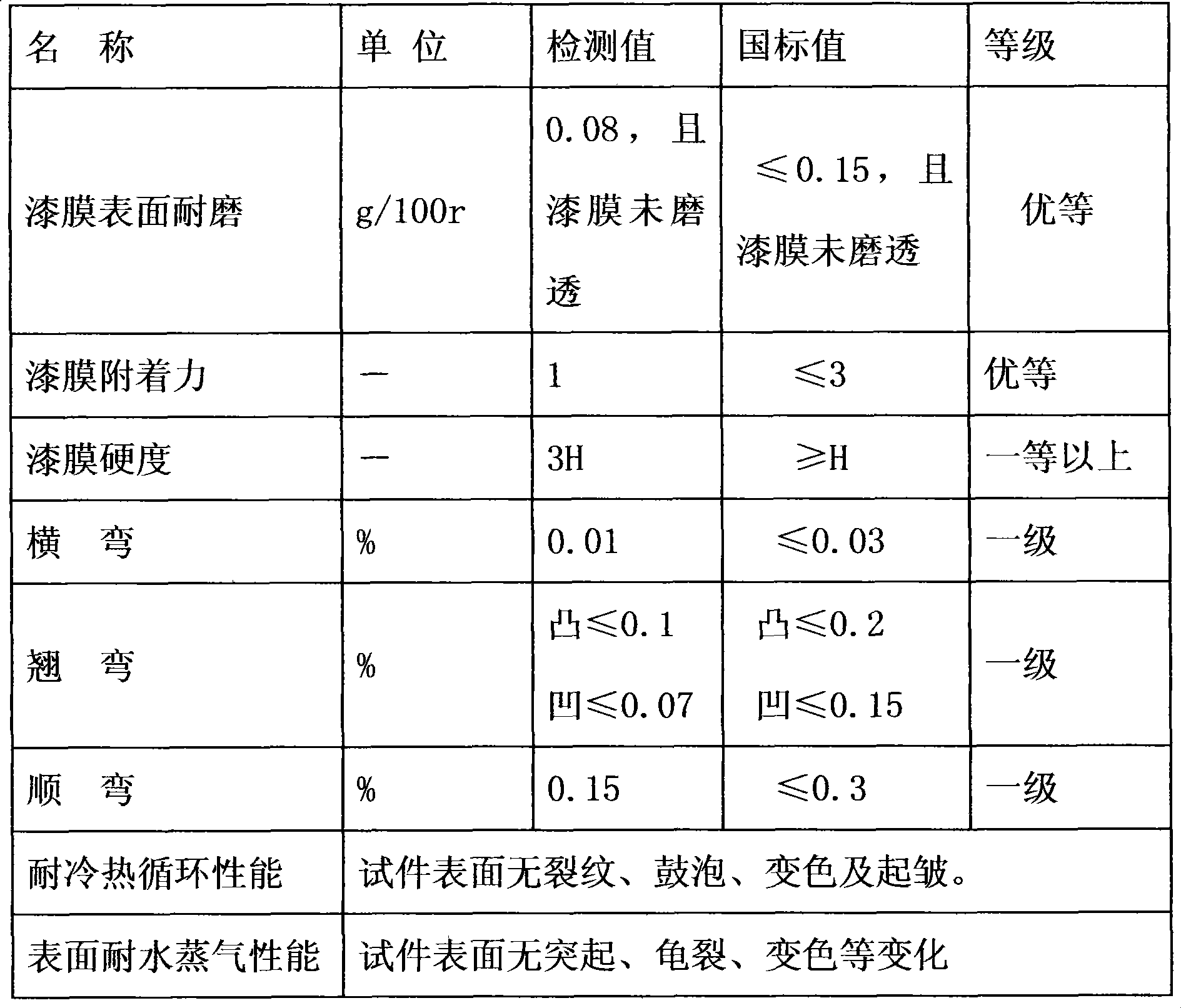
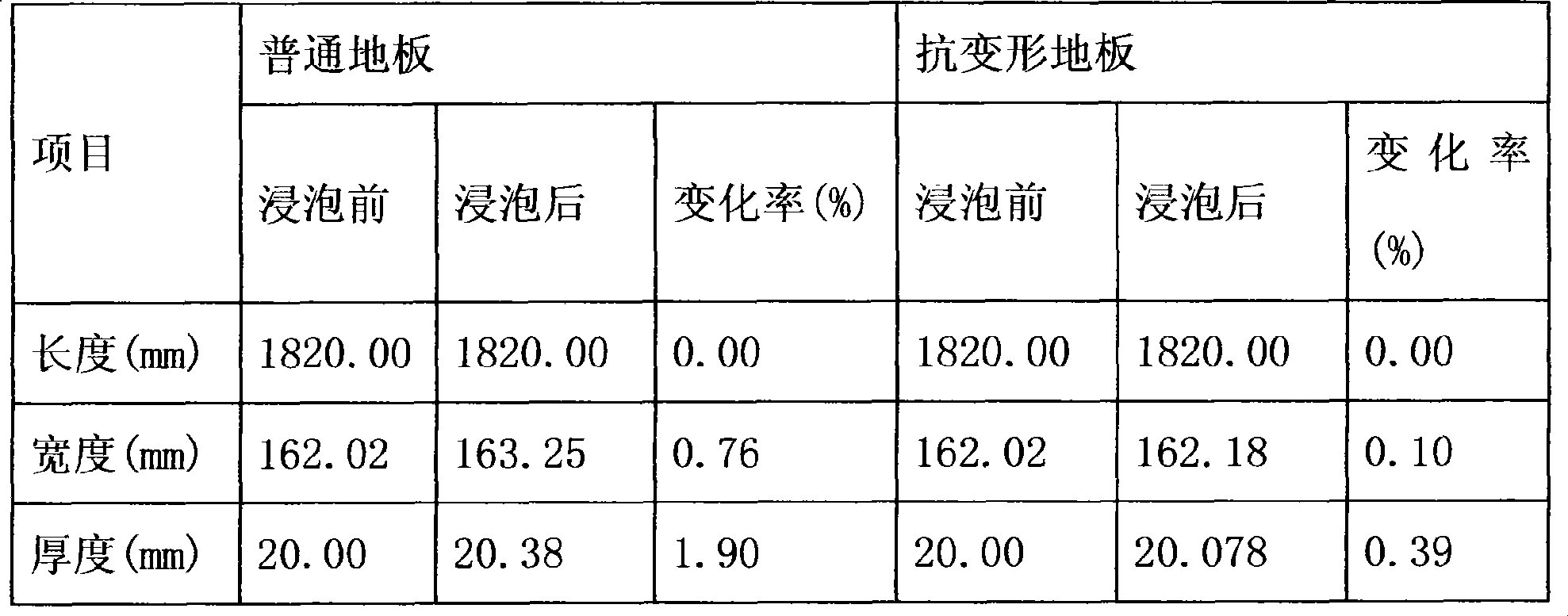
Ultra length and width real wood floor manufacture method
InactiveCN101417453AReduce entryMoisture content remains constantFlat surfacing machinesWood dampingEpoxyPass rate
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of super long wide solid wood floors, which adopts tree species of balsam pigeon peas as the material and includes the following production steps of: material selecting: tree species of balsam pigeon peas are adopted as blanks; drying: an efficient energy-saving steam heating drying kiln is used in a low-temperature intermittent drying process for carrying out drying and moisture content control to the floor blanks of balsam pigeon peas; and curing, blank processing and then oiling and coating are done to better close six faces of blank plates and epoxy resin waterproof paint is used in the six faces, and six faces are sealed with paints and the bottom is coated with paint. The moisture content and pass rate of solid wood floors manufactured with the method reach over 99.9 percent. The method overcomes size changes of the super long wide solid wood floors caused by changes of moisture variation of application environment, thus eliminating or preventing the deformation problem of the wood floors due to changes of moisture contents. The regional areas of the solid wood floors are expanded to cause more people to enjoy the benefits of natural wood floors.
Owner:姜金法
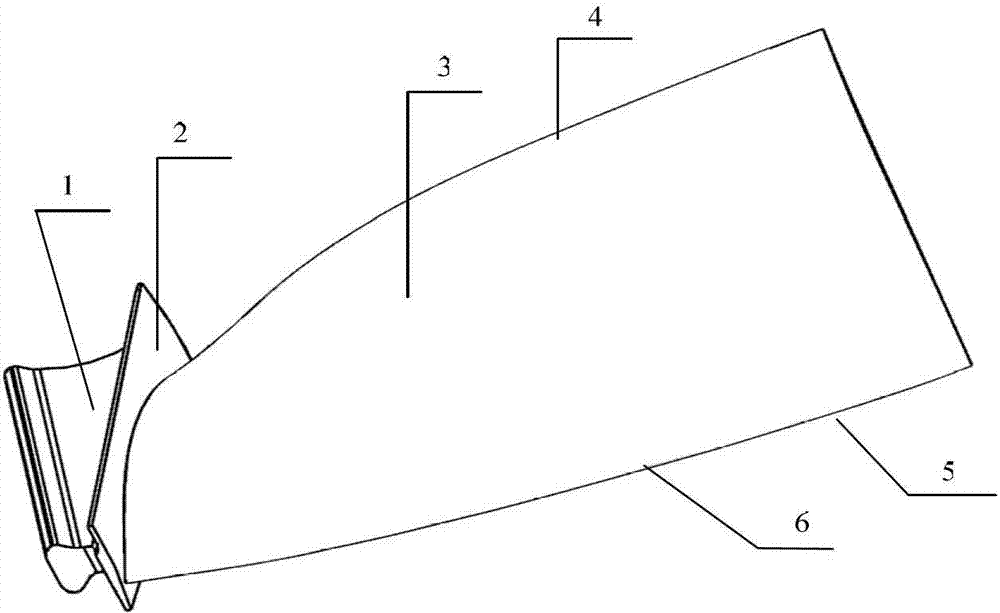
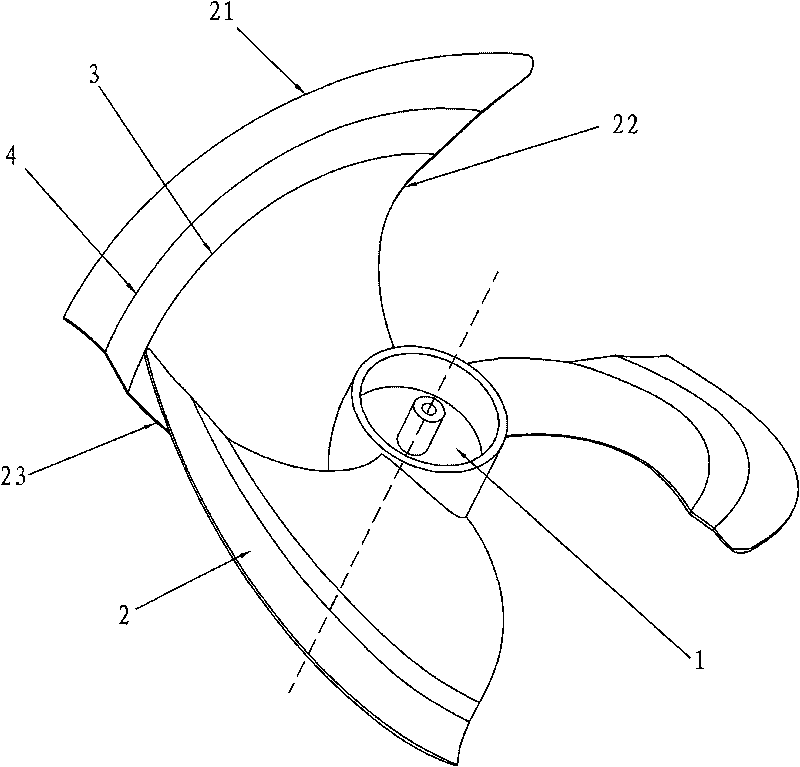
Middle-bent axial flow fan blade
InactiveCN101725566AImprove the mobility environmentReduce vortexPump componentsPumpsWave shapeContinuous wave
The invention discloses a middle-bent axial flow fan blade, which comprises a hub and a blade. The blade comprises an outer periphery, a front edge and a rear edge. The middle-bent axial flow fan blade is characterized in that: the blade is in a wave shape that at least one continuous wave crest and wave trough are arranged in the radial direction from the front edge to the rear edge. Due to the adoption of the structure, high pressure transferred to the outer periphery is dispersed and prevented. The middle-bent axial flow fan blade can reduce the vortex and turbulence caused by radial flow, thereby improving the air flowing environment, improving the static pressure and the efficiency, and reducing the noise. The middle-bent axial flow fan blade can solve the common deformation problem existing in fan blade molding in the mold production, thereby reducing the manufacturing cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG SUNWILL PRECISING PLASITC CO LTD
Rapid laser sintering molding material based on polycarbonate powder
The invention relates to a rapid laser sintering molding material based on polycarbonate powder. Polycarbonate, stilbene flexibilizer, ABS resin and styrene / maleic anhydride copolymer and ABS graft copolymer are mixed for granulation and crushed into polycarbonate power material at low temperature; sulfonic acid surfactant and silane coupling agent are dissolved in absolute alcohol and evenly sprayed on the surface of the polycarbonate powder material, and absolute alcohol is removed to be made into base material; benzophenone light absorber, nano carborundum powder, and non-ionic antistatic agent and organic filler are added into the base material and mixed to be uniform, thus obtaining the rapid laser sintering molding material based on polycarbonate powder. The rapid laser sintering molding material of the invention can better solve buckling deformation problem of a sintering piece, greatly improves mechanical property of the sintering piece and has great advantages in rapid making of thin-wall spare parts, precision parts, complex parts and parts resistant to high temperature and low temperature.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Method for determining maximum stress of annular thin film with rigid plate in center under uniformly distributed load
ActiveCN105956379AInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsMechanical engineeringDeformation Problem
The invention discloses a method for determining a maximum stress of an annular thin film with a rigid plate in the center under a uniformly distributed load. The method comprises the steps of fixing and clamping the annular thin film which has the thickness of h, the Young's elastic modulus of E and the Poisson's ratio of v and is provided with the rigid plate with the radius of b in the center by adopting a clamping apparatus with the inner radius of a to form an axial symmetric annular thin film which has the outer diameter of a and the inner radius of b, is fixed and clamped at the periphery and is provided with the rigid plate in the center; transversely applying the uniformly-distributed load q to the annular thin film; and determining the maximum stress sigma m of the annular thin film by utilizing a measurement value of the uniformly-distributed load q based on static balance analysis of an axial symmetric deformation problem.
Owner:太湖县市场监督检验所(太湖县功能膜检测研究院)
Thin film evaporation coating apparatus, and method for making OLED display device
InactiveCN103866235AIncrease the effective use areaHigh strengthVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDisplay deviceEvaporation
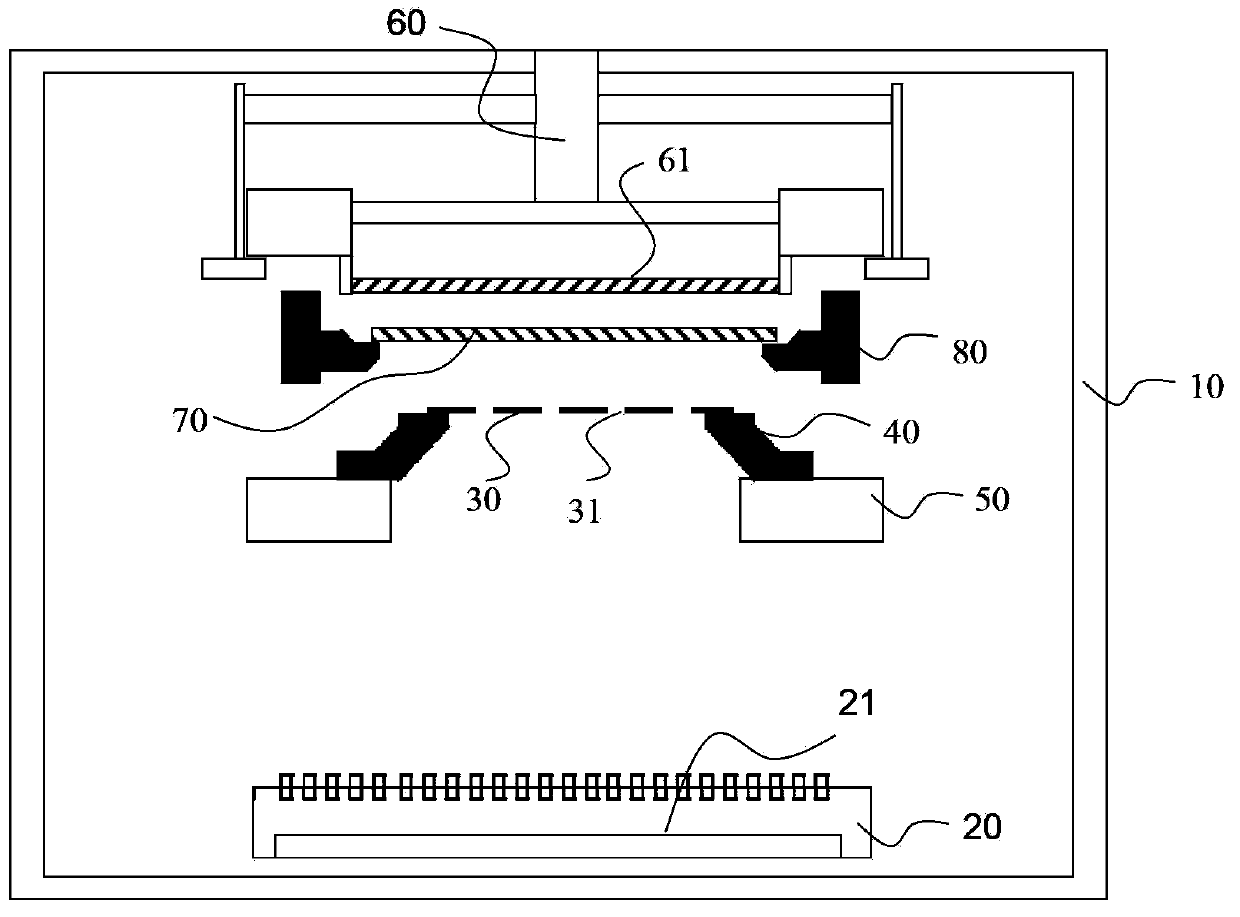
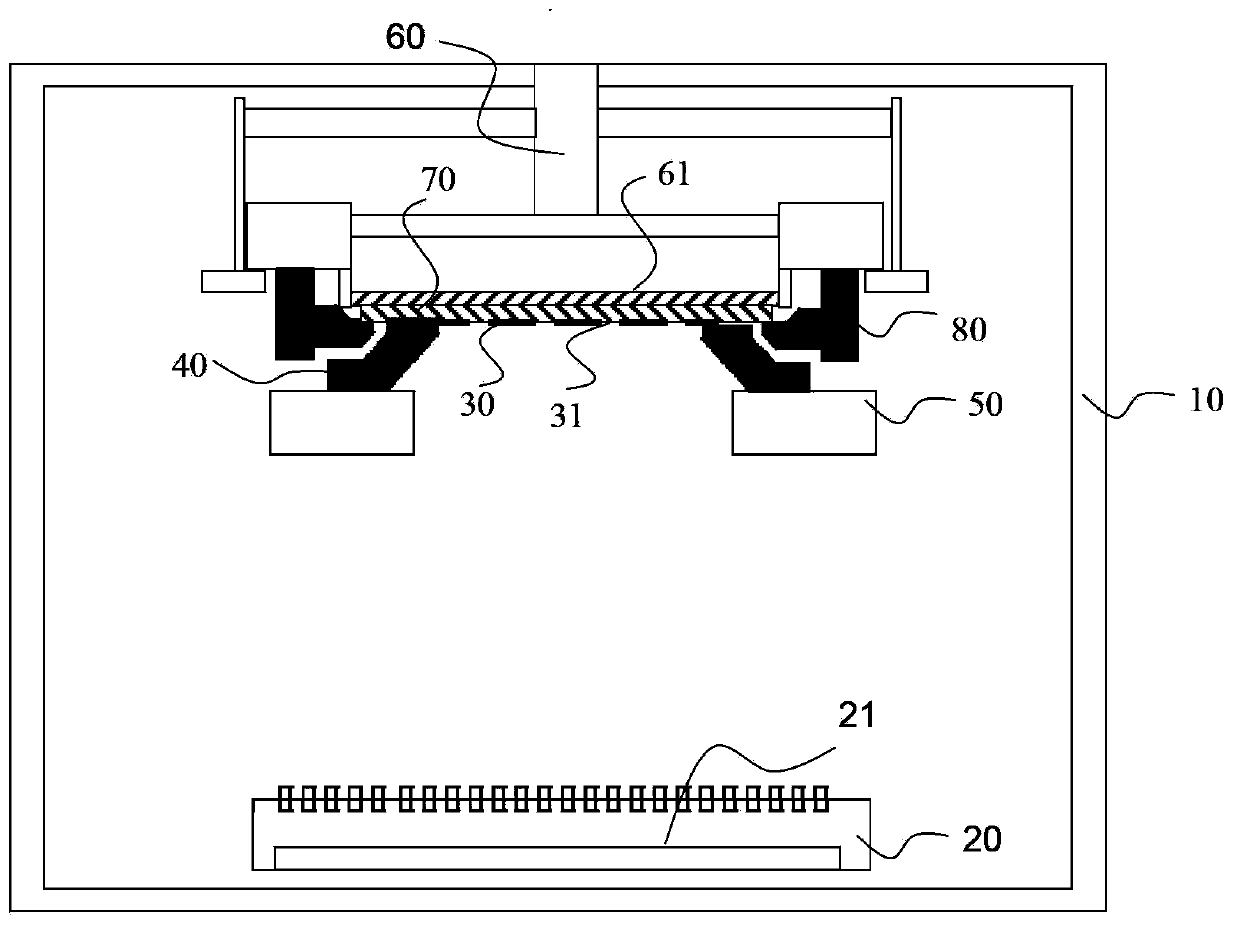
The invention provides a thin film evaporation coating apparatus, and a method for making an OLED display device by utilizing the apparatus. The apparatus comprises: a cavity, wherein an evaporation source accommodation part used for accommodating an evaporation source is arranged in the cavity; a press plate and a movable mechanism driving the press plate to move up and down; a substrate carrying clamp used for carrying a substrate; a frame used for bearing a mask plate; and an electrostatic thin film layer arranged on the lower surface of the press plate. The electrostatic thin film layer enables the substrate to be evenly adsorbed on the press plate in an electrostatic adsorption manner and to be separated from the support of the substrate carrying clamp, and the substrate is applied to the mask plate in order to carry out thin film evaporation coating. The apparatus can improve the effective use area of the substrate, and the morphological structure of a frame is not restricted by the morphological structure of the substrate carrying clamp, so the morphological structure having a high strength can be adopted to avoid the easy deformation problem of the frame.
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com