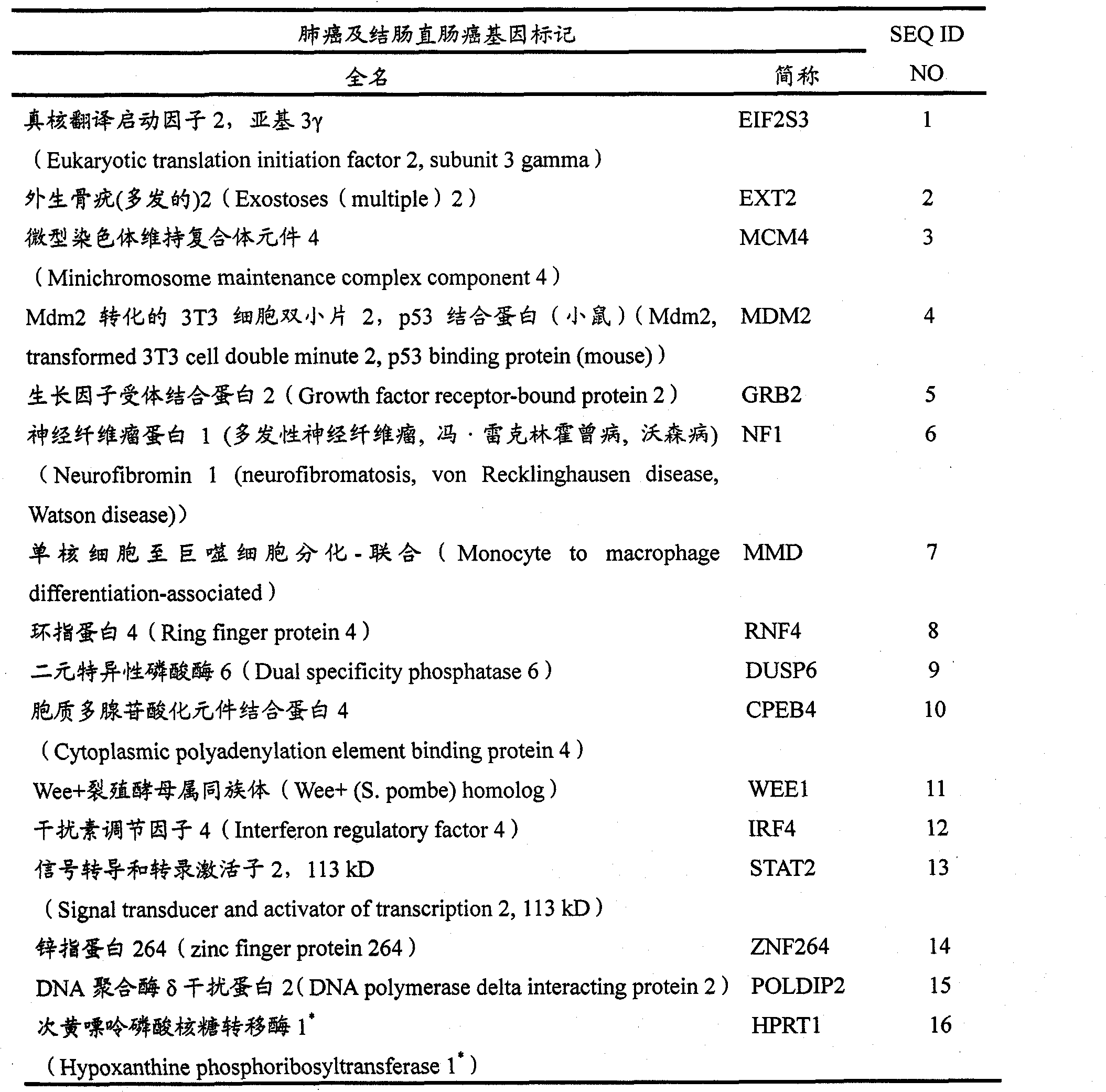
Molecular markers for lung and colorectal carcinomas
A technology for colorectal cancer and lung cancer, applied in the field of molecular markers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0150] Blood testing steps for molecular markers of lung cancer and colorectal cancer
[0151] Preparation of monocytes. Take peripheral blood (5-8ml) from patients with lung cancer and colorectal cancer, and use BD vacutainer CPT TM Tube (BD, USA), according to its instructions, isolated mononuclear cells (MNC) from normal individuals. The MNC part was added into PBS buffer three times the volume of the whole blood sample, and centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 10 minutes. Then the MNC part was washed with 1 ml of PBS buffer, and centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 5 minutes. Add the final pellet to 2ml of Super RNApure TM reagent (included in SuperRNApure TM kit, Genesis, Taiwan).
[0152] Real-time PCR (Real-time PCR) analysis of cancer marker gene expression. Using Super RNApure TM The kit, according to the instructions, extracts the total RNA from the MNC part. The RNA pellet was dissolved in DEPC-treated water and stored at -80°C until use. Analyze the quality of RNA by 1% ...
Embodiment 2
[0166] Blood tests for molecular markers of lung cancer
[0167] Materials and methods
[0168] Blood samples were taken from lung cancer patients. In this embodiment, 150 lung cancer patients (selected from 3 different hospitals) confirmed by tissue sections were analyzed. Among them, 40 were from National Taiwan University Hospital (Taipei, Taiwan; Region A), 30 were from the General Hospital of the Armed Forces (Taipei, Taiwan; Region A), and 80 were from Taichung Veterans General Hospital (Taichung, Taiwan; Region B) (2006 between April and March 2007). The last group consisted of 28 relapsed lung cancer patients. Table 3 lists all detailed clinicopathological features, including all lung cancer patients (n=150), and new lung cancer patients (n=122). All patients were approved by the Institutional Research Board (IRB) of each hospital.
[0169] table 3
[0170]
[0171] * : NSCLC means non-small cell carcinoma ** : SCLC means small cell carcinoma
[0172] Contr...
Embodiment 3
[0187] Gene signature and prediction of clinical outcome in lung cancer
[0188] The prediction model is established based on the mRNA expression of the gene to be detected, and is used to predict the risk of lung cancer and evaluate the treatment outcome of a specific drug or course of treatment. The equation of the predictive model is a stepwise variable selection method using multiple regression, and the p-value (p-value) is less than 0.1.
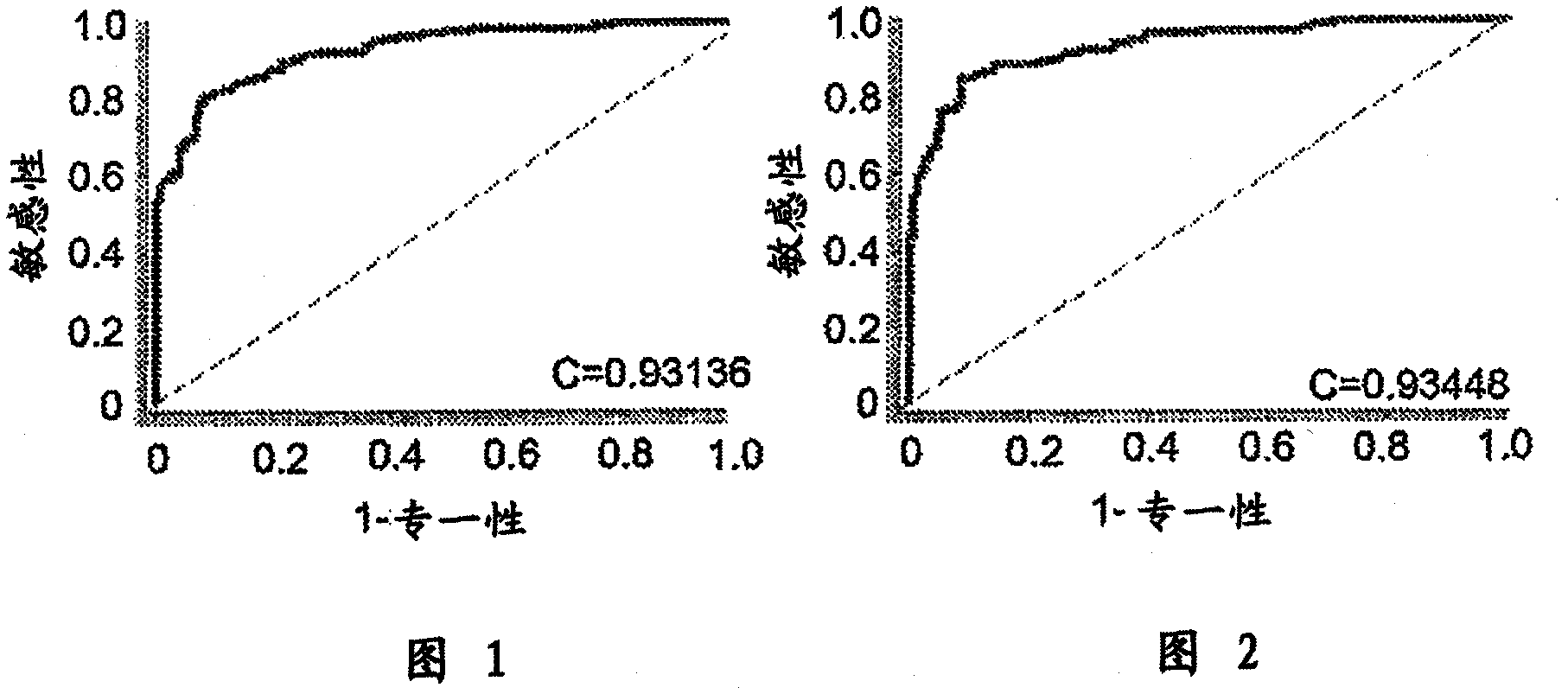
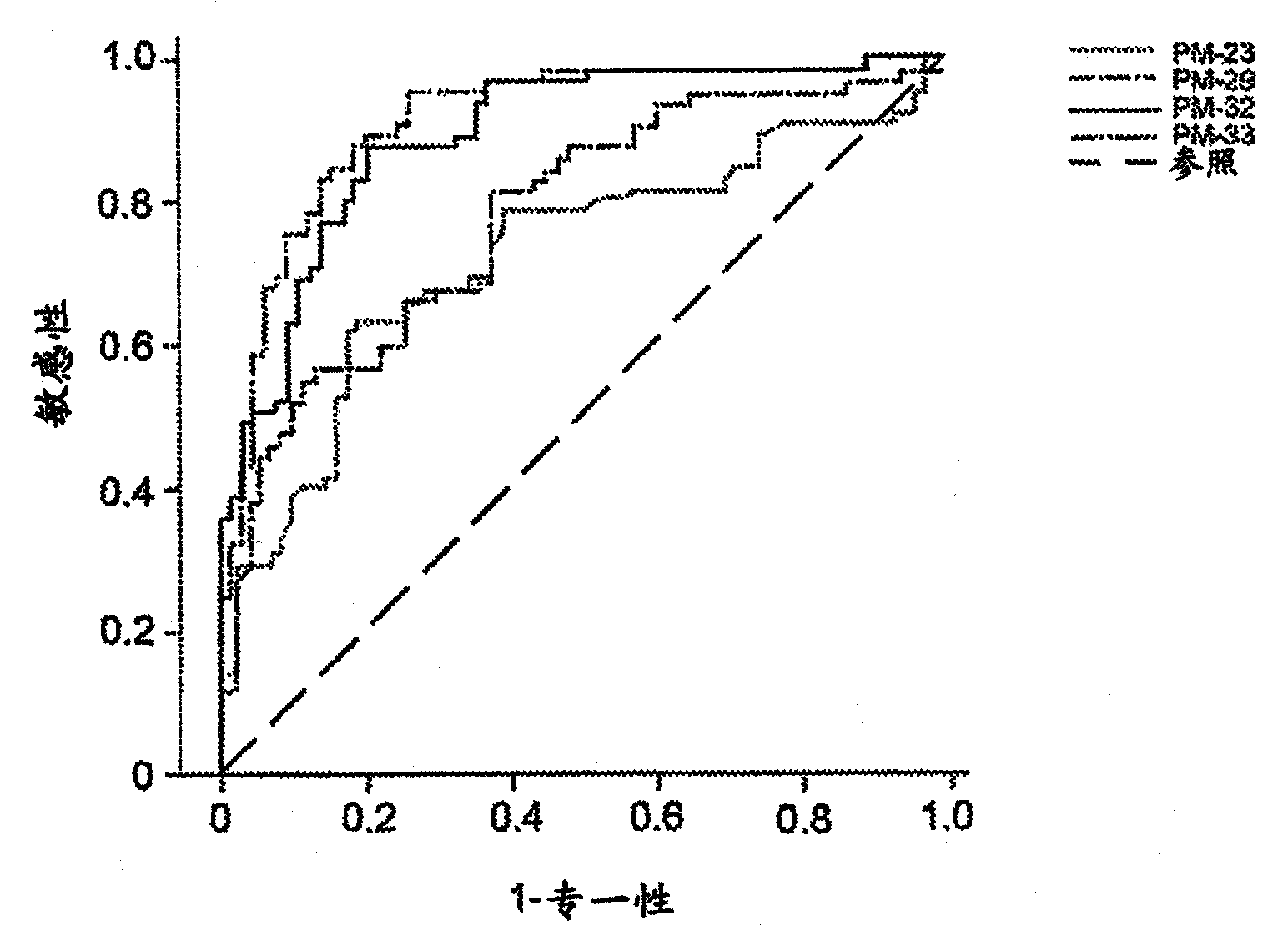
[0189] First, the DUSP6 gene was selected using statistical analysis software, and logistic regression was used to form prediction models of N=300 and N=272. The same analysis was performed by including the EIF2S3 gene in the prediction model. Then add other important genes in sequence, and add them in sequence with the aforementioned process until the ideal effective indicators in the case and control study groups of N=300 and N=272 are satisfied, such as sensitivity greater than 80%, specificity greater than 80%, accuracy greater th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com