Laser cladding technological method and alloy material for laser cladding
A technology of laser cladding and alloy materials, which is used in the repair of journals, end faces of high temperature and high pressure valves, laser cladding process methods and the fields of alloy materials, which can solve unsatisfactory mechanical properties, high laser power density and process control requirements. High and other problems, to achieve good anti-cavitation performance, simple and easy operation, good process adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment 1: An alloy material for laser cladding, the chemical composition (weight percentage) of alloy elements is C: 0.85%; Cr: 35%; Fe: 5%; Si: 0.5%; W: 5.0%; Mo: 1.2%; Ni: 7%; V: 1.5%; Ti: 1.0%; B: 0.5%; Nb: 0.3%; Re: 0.6%; Co: balance.
[0023] The preparation method is as follows:
[0024] 1. Calculate the addition amount of various master alloys such as ferrochrome, ferrovanadium, ferrosilicon, and ferroboron (considering the different burning loss rates of each element when calculating).
[0025] 2. After weighing, bake in an oven at 200°C.
[0026] 3. Add high melting point and magnetic elements first, and then add elements that are easy to burn.
[0027] 4. After melting, remove slag, refine and add rare earth elements.
[0028] 5. Open the water and gas circuit, control the pressure and liquid level.
[0029] 6. Place the preheated middle leakage bag on the nozzle, and pour the alloy liquid in the furnace into the middle leakage bag.
[0030] 7. After ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] An alloy material for laser cladding, the chemical composition (weight percentage) of alloy elements is C: 0.95%, Cr: 42%, Fe: 3%, Si: 1.2%, W: 5.5%, Mo: 1.5% , Ni: 6%, V: 1.8%, Ti: 2.0%, B: 1.2%, Nb: 0.5%, Re: 1.0%, Co: balance.
[0034] The preparation method is the same as in Example 1.
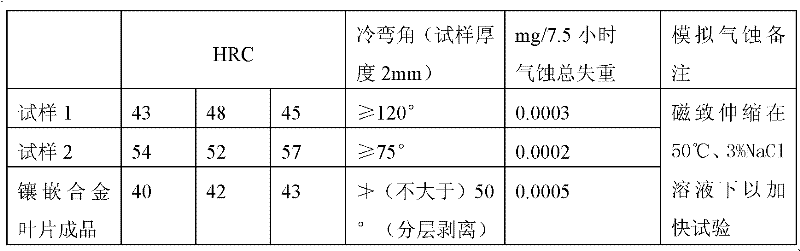
[0035] The hardness of the cladding layer prepared by laser cladding with this ratio of alloy powder is HRC52-57. In addition to being applied to steam turbine blades, it can also be applied to the repair of shaft journals and valve end faces, with the same performance and effect.
Embodiment 3
[0037] A laser cladding process method for substituting steam turbine blade inlaid alloy sheets, comprising the following steps:
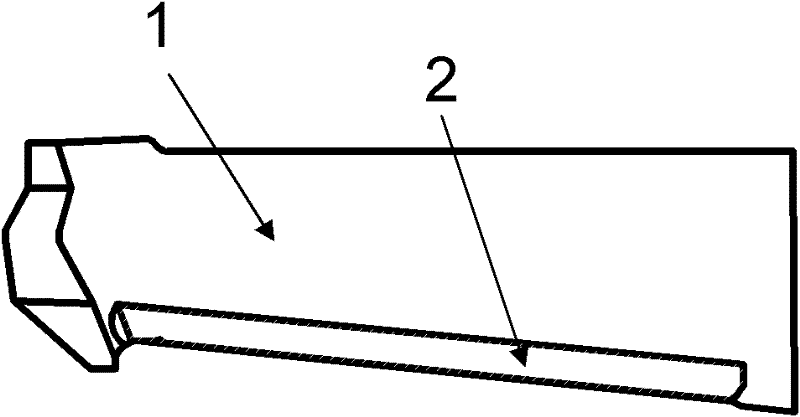
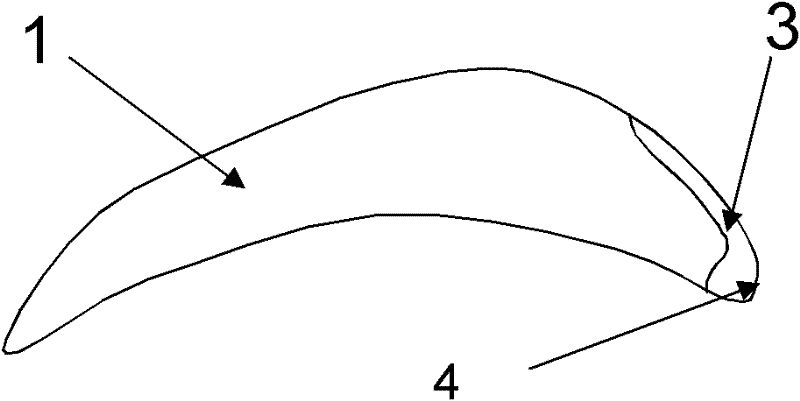
[0038] 1. If figure 1 As shown, the back arc of blade 1 (including the original R side) is milled off by 1 mm to form milling groove 2; the back arc side is milled off to 1 / 5 of the thickness, but the total depth does not exceed 1 mm; the forming knife can be used to complete it in one step by CNC milling machine .
[0039] 2. According to the size of the milled part, the robot motion track is compiled, and the overlap rate of cladding programming is 55%.
[0040] 3. Adopt optical fiber or semiconductor laser, select the powder of embodiment 1 and embodiment 2, and its particle size is -140+325 mesh (particles are lower than 140 mesh, higher than 325 mesh, and the particle size is within this range), dispatch The powder amount is 14g / min, and the powder is fed by inert gas; the spot diameter is 5mm, the power is adjusted to 1800W, the laser scann...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com