Method for calibrating triangle scanning deviations in light beam acquiring system based on target reflection signals
A technology of reflected signal and calibration method, applied in optics, optical components, telescopes, etc., can solve the problem that the convergence speed of the algorithm cannot be guaranteed, and achieve the effect of improving real-time and controllability, shortening deviation correction time, and improving real-time performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
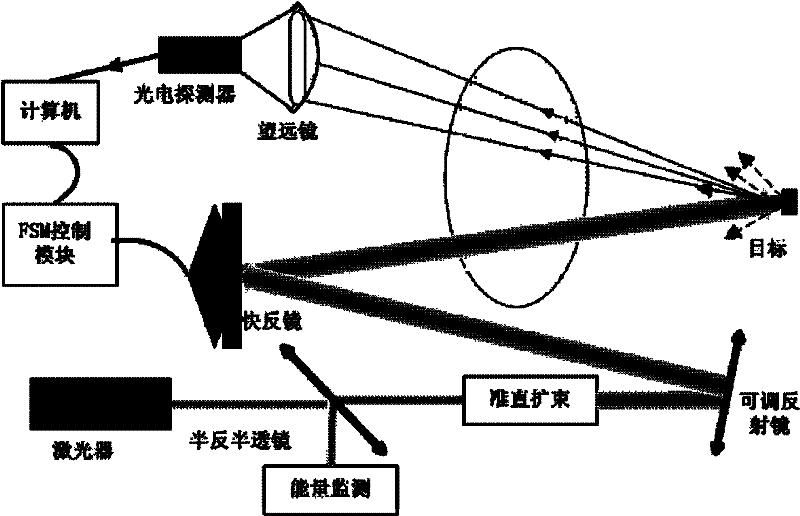
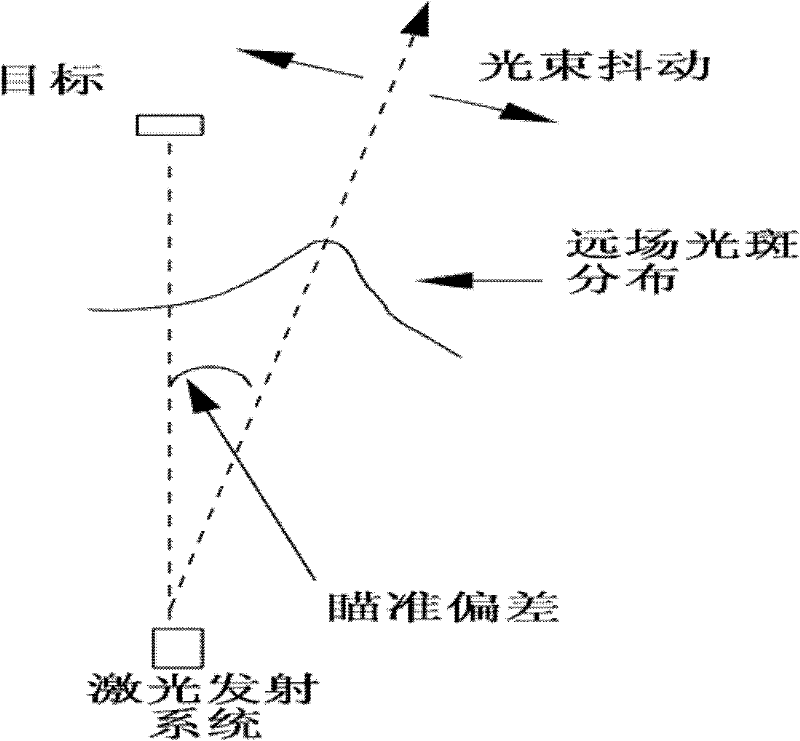
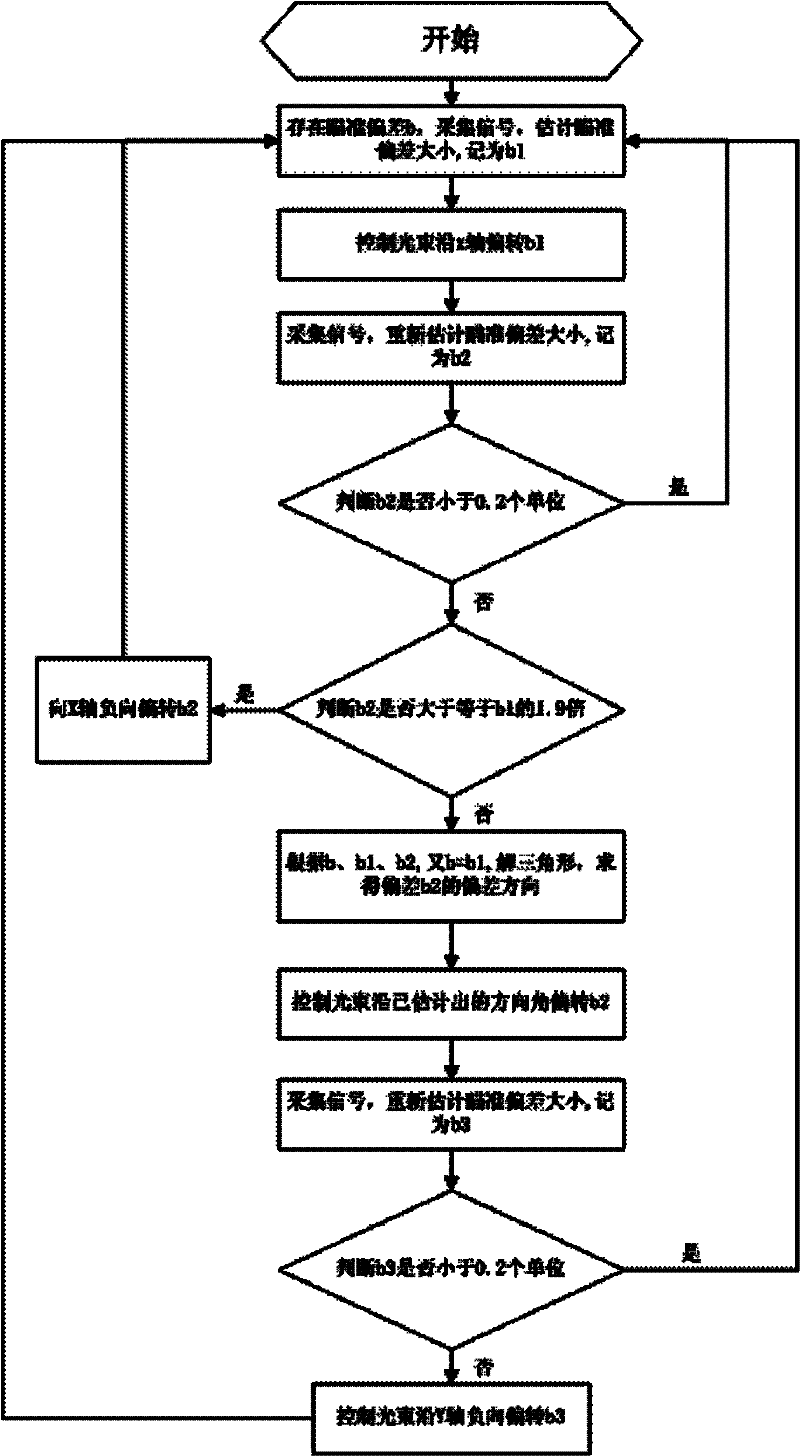
[0040] The beam aiming system used in the present invention is as figure 1 Shown: The Gaussian beam output by the laser is collimated and expanded to point to the space target through the control of the fast reflector, and the optical signal reflected from the target is received by the telescope, converted by the photoelectric detector and digitized by the data acquisition system, and input into the computer The aiming error estimation module estimates the deviation of the target relative to the statistical center of the beam, and inputs the deviation signal into the controller to drive the fast mirror to deflect and calibrate the beam deviation to form a closed-loop aiming system for aiming control; and it is set in the whole aiming process In , the position of the target remains unchanged relative to the aiming field of view, or the target is in the fine tracking state of the aiming system.
[0041] The beam aiming system involved in the present invention is established as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com