Screening method for identifying patients at risk of adverse hepatologic events
A patient-selected technology, applied in metabolic diseases, disease diagnosis, cardiovascular system diseases, etc., can solve the problem of low specificity of transaminase alone
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0107] Example 1: Increased ALT alone predicts poor liver toxicity
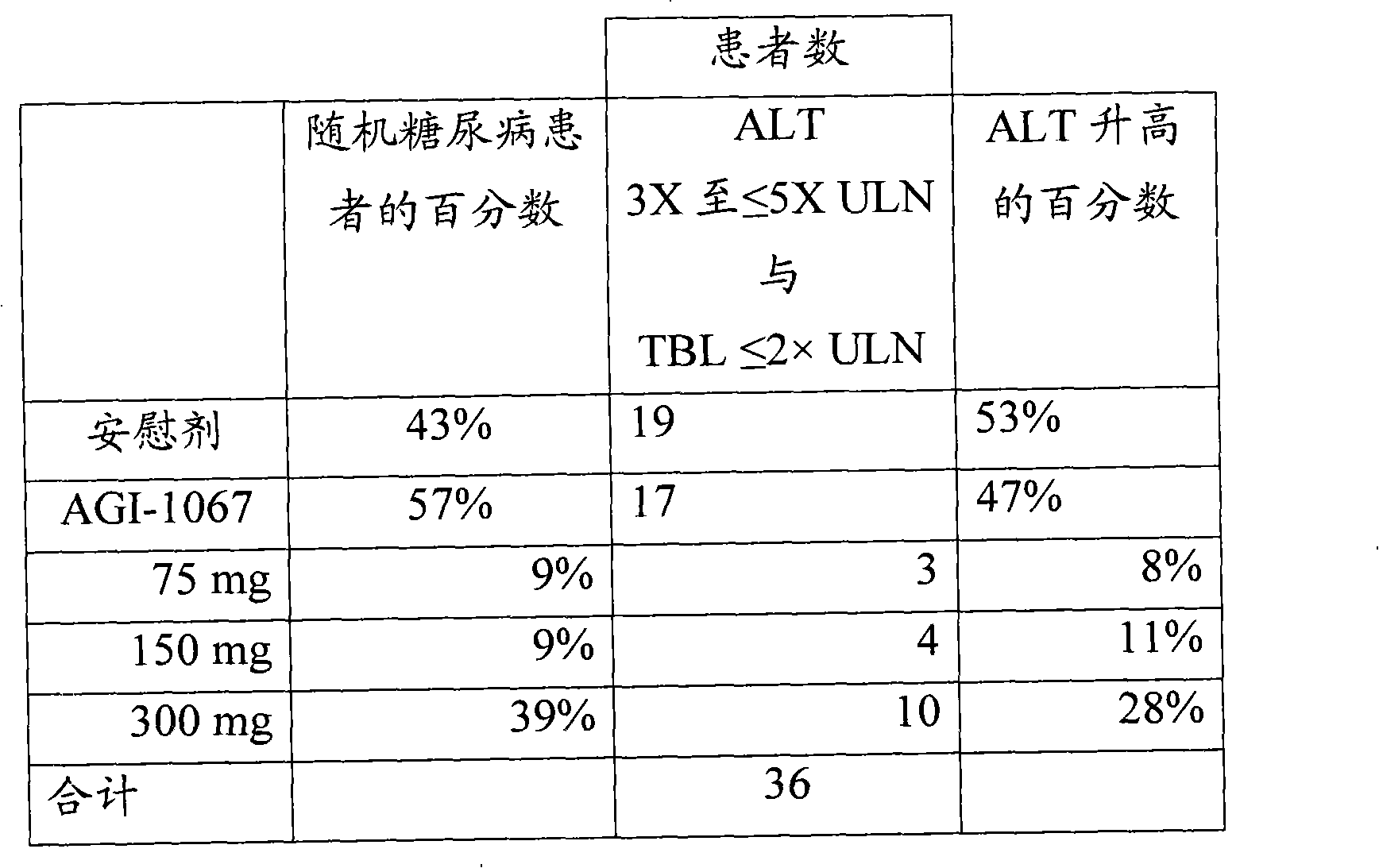
[0108] Thirty-six patients in the pooled data set of diabetic patients had elevated ATL peaks between 3× and <5×ULN. Data for the treatment groups are summarized in Table 1. AGI-1067- and placebo-treated patients had comparable incidences of ALT elevations in this range. ALT levels are therefore of limited value in assessing potential hepatotoxicity.
[0109] Table 1.
[0110]
Embodiment 2
[0111] Example 2: Elevated ALT Combined with Total Bilirubin Levels Are Useful Indicators of Hepatic Events
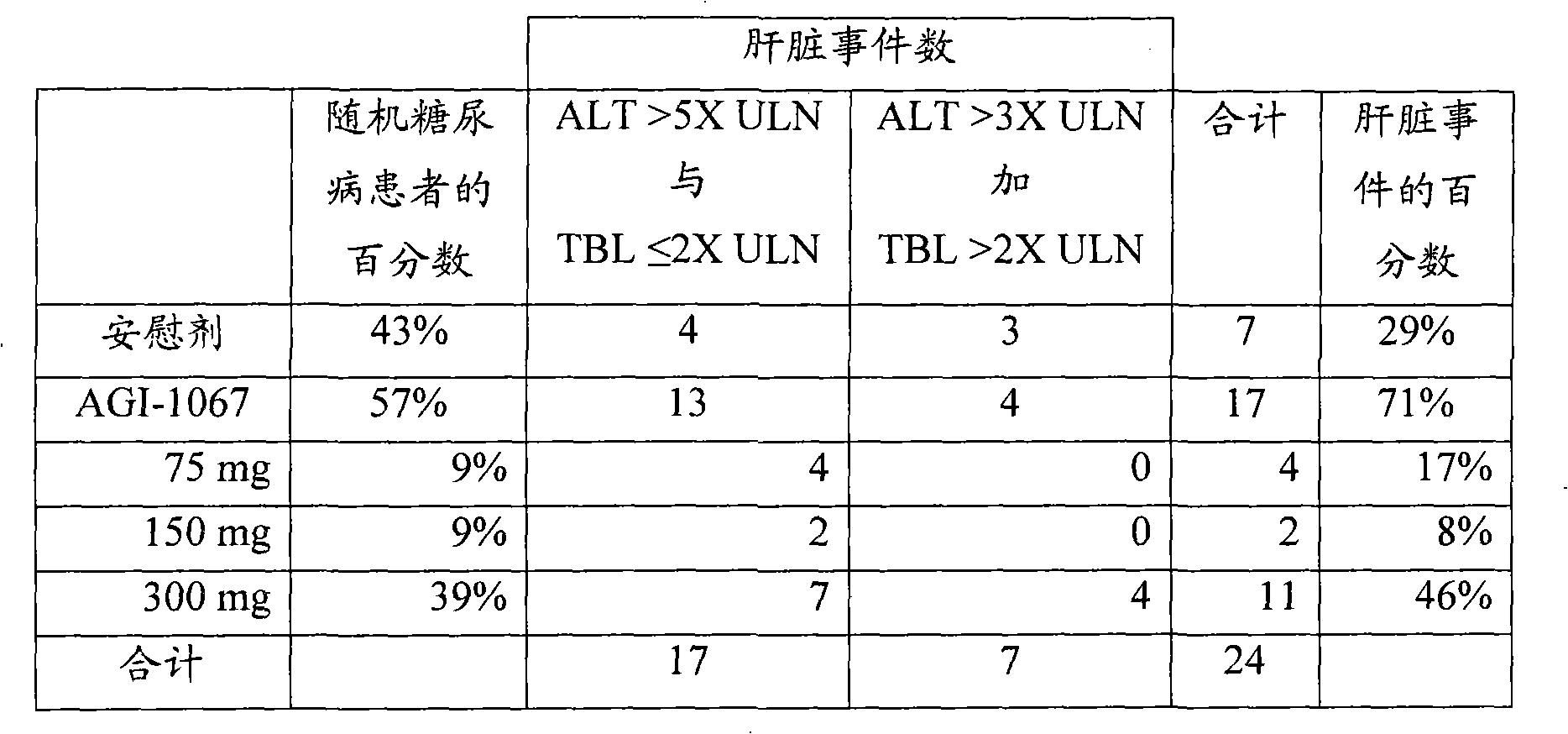
[0112] There were 24 diabetic patients in the pooled data set with hepatic events when using ALT > 5X ULN plus TBL 3X ULN plus TBL > 2X ULN criteria. Table 2 summarizes the treatment groups and patients administered AGI-1067. Randomly sampled, 57% of patients were in the AGI-1067 group and 43% in the placebo group, resulting in an AGI-1067 to placebo ratio of 1.3. Of the 24 hepatic events, 17 occurred in AGI-1067-treated patients and 7 occurred in placebo-treated patients.
[0113] Table 2.
[0114] Before using the risk identification tool
[0115]
Embodiment 3
[0116] Example 3: ApoA1 levels are directly related to adverse liver events.
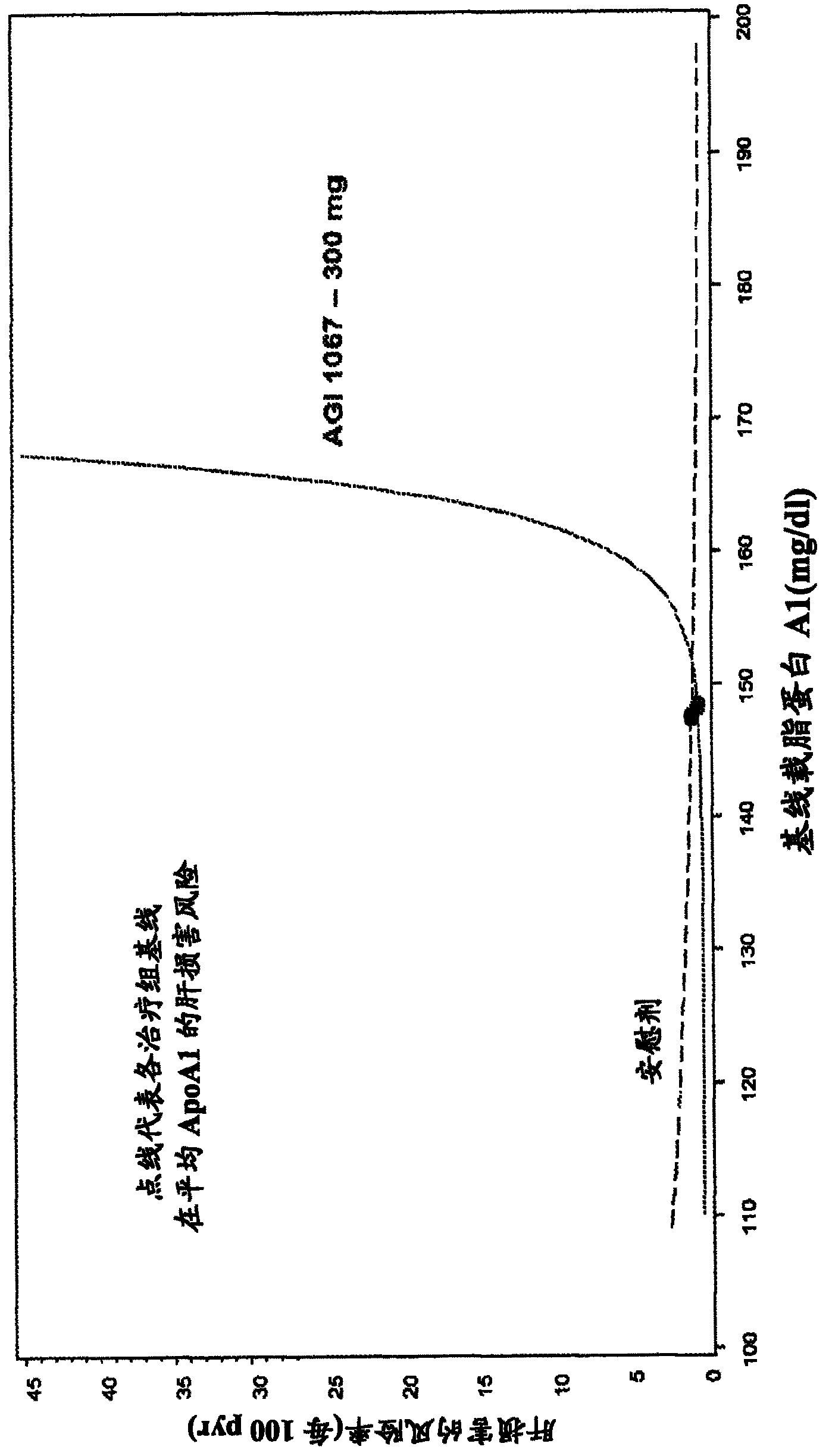
[0117] ApoA1 measurements are both sensitive and specific for identifying subsequent hepatic events. Events were determined when ALT > 5X ULN and TBL 3X ULN and TBL > 2X ULN were measured. figure 1 Cox proportional hazards models generated from data in patients with type 2 diabetes showed an age-adjusted effect of the 5th-95th percentile range of baseline ApoA1 on subsequent hepatic events. As a point of reference, the ULN for ApoAl in this assay is 165 mg / dL. Solid and dashed lines represent AGI-1067 and placebo data, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com