Method and device for storing data in database
A technology for storing data and storage devices, applied in the field of databases, can solve problems such as increased burden on storage devices, data loss, complex data migration, etc., and achieve the effect of smooth expansion and small burden on storage devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
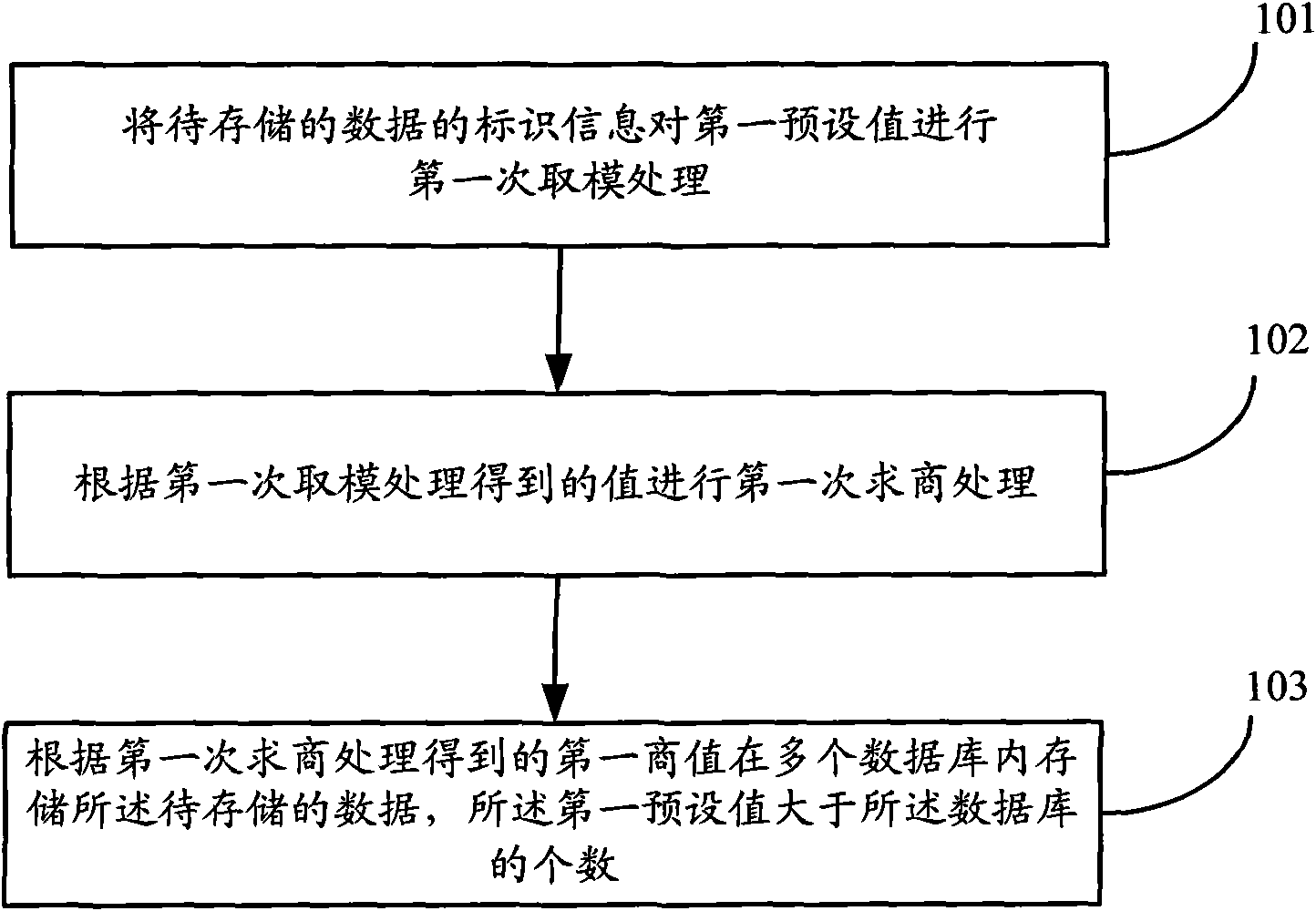
[0034] Embodiment 1 of the present application provides a method for storing data in a database, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0035] Step 101, performing the first modulo processing on the first preset value of the identification information of the data to be stored;
[0036] Step 102, performing the first quotient processing according to the value obtained in the first modulo processing;
[0037] Step 103, storing the data to be stored in multiple databases according to the first quotient value obtained by the first quotient seeking process, and the first preset value is greater than the number of the databases.
[0038] Preferably, the first divisor of the first quotient seeking process is the number of the database.
[0039] Preferably, the first preset value is an integer multiple of the number of the databases.
[0040] Preferably, storing the data to be stored in multiple databases according to the first quotient value obtained by the first quotient seeking pr...
Embodiment 2
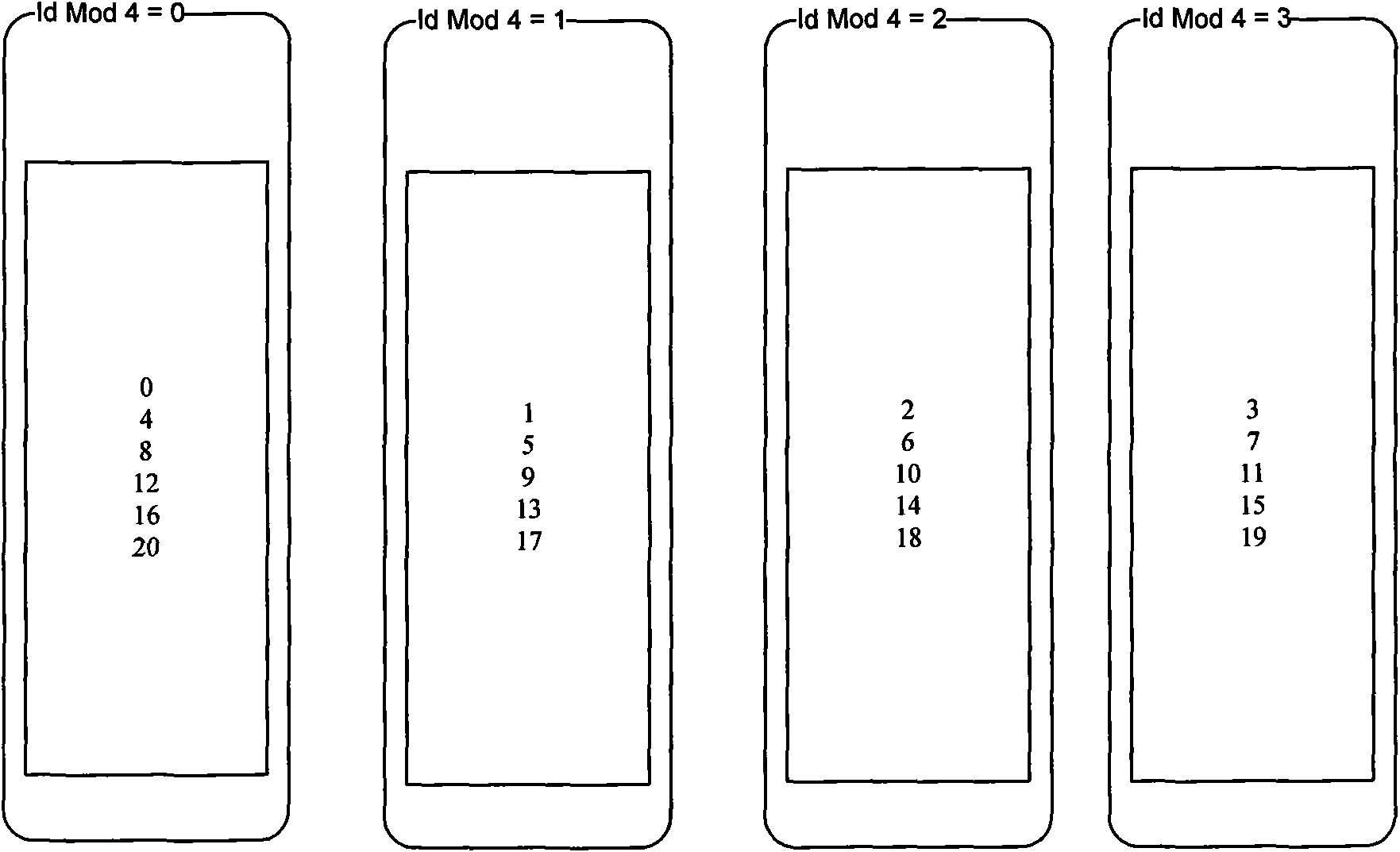
[0061] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the second embodiment of the present application is based on the first embodiment, and performs a segmentation operation on any one of the multiple databases in the first embodiment, that is, the Any database is divided into multiple sub-databases, specifically including the following steps:
[0062] Step 104 , performing a second modulo processing on the second preset value of the identification information of the data stored in the divided database; the second preset value may be the same as or different from the first preset value.
[0063] Step 105, according to the value obtained in the second modulo-taking process, store the data stored by the divided database in multiple sub-databases.
[0064] In order to more clearly illustrate the method for storing data in the database in the second embodiment, a further detailed introduction will be made below in combination with specific implementation scenarios, wherein the device performing da...
Embodiment 3
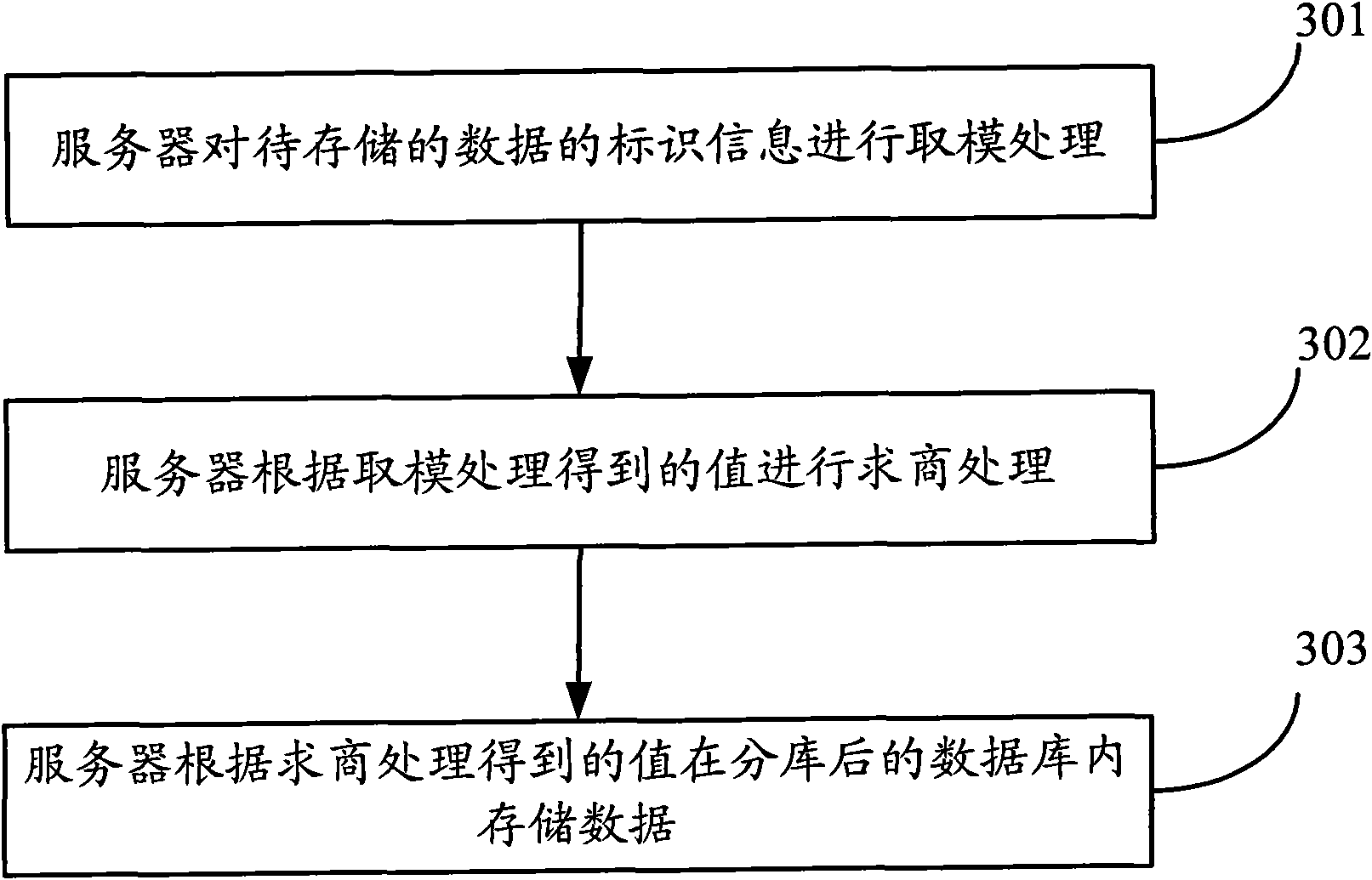
[0070] Embodiment 3 of the present application is also based on Embodiment 1, and performs a segmentation operation on any one of the multiple databases in Embodiment 1, that is, any one of the multiple databases The database is divided into multiple sub-databases, such as Figure 6 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0071] Step 106, performing a third modulo processing on the third preset value of the identification information of the data stored in the divided database;
[0072] Step 107, performing a second quotient process on the result of the third modulo-taking process;
[0073] Step 108, according to the second quotient obtained by the second quotient processing, store the data stored in the divided databases in multiple sub-databases.
[0074] In the third embodiment, since the first preset value in the first modulus processing in the first embodiment is greater than the number of databases, when any database in the first embodiment is divided ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com