A laying method and auxiliary device for laying glass fiber cloth at the root of wind power blades
A technology for wind power blades and auxiliary devices, which is applied to other household appliances, household appliances, household components, etc., can solve problems such as inability to meet large-scale production, unfavorable blade production efficiency, and unfavorable large-scale production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
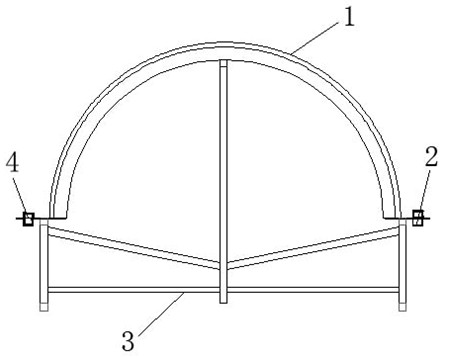
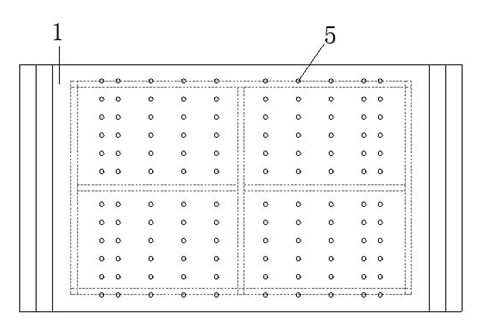
[0016] by attaching Figure 1-4 It can be seen that the present invention relates to a method for laying glass fiber cloth at the root of wind power blades. First, a fixing bracket is fixed, and then the semicircular steel plate profile is installed on the fixing bracket, and the glass fiber cloth fixing groove is installed on the At both ends of the semicircular steel plate surface, fully unfold the glass fiber cloth to be laid, and cover it on the semicircular steel plate surface, and at least ensure that the two ends of the first and last two layers of glass fiber cloth exceed the glass fiber cloth fixing groove, When the glass fiber cloth fixing square steel is pressed on the glass fiber cloth fixing groove, the glass fiber cloth can be pressed down, and then the glass fiber cloth fixing square steel is pressed on the glass fiber ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com