Skeleton extraction method and device for polygonal image
A skeleton extraction and polygon technology, which is applied in the directions of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer parts, etc., can solve the problems of burr connectivity of skeletons, inaccurate skeleton positions, and difficulty in obtaining guarantees. Accurate Smooth lines for improved accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
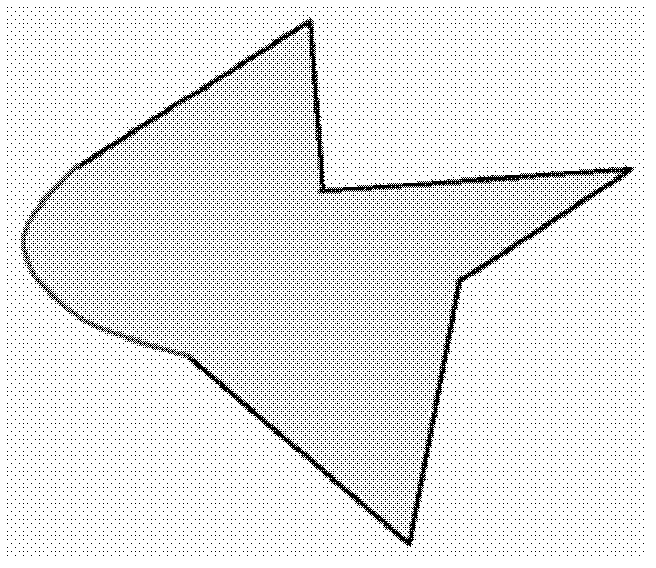
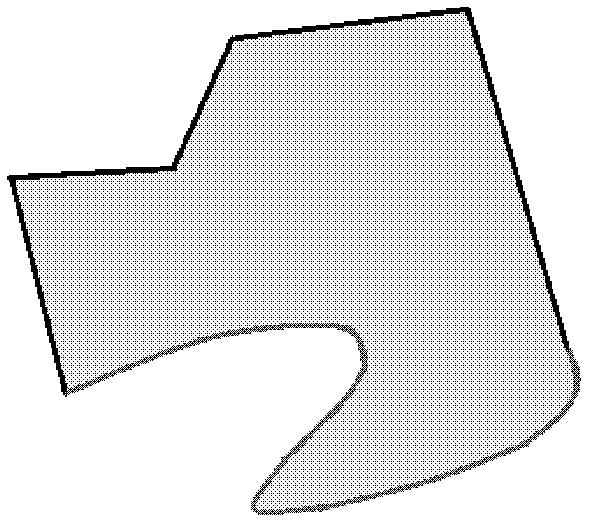
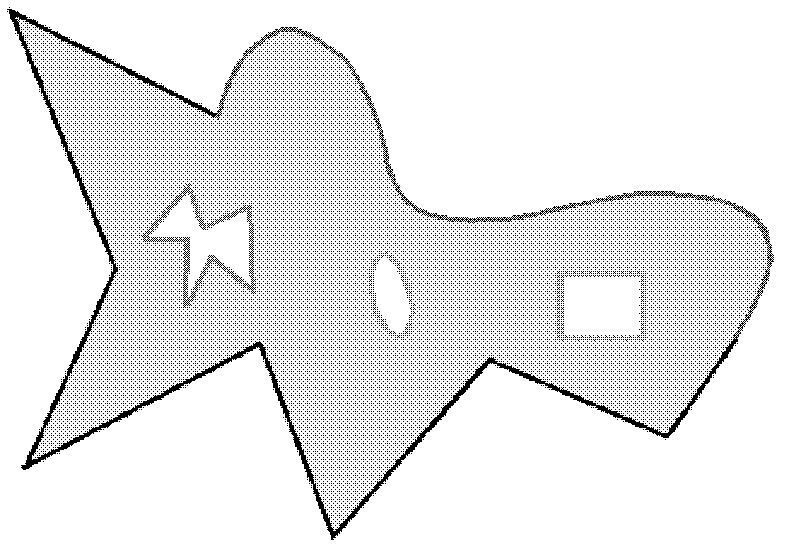
[0062] In the field of geoscience computing, it is necessary to face various complex spatial objects, that is, calculations that require skeleton extraction for various complex polygonal images. Ideally, the sides of a simple polygon are straight line segments, but in practical applications, most of the real space objects correspond to polygons with arbitrary boundaries. The sides of the polygon include not only straight line segments, but also arcs and free curves (see Figure 1A , Figure 1B shown), there may also be irregularly shaped "holes" and "islands" inside, and even any combination of free curves, arcs, "holes" and "islands" (see Figure 1C , figure 2 shown) complex situation.
[0063] That is, polygons should not only include general simple polygons (including convex polygons and concave polygons), but should also cover polygons with island holes and special polygons with curve segments in their sides. Such polygons are more in line with the actual situation.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com