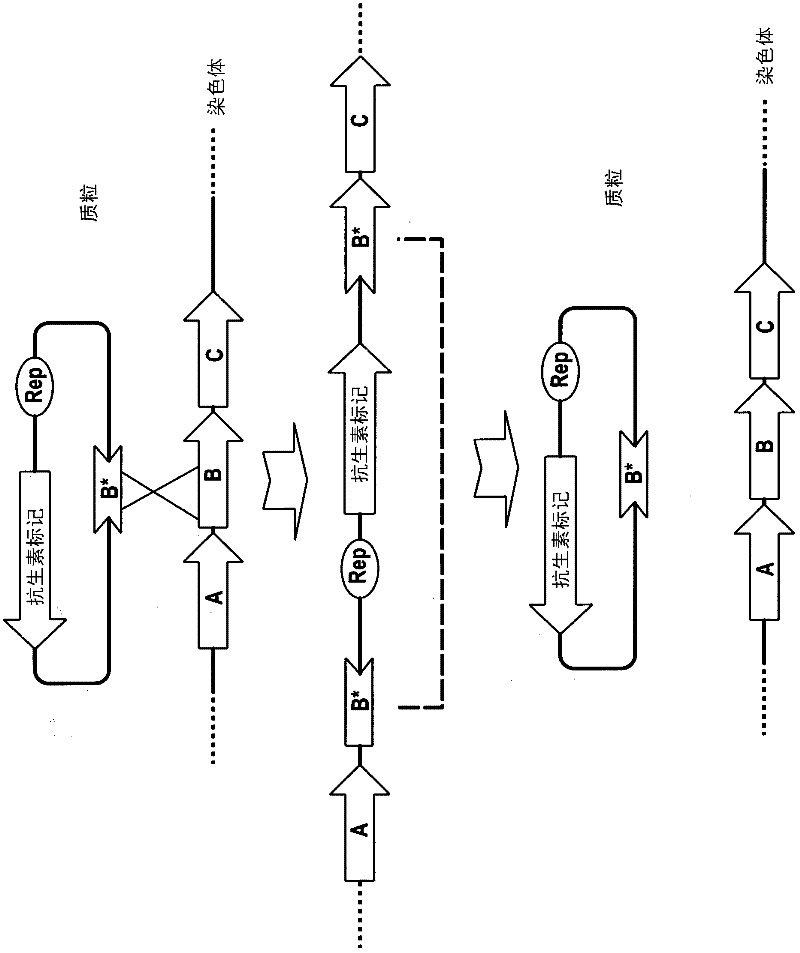
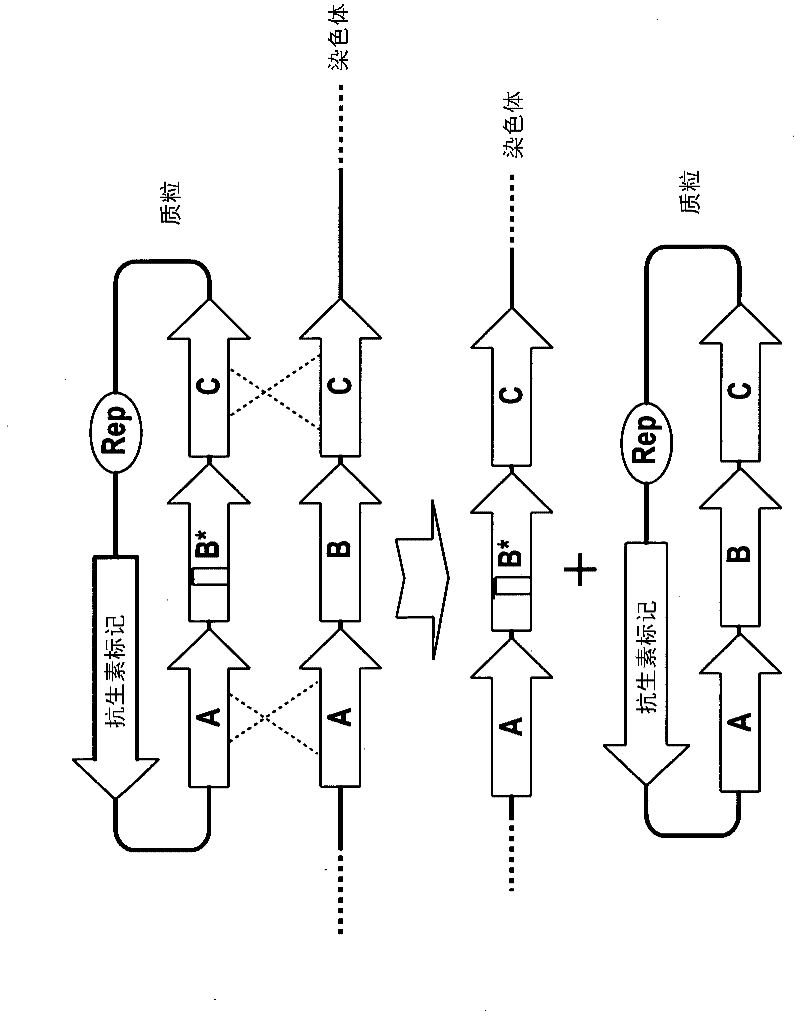
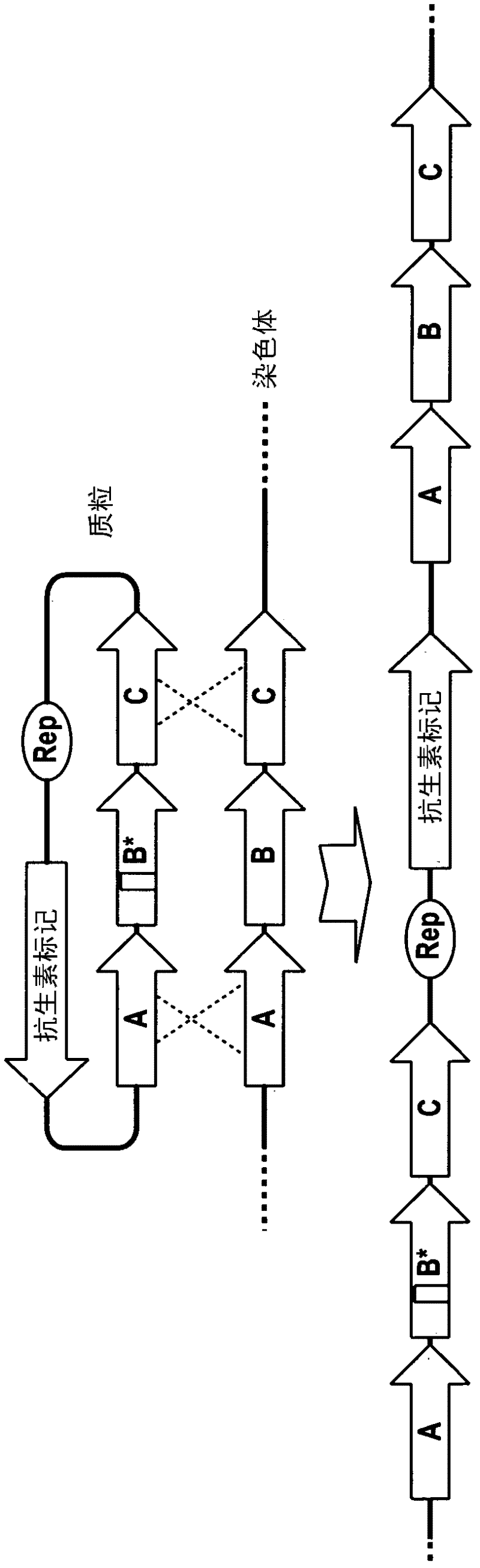
Method of double crossover homologous recombination in clostridia
A technique of homologous recombination and double crossover, applied in other methods of inserting foreign genetic material, recombinant DNA technology, biochemical equipment and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0081] Construction of codA expression plasmid
[0082] The codA expression cassette was isolated from the vector used by Fox et al., Gene Therapy. (1996) 3: 173-178 and cloned into pMTL960. This plasmid was used to test the function of the codA gene in E. coli and C. difficile. In E. coli, the construct worked as expected, allowing growth in the absence of FC but not in the presence of FC. Similarly, as in Figure 4 It was shown that when transformed into Clostridium difficile and grown on minimal medium containing 100 μg / ml FC (modified from the recipe described by Karlsson et al. (1999) Microbiology 145:1683-1693), codA mooring The Clostridium difficile cells of the box can be distinguished. That is, cells expressing codA did not grow.
[0083] The medium described by Karlsson et al. contains:
[0084]
[0085] * Amino acids in minimally defined medium (MDM)
[0086] ** Amino acids are added a little more to give supplemental defined medium (SDM)
[0087] *** Ami...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com