Method for directly identifying homologous recombination of higher plant DNA
A homologous recombination and plant technology, applied in the field of plant genetics, can solve problems such as traits or a site that is difficult to identify homologous recombination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
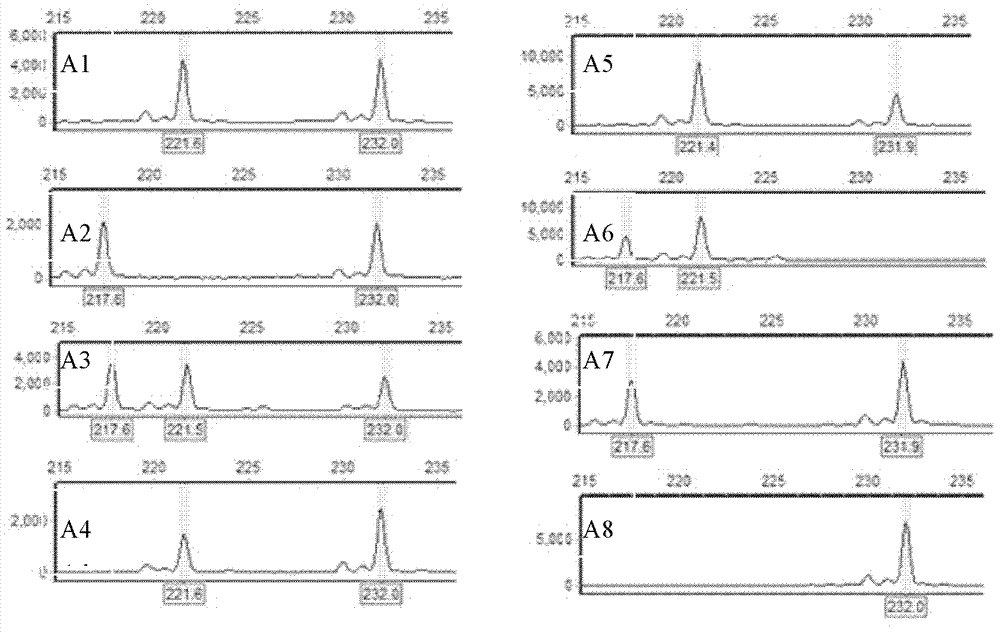
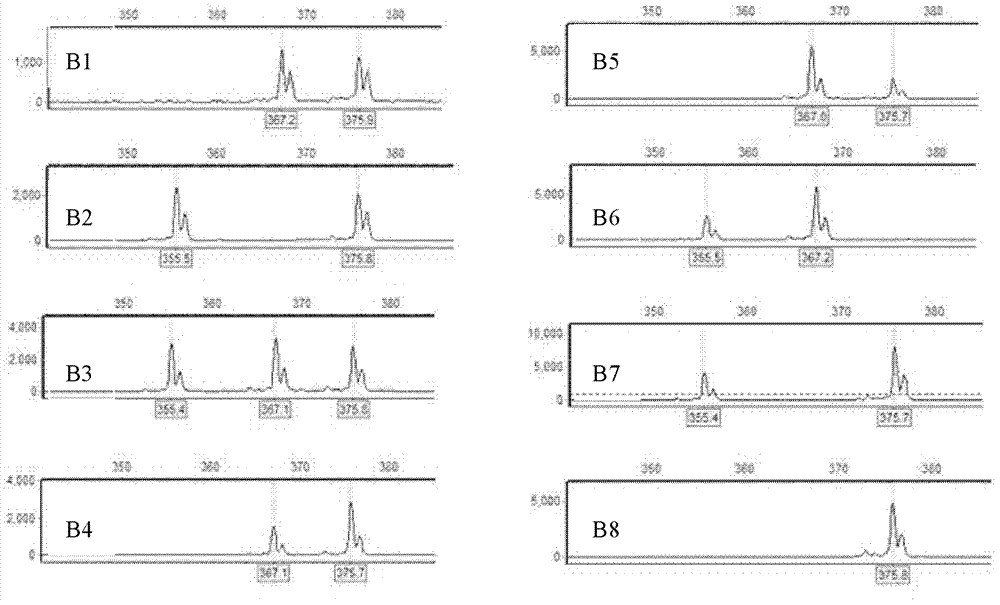
[0017] Example 1 Detection of homologous recombination of 'Zheyin No. 3 poplar' during sporocyte meiosis
[0018] 1. Test materials:
[0019] Maternal material to be tested: 'Zheyin 3 poplar' (P.pseudo-simonii×P.nigra'Zheyin3#');
[0020] Male material: 'Beijing Yang' (P.×beijingensis).
[0021] 2. Test methods and test results
[0022] When the embryo sac development stage of 'Zheyin No. 3 poplar' is in the uninucleate embryo sac stage, the embryo sac is subjected to physical and chemical treatment (soaking the female inflorescence 6-48 with 0.3-0.5% colchicine solution) hours) to obtain 2n female gametes with two sister chromosomes coexisting in the same gamete; cross the 2n female gametes with the male gametes of 'Beijing Poplar' (P.×beijingensis) to obtain triploid plants;
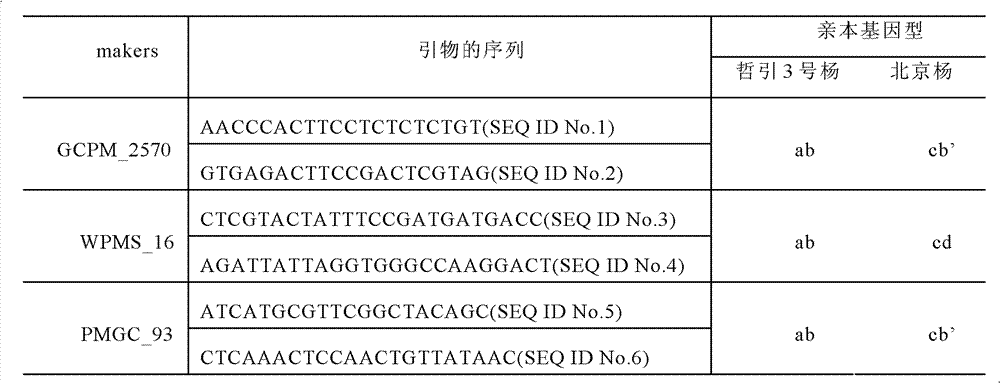
[0023] According to the poplar SSR database (http: / / www.ornl.gov / sci / ipgc / ssr_resource.htm), there are differences between 'Zheyin 3 poplar' and 'Beijing poplar', and 'Zheyin 3 poplar' Three pairs of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com