Method for testing adhesive force life of steel wire tire cord in radial tire
A radial tire and steel cord technology, which is applied in the field of tire performance evaluation, can solve the problems of tire adhesion life and cannot provide a reference basis, and achieve the effect of simple and easy operation of the experimental method, accurate experimental results and strong feasibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The radial distribution determination of the elements in the unaged brass steel cord of the present embodiment operates in the following steps:
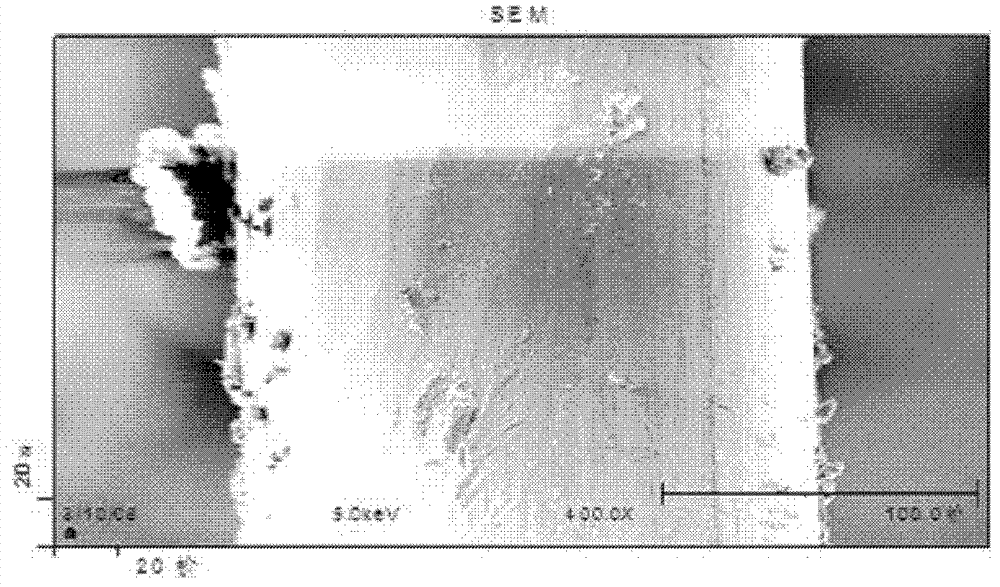
[0024] In the radial distribution of the steel wire, we adopted the AES (Auger Electron Method) method to determine the elements and their composition. Auger electrons sputter electron current from the position shown in the figure, and carry out step-by-step analysis and detection from the surface to the axis center with every 5nm as a unit (that is, every 5nm as a layer), and the elements and their composition data of a layer every 5nm .
[0025] Figure 1(a) is the scanning electron microscope (SEM)-electron energy profile diagram of the steel wire. The measurement parameters are shown in the figure (the current size is 50eV, the sputtering area is 2mm*2mm, and the picture is a magnification effect picture of 400.0 times). Figure 1 (b) is the overall shape, (c) is the local shape, from which it can be seen that there is stil...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Use a flat vulcanizer to vulcanize the radial tire test sample at 155°C for 10 minutes, then place it in liquid nitrogen and cool it for 5 minutes, and immediately remove the rubber material by tapping with a hammer to obtain a steel cord sample. Dicumene was soaked at 60°C for 24 hours, dried in vacuum and left for testing and analysis.
[0028] Diisopropylbenzene is a rubber removal agent. After the rubber material is crushed, there will be a small amount of rubber on the steel wire. Dissolving the remaining rubber with diisopropylbenzene can obtain the steel cord after the rubber material is removed. It will affect the element content on the surface of the steel cord.
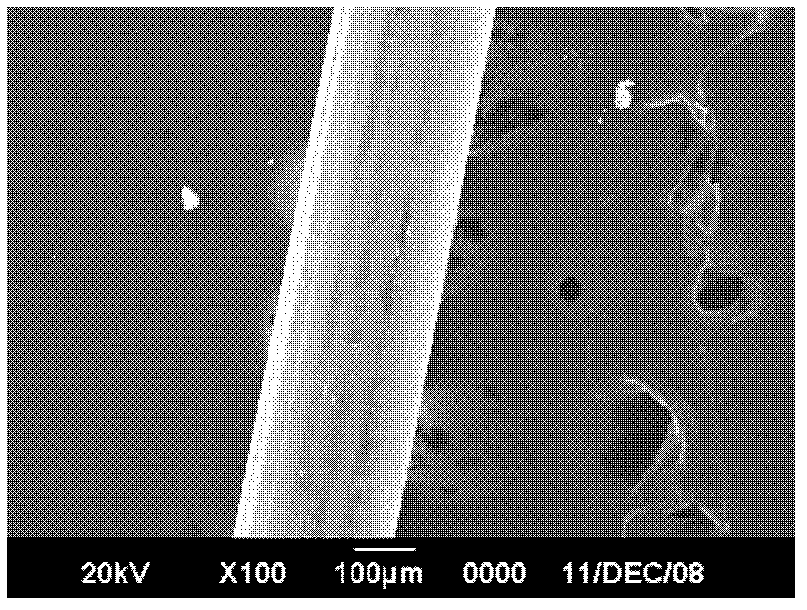
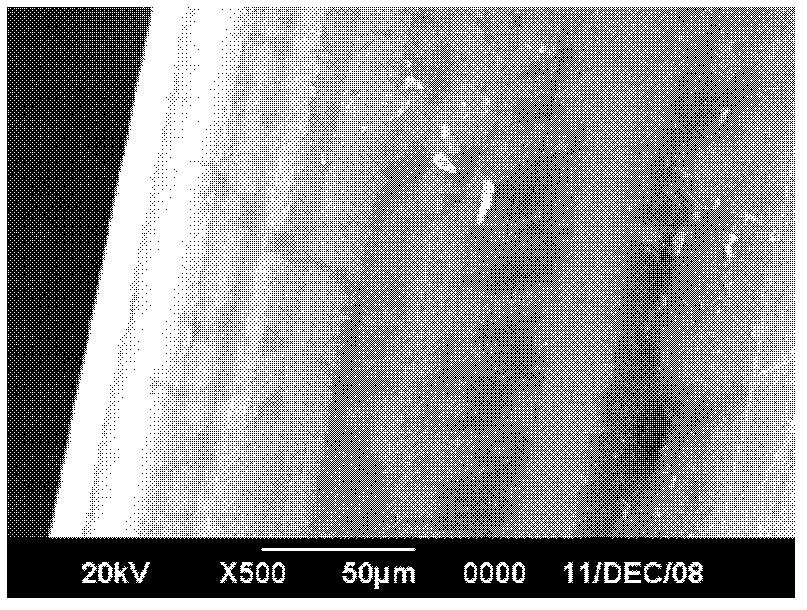
[0029] Figure 2(a), (b), (c), and (d) show the scanning electron micrographs of the steel cord obtained under the vulcanization condition at 155°C at magnifications of 500 times, 4000 times, 5000 times and 10000 times, respectively. At 5,000 and 10,000 times, there are a few white dots and flakes tha...
Embodiment 3
[0034] The steel cord sample prepared in Example 2 was placed in a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined autoclave, heated at 100°C and 120°C for 14 days in an electric thermostatic oven, and then scanned with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X Energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) was used to analyze the aging of the interface of the sulfide layer.
[0035]The higher the aging temperature, the faster the rate of decrease in the adhesion will be. The main reason is that the higher the temperature, the faster the reaction rate of copper, zinc and sulfur is. Figure 3(a) and (b) are scanning electron micrographs of the steel cord samples after vulcanization in Example 3, which were thermally aged at 100°C and 120°C for 14 days, respectively. It can be seen from the figure that the thermal aging at 120°C is obvious It is faster than the thermal aging at 100°C, and a large amount of copper and zinc sulfides have appeared on the surface. Table 2(a) and (b) respectively represent the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com