Method for producing Fengxian County Dahongpao prickly ash
A production method, the technology of Zanthoxylum bungeanum, applied in the crop field of Zanthoxylum bungeanum, can solve the problems of serious pests and diseases, insecure quality, and low-quality products, and achieve the effect of high yield, standardized operation, and less pests and diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] Zanthoxylum bungeanum production technology of the present invention implements according to the following steps:
[0020] 1. Variety requirements and seed harvesting
[0021] 1.1 Variety requirements: Dahongpao and Doujiao are native to Feng County.
[0022] 1.2 Seed collection and storage
[0023] 1.2.1 Seed Harvesting
[0024] (1) Selection of seed origin: It is required to collect seeds on the spot and raise seedlings on the spot. If it is necessary to adjust the seeds, it should be adjusted within the scope stipulated in the protection of the area of origin of Fengjiao to maintain the purity of the variety.
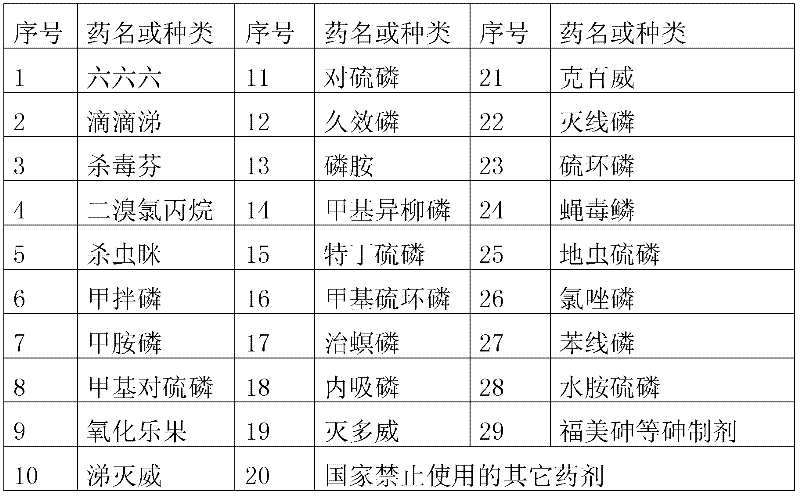
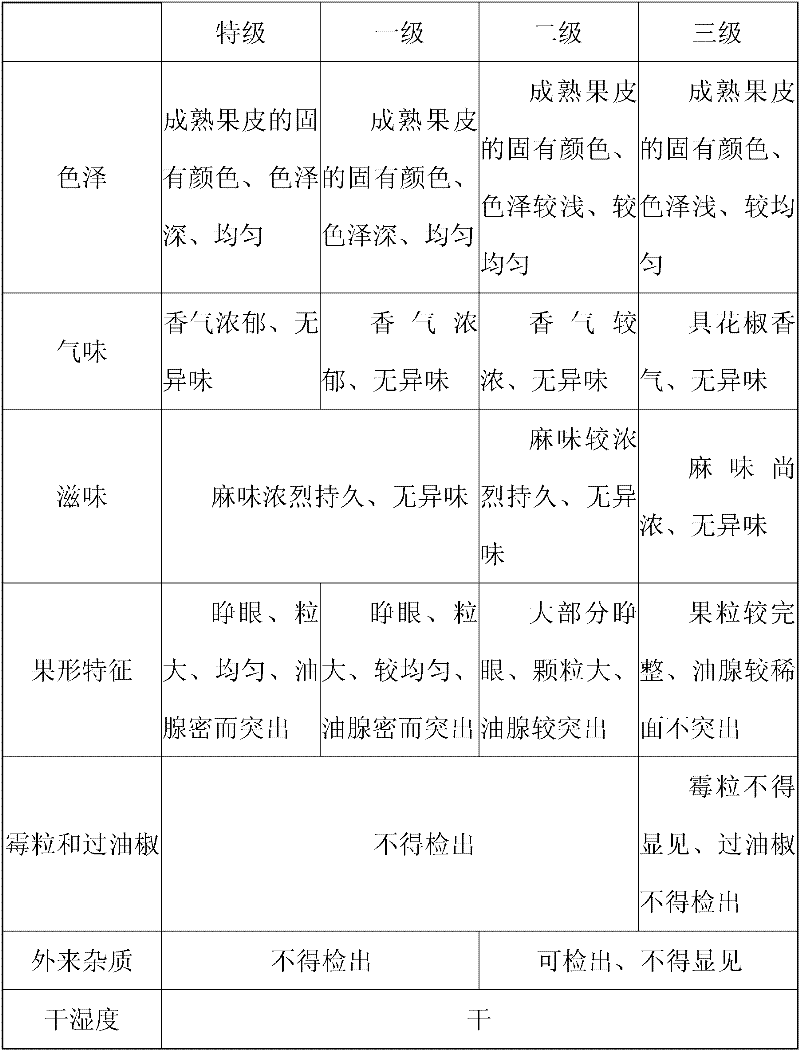
[0025] (2) Selection of mother tree for seed collection: Seeds must be collected from excellent mother trees that grow within the protected area of the area of origin of the phoenix pepper, and the mother tree for seed collection should be selected from sunny terrain, strong growth, good quality, no pests and diseases, and a fruiting age of 10-15 year...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com