Method for measuring interfacial heat transfer coefficient of rapid cooling process of steel
A technology of interface heat transfer coefficient and rapid cooling, which is applied in the field of measuring the interface heat transfer coefficient in the rapid cooling process of steel, which can solve the problem that the interface heat transfer coefficient is difficult to accurately determine, and achieve the effect of accurate test results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
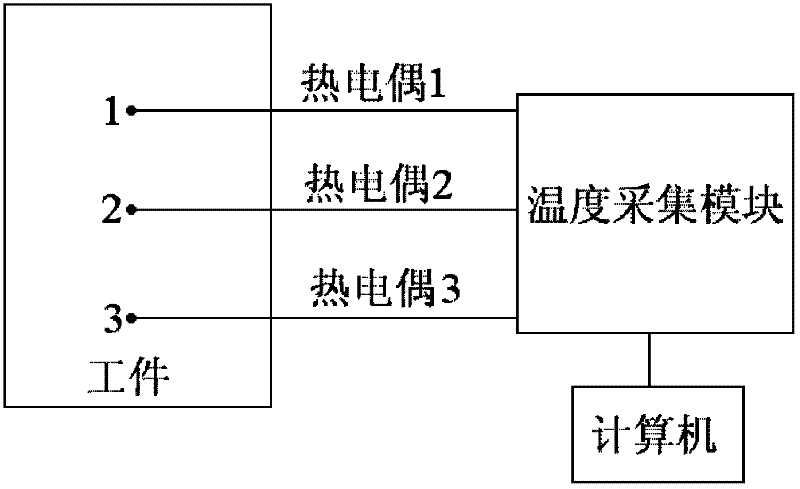
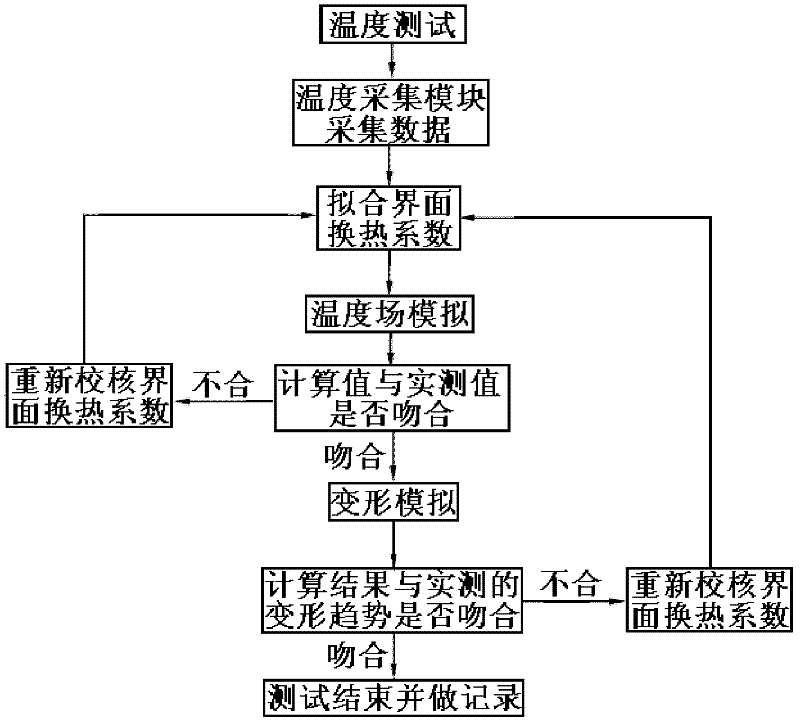
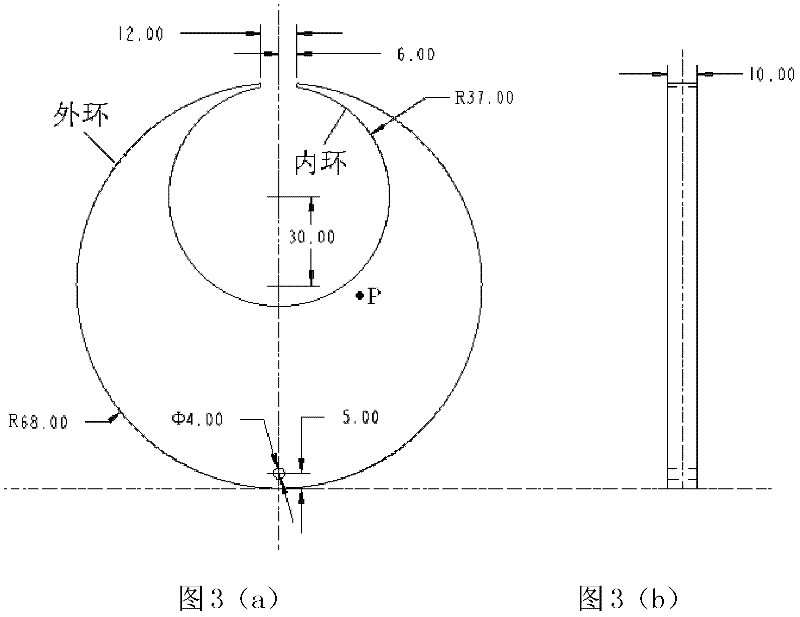
[0033] The present invention is used to test the interface heat transfer coefficient of the austenitic stainless steel notched disc in Fig. 3 1050°C water cooling, and simulate the temperature field and deformation of the notched disc after water cooling. As shown in Figure 3, the notched disc is a notched disc formed between the outer ring and the inner ring in the outer ring. The main reason for using the notched disc for the test is based on the following two points: one is the shape characteristics of the disc itself , it can be seen that the size of the disc increases continuously from the notch to both sides, which is excessively obvious, and deformation is easy to occur near the notch after water cooling; second, it is convenient to measure the deformation result. In this embodiment, a vernier caliper is used to directly measure the size of the notch, and then Just compare with the original size of the notch.
[0034] The temperature field change after the water cooling...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com