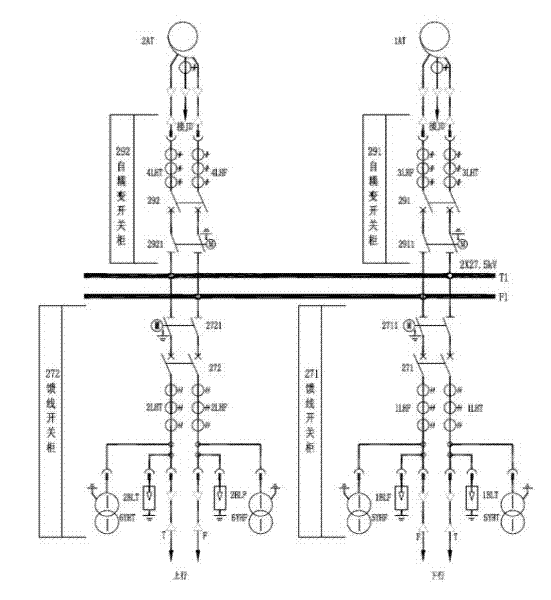
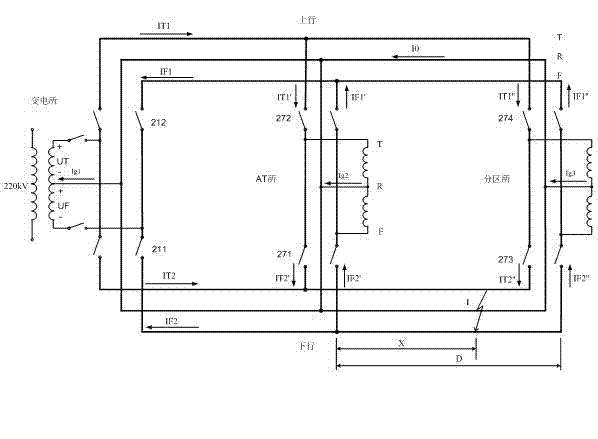
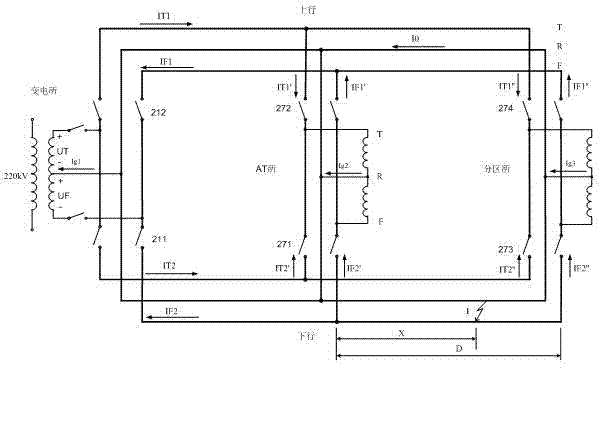
Method for distinguishing fault type and direction of AT (auto-transformer) contact network without depending on GPS (global positioning system) time synchronization
A fault type and direction identification technology, applied in the fault location, measuring device, instrument and other directions, can solve the problem of affecting the location of the fault point, unable to judge whether the fault direction is upstream or downstream, not installing current transformers, etc., to ensure data. Synchronization, shorten troubleshooting time, and restore power in time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0014] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. The drawings and specific embodiments do not limit the scope of protection claimed by the present invention.
[0015] The principle of the suction current ratio is to use the suction current of the AT autotransformer on both sides of the fault point to measure the fault point. The suction current on both sides of the fault point must be the value at the same time after the fault. When a short-circuit fault occurs on the line, no matter where the short-circuit point is, the voltages of the T-line and F-line of the substation, AT station, and divisional station will suddenly drop from 27.5KV. The inventor uses this feature to ensure that each distance measurement on the line Synchronization of fault time data collected by the device. The specific implementation method is: the fixed value of the voltage mutation can be set on each device....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com