Movement control method and control system of glass wiping robot
A technology of glass-wiping robot and control method, which is applied in the field of intelligent robots, can solve the problems of heavy workload, high labor intensity, repeated wiping, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing work intensity, high intelligence level, and evenly wiping glass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the mobile control method of the glass-wiping robot specifically includes the following steps:
[0086] Step S100: start the robot;
[0087] Step S115: the robot walks forward;
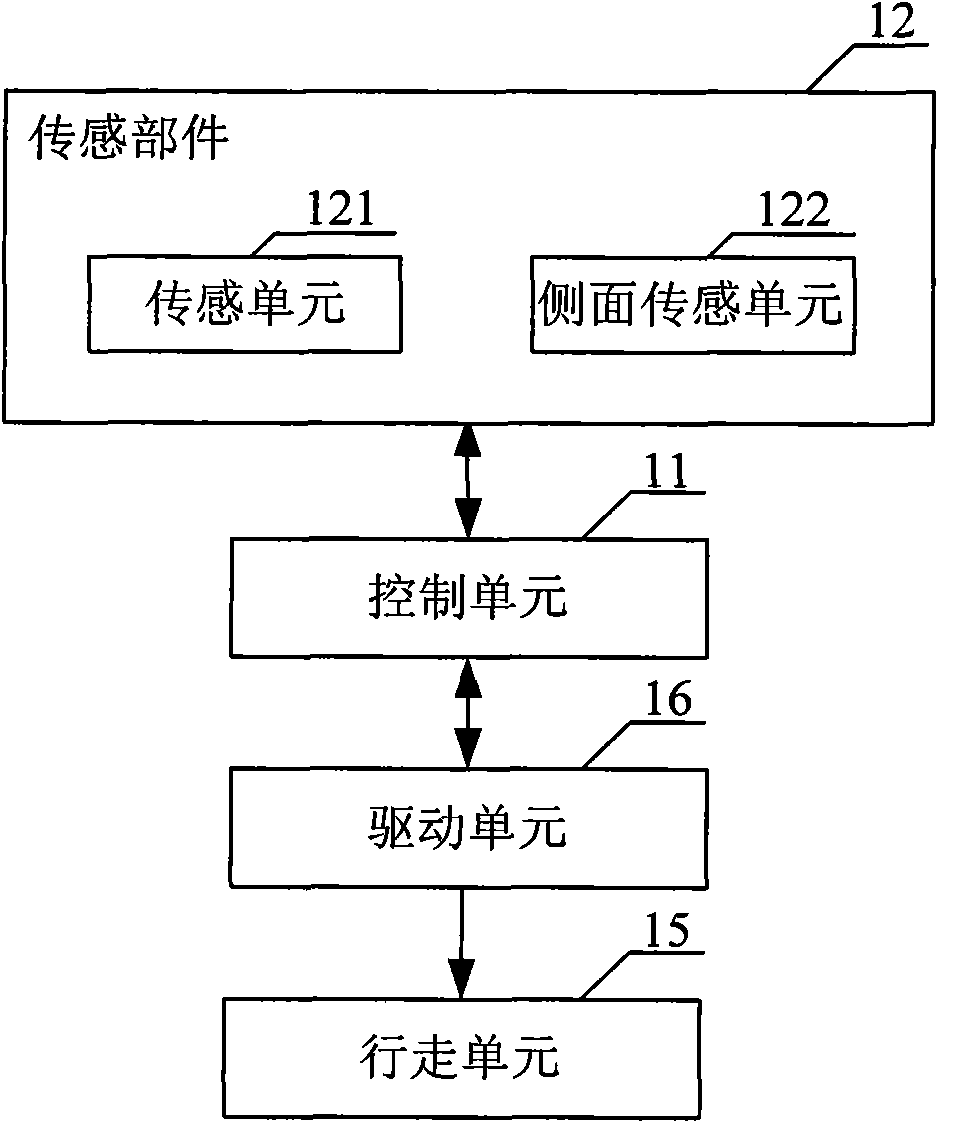
[0088] Step S120: If the control unit 11 of the robot receives the signal from the sensing unit 121 at the front end of the robot, go to step S130; otherwise, go back to step S115;
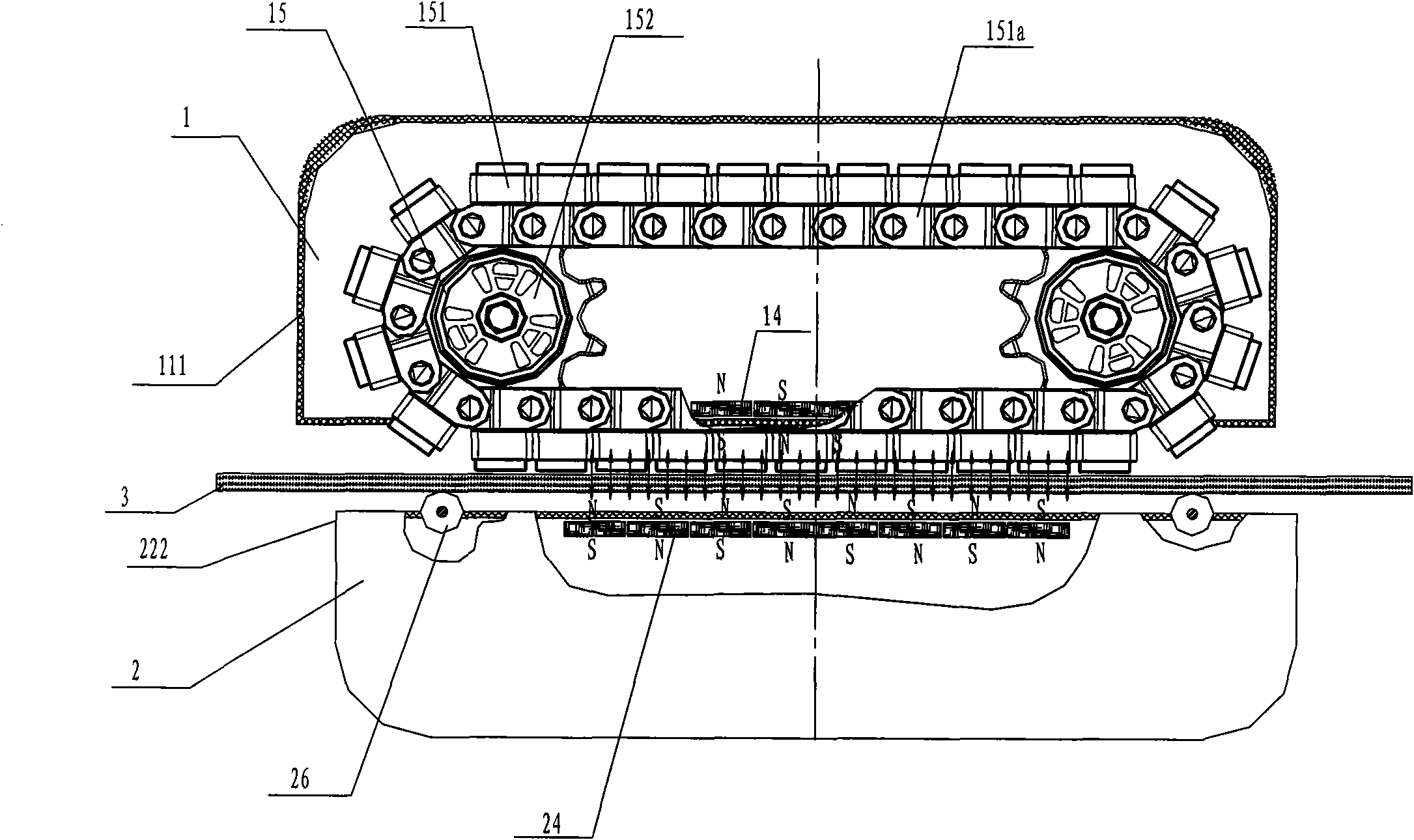
[0089] Step S130: the walking unit 15 of the robot is rotated by 90°;
[0090] Step S135: the robot walks alongside;
[0091] Step S140: If the control unit 11 receives the signal from the sensing unit 121 at the front end of the robot, proceed to step S146; Step S146: the robot drives the walking unit 15 to rotate through the differential operation of the two drive motors in the drive unit 16, and after adjusting the attitude, the robot Basically parallel to the running route of step S135 and separated by a certain distance; otherwise, return to step S135.
[0092] Step S152: the r...
Embodiment 2
[0098] Such as Figure 5 As shown, on the basis of embodiment 1, the control method of embodiment 2 further includes the following steps.
[0099] The following steps are also included between step S100 and step S115:
[0100] Step S105: the acceleration sensor inside the robot adjusts the position of the robot, and corrects the positional deviation of the robot;
[0101] Step S110: the control unit 11 receives the signal from the acceleration sensor, if it judges that the robot is in an ideal state, go to step S115; otherwise, go back to step S105.
[0102] Step S121: The control unit 11 receives the signal from the sensor unit 121 at the front end. If the control unit 11 judges that the robot is in the opposite state, proceed to step S130; otherwise, proceed to step S122; where the opposite state is that the control unit receives the signal from the front end of the robot at the same time. The signals of the sensors on the left and right sides of the
[0103] Step S122: t...
Embodiment 3
[0117] Such as Figure 6 As shown, on the basis of embodiment 2, the control method of embodiment 3 further includes the following steps.
[0118] The following specific steps are also included between step S120 and step S130:
[0119] Step S123: the two driving motors in the driving unit 15 rotate in reverse, driving the traveling unit 15 to move;
[0120] Step S124: the robot walks forward;
[0121] Step S125: If the control unit 11 receives a signal from the sensing unit 121 at the front end of the robot, go to step S130; otherwise, go back to step S124.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com