Method and device for data processing of JAVA card
A data processing and memory technology, applied in the field of smart cards, to achieve the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
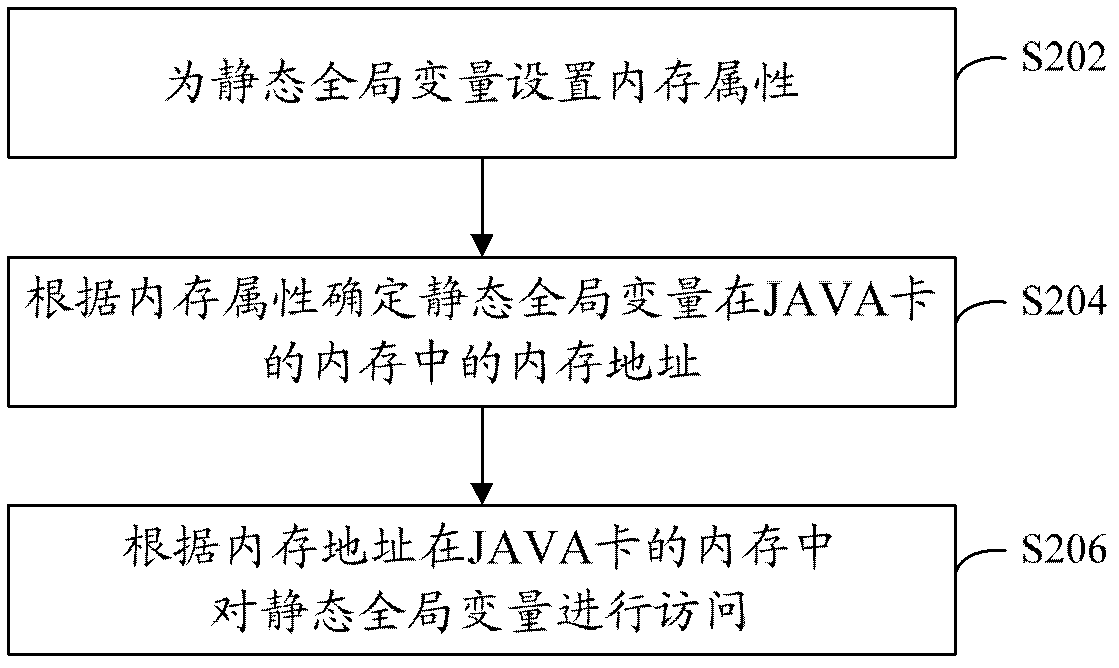
[0031] Reference figure 2 , Shows a flowchart of the steps of a JAVA card data processing method according to the first embodiment of the application.
[0032] The data processing method of the JAVA card of this embodiment is used to access static global variables in the memory, and includes the following steps:
[0033] Step S202: Set memory attributes for static global variables.
[0034] Wherein, the memory attribute is used to instruct the static global variable to be processed corresponding to the memory attribute in the internal memory of the JAVA card.
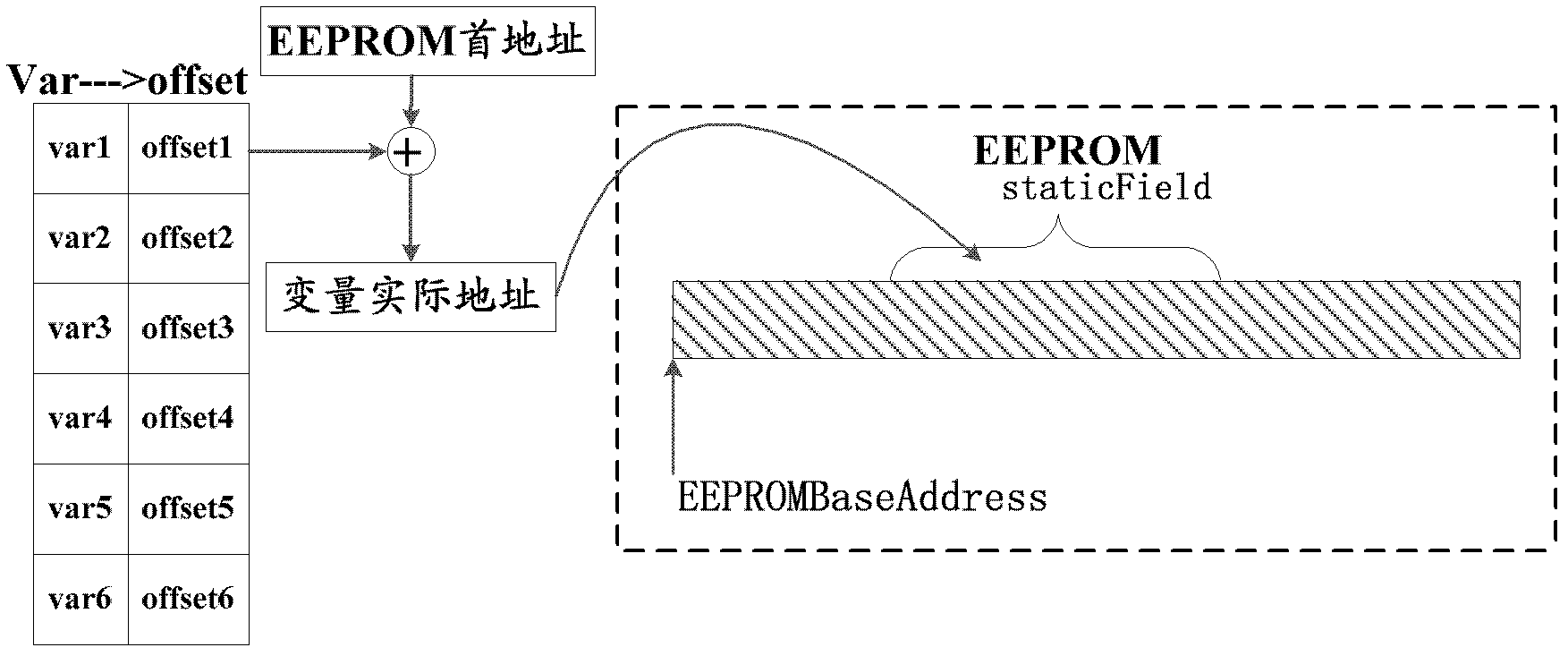
[0035] In this step, for those static global variables that do not need to be stored for a long time or permanently, set the memory attributes for them to indicate that the processing (such as reading, writing, deleting, modifying, etc.) is performed in the memory, no more Access EEPROM many times and repeatedly.
[0036] Step S204: Determine the memory address of the static global variable in the memory of the JAVA card accord...
Embodiment 2
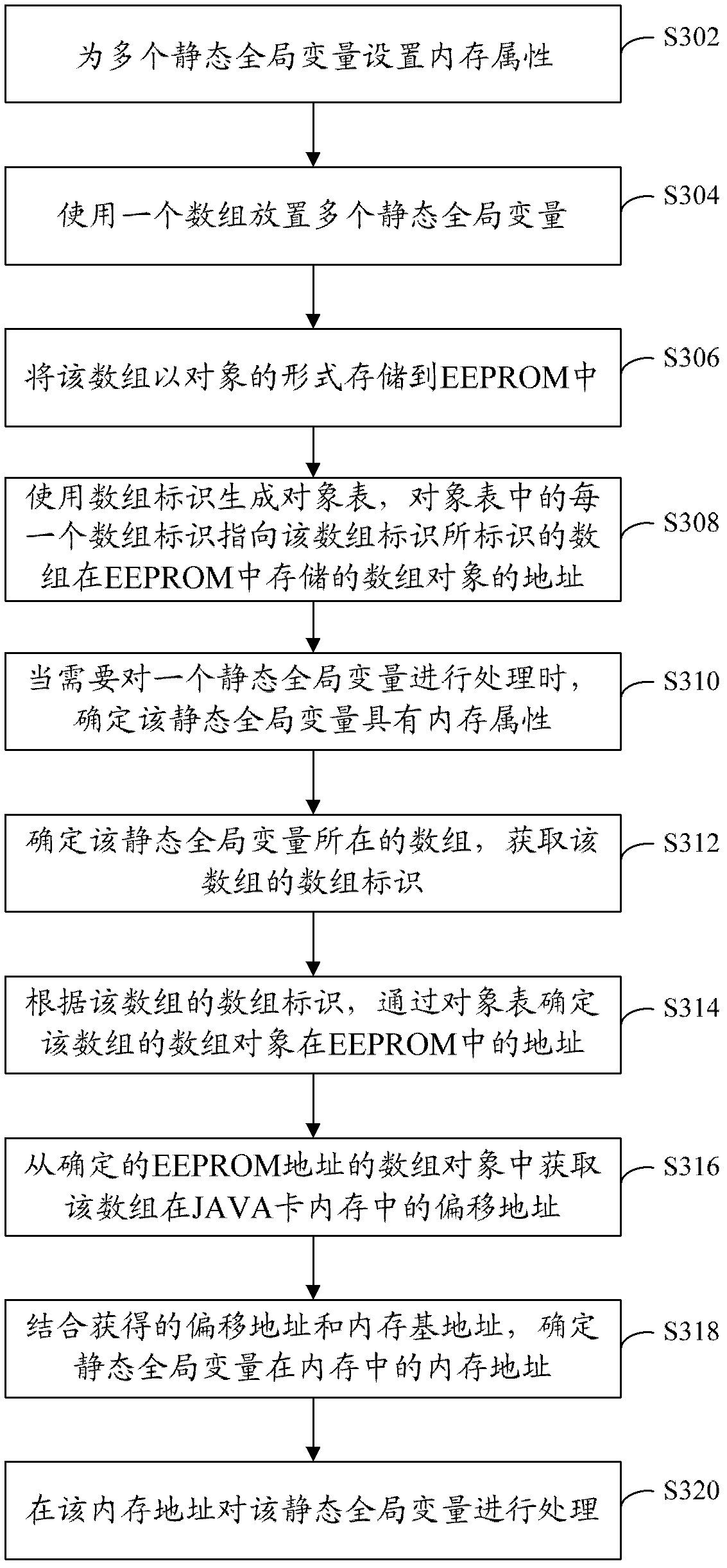
[0041] Reference image 3 , Shows a step flow chart of a JAVA card data processing method according to the second embodiment of the present application.
[0042] The data processing method of the JAVA card of this embodiment is used to access static global variables in the memory, and includes the following steps:
[0043] Step S302: Set memory attributes for multiple static global variables.
[0044] Step S304: Use an array to place multiple static global variables.
[0045] The array has an array identifier, such as an array ID.
[0046] It should be noted that when there are many static global variables, multiple arrays can be used, and each array has an array identifier. Preferably, a temporary array is used, which can meet actual needs without occupying space for a long time.
[0047] Step S306: Store the array in the EEPROM in the form of an object.
[0048] Among them, the array object stores the offset address of each static global variable in the array in the memory of the JAVA ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Reference Figure 5 , Shows a flow chart of the steps of a JAVA card data processing method according to the third embodiment of the application.
[0064] This embodiment takes specific JAVA development as an example to illustrate the data processing method of a JAVA card, including the following steps:
[0065] Step S502: Set memory attributes for static global variables.
[0066] First, add an annotation attribute (memory attribute) to the field (field, which is a field in the form of a static global variable). The value of the attribute is COD (clear_on_deselect) or COR (clear_on_reset). The COD or COR attribute makes the COD value or COR value appear in the annotation attribute of the declared field when the JAVA file is generated.
[0067] Generally, in a JAVA file, an attribute is represented by an attribute_info (attribute information) structure, which is as follows:
[0068]
[0069] When setting the memory attribute, that is, the annotation attribute, you can add a Runt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com