Embedded real-time scheduling system of wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and real-time scheduling technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as limiting the application range of WSN, increasing system development costs, and not having an independent OS layer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
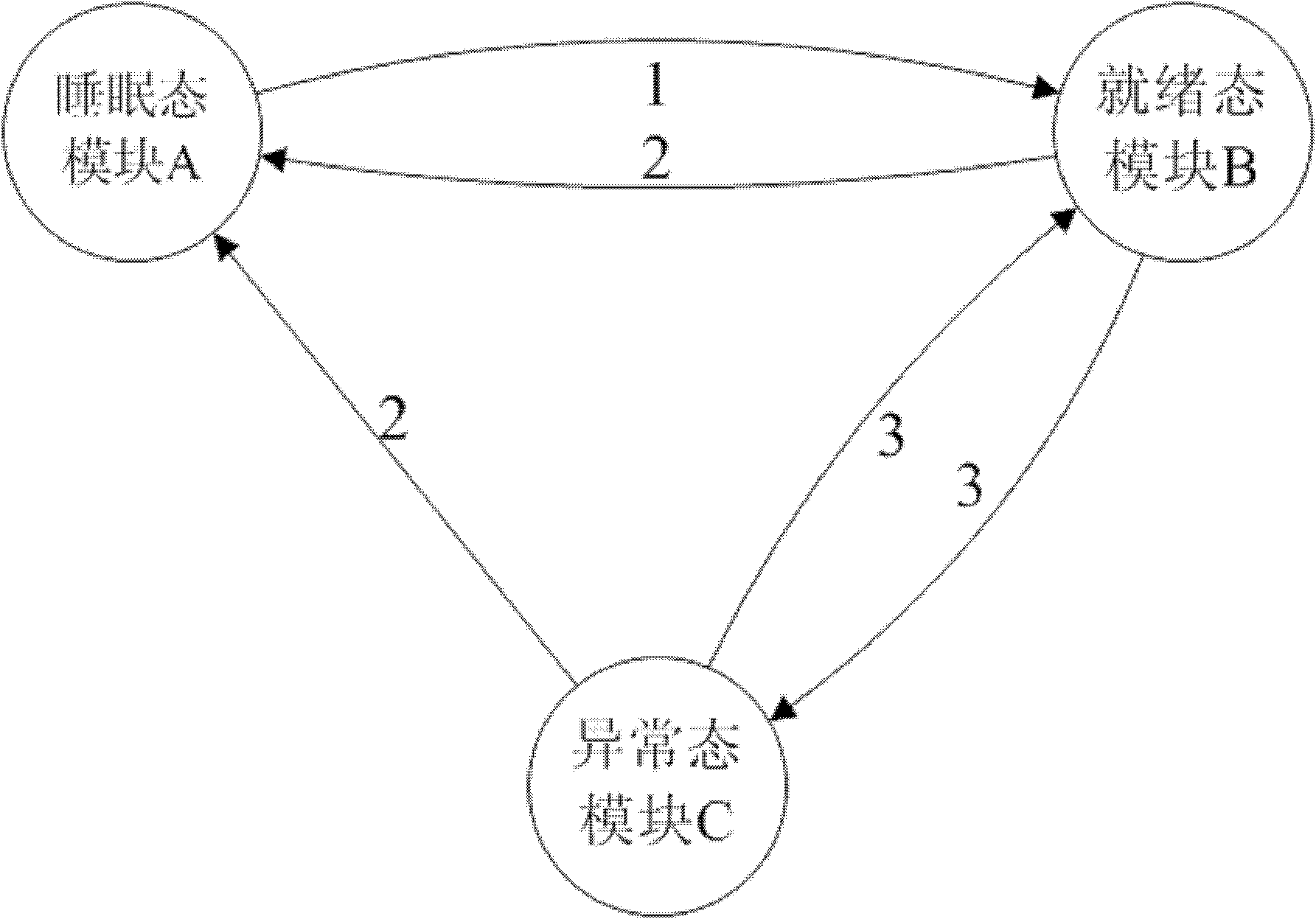
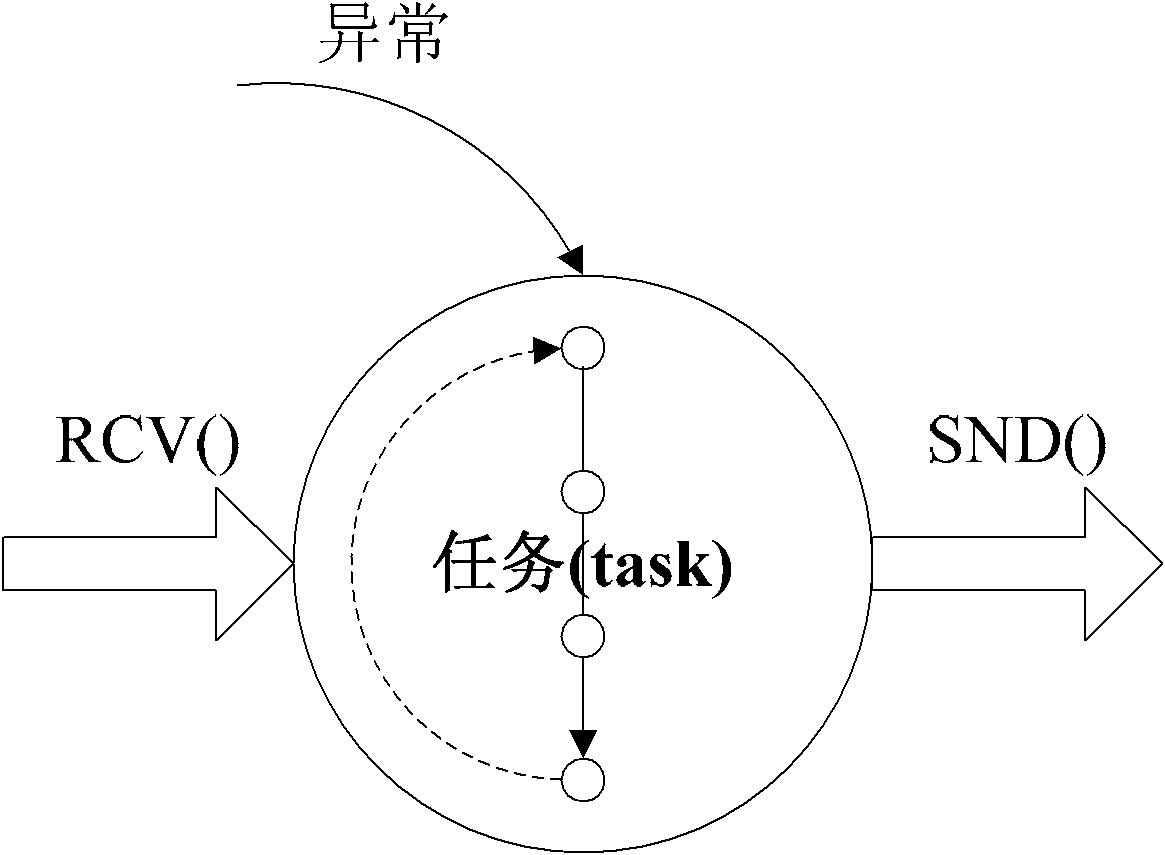
[0026] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 and figure 2 Describe this embodiment, this embodiment includes a state module and a state transition module, the state module includes a sleep state module A, a ready state module B, an abnormal state module C and a suspension state module D; the state transfer module includes an activation module 1, a revocation module 2. Scheduling module 3, suspend module 4 and wake-up module 5;
[0027] The activation module 1 is used to activate and transfer the tasks in the sleep state module A to the ready state module B, that is, it is called to activate a sleep state task. When this task is assigned a specific task, the sleep state of the task changes is ready;
[0028] Undo module 2 is used to transfer the end task in the ready state module B to the sleep state module A, and is also used to transfer the abnormal task in the abnormal state module C to the sleep state module A, and is also used to transfer the suspended stat...
specific Embodiment approach 2
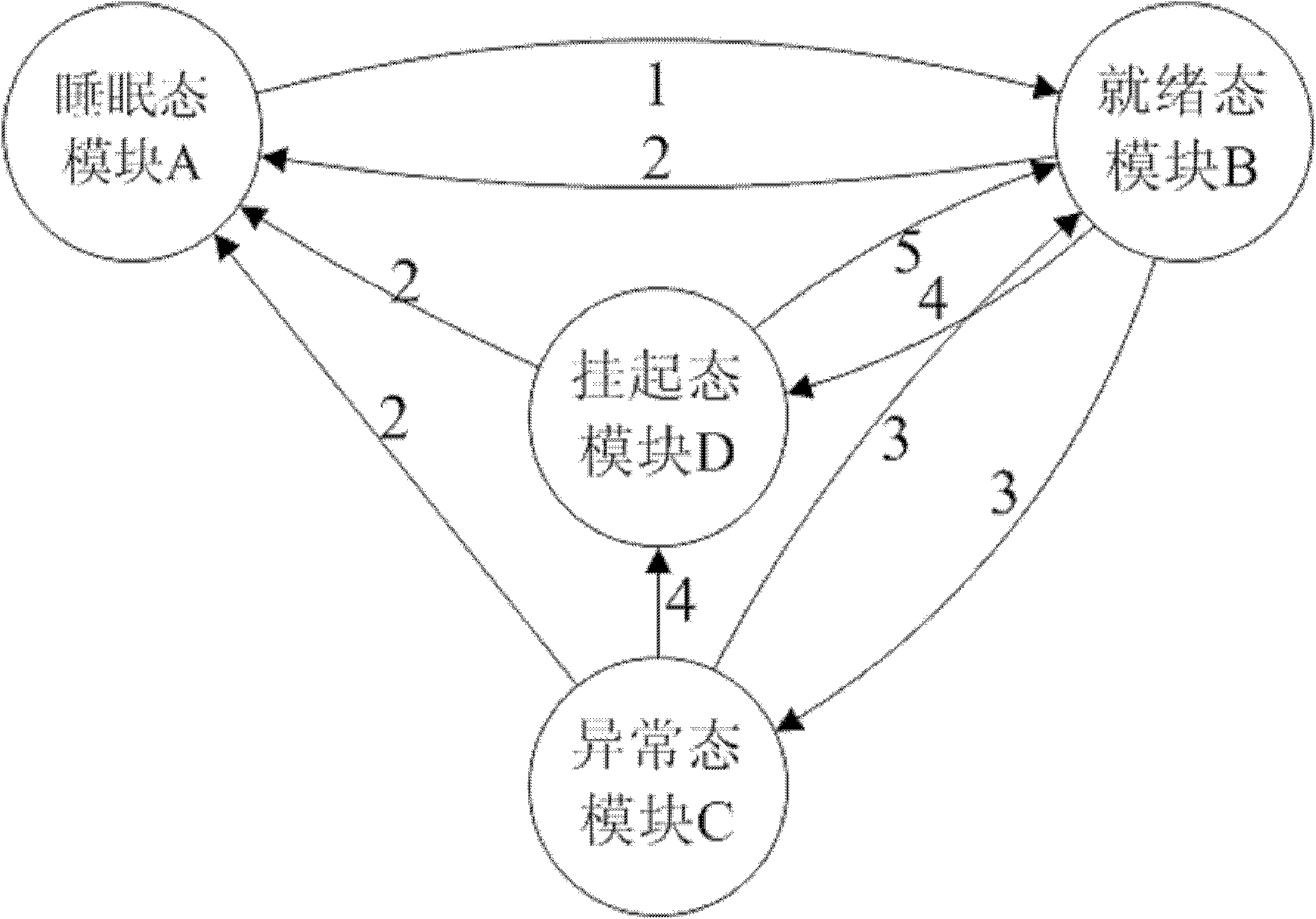
[0036] Specific implementation mode two: combination image 3 and Figure 4 Describe this implementation mode. The difference between this implementation mode and the specific implementation mode is that the tasks executed in the modules include periodic tasks and priority tasks;
[0037] Periodic tasks are used to acquire sensor signals (such as ECG, images, body temperature, etc.) or control actuator signals; periodic tasks can be interrupted at fixed time intervals; periodic tasks have very short execution time and deterministic Response time, while having the highest priority variable (10); periodic tasks are interruptible and non-preemptive;
[0038] When the executed task is a periodic task, the sleep state module A, the ready state module B, the abnormal state module C, the activation module 1, the revocation module 2 and the scheduling module 3 are used for scheduling;
[0039] Priority tasks, for time-bound applications. Priority tasks can be interrupted at variabl...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0045] Specific implementation mode 3: The difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode 2 is that the priority of a unit will determine its execution probability in the system. When multiple units need to run at the same time, only a reasonable allocation of priority can Ensure that the system can complete all or as many tasks as possible before the deadline of each unit, ensure that important tasks are executed first, and use equipment resources as much as possible without affecting important tasks. Priority setting:
[0046] According to the time label set τ of the unit object of the priority task, the priority of the unit object of the priority task is set by using the method of combining static setting and dynamic adjustment,
[0047] In the unit release initialization phase, the task priority will be statically set based on the absolute deadline of the task, following the principle of 'EDF (earliest-deadline-first)', that is, 'the task obje...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com