Pilot protection method based on signal distance and n-type circuit model
A line model and longitudinal protection technology, applied in the direction of fault location, etc., can solve the problems of reliability dependence of criterion, poor setting of setting value, incorrect action of protection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
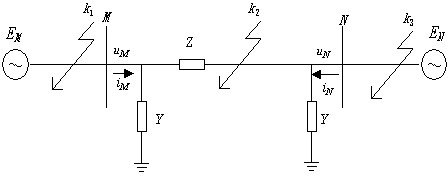
[0046] Embodiment 1: Simulation system such as figure 1 As shown, the transmission line M-N adopts the J.Marti frequency-dependent line model, and the total length of the line is 150km. The total capacitance of the line α-mode is 2.1324e-6F, the line α-mode resistance R=2.8143e-005Ω / m, the line α-mode capacitance C= 1.4215e-05uF / m, the line α-mode inductance L=8.0223e-007 H / m . A single-phase ground fault occurs outside the M-N reverse zone of the line, and the fault location is 40km away from the M terminal, such as figure 1 middle k 1 , Transition resistance 100 ohms.
[0047] When the transmission line fails, the simulated sampling frequency is set to 20kHz, and within a short time window of 3ms, the voltages at points M and N at the protective installations at both ends of the transmission line are measured u M 、u N and current i M 、i N , by analyzing the concentrated parameter Π-type equivalent circuit of the transmission line, according to Kirchhoff's current...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2: Simulation system such as figure 1 As shown, the transmission line M-N adopts the J.Marti frequency-dependent line model, and the line parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1. A phase-to-ground fault occurs in the M-N area of the line, and the fault location is 10km away from the M terminal. figure 1 middle k 2 , Transition resistance 10 ohms.
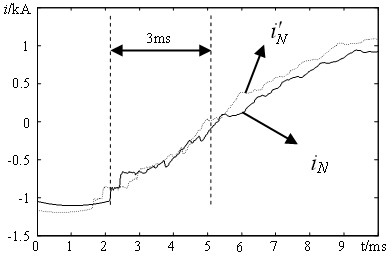
[0060] After the transmission line fails, take the simulation sampling frequency as 20kHz, and within the short time window of 3ms, follow the same method as in Embodiment 1 to simulate and calculate the end of the transmission line ( N side) current . Current measured at point N at the end of the line i N with analog current waveform like image 3 shown.
[0061] Take the tuning factor k a =0.6, set the setting value is 0.35. After calculation, within the time window of 3ms, the analog current and measured current i N Mutual distance =0.986,
[0062] > , it is judged as a fau...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3: simulation system such as figure 1 As shown, the transmission line M-N adopts the J.Marti frequency-dependent line model, and the line parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1. A phase-to-earth fault occurs outside the forward direction of line M-N, and the fault location is 70km away from the N terminal. figure 1 middle k 3 , Transition resistance 100 ohms.
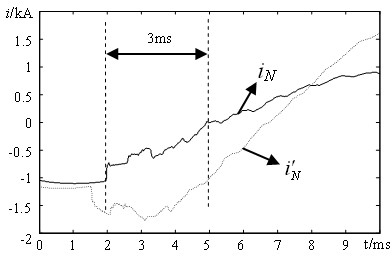
[0064] After the transmission line fails, the simulation sampling frequency is set to 20kHz, and within a short time window of 3 ms, the current at the end (N side) of the transmission line is simulated and calculated according to the same method as in Example 1 .
[0065] Take the tuning factor k a =0.6, set the setting value is 0.35. After calculation, within the time window of 3ms, the analog current and measured current i N Mutual distance =0.145, ≤ , it is judged as an out-of-area fault of the transmission line.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com