Data truncation method in radar signal processor
A radar signal and processor technology, applied in the field of data interception, can solve the problems of low degree of automation, low precision, slow response time, etc., and achieve the effect of high degree of automation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
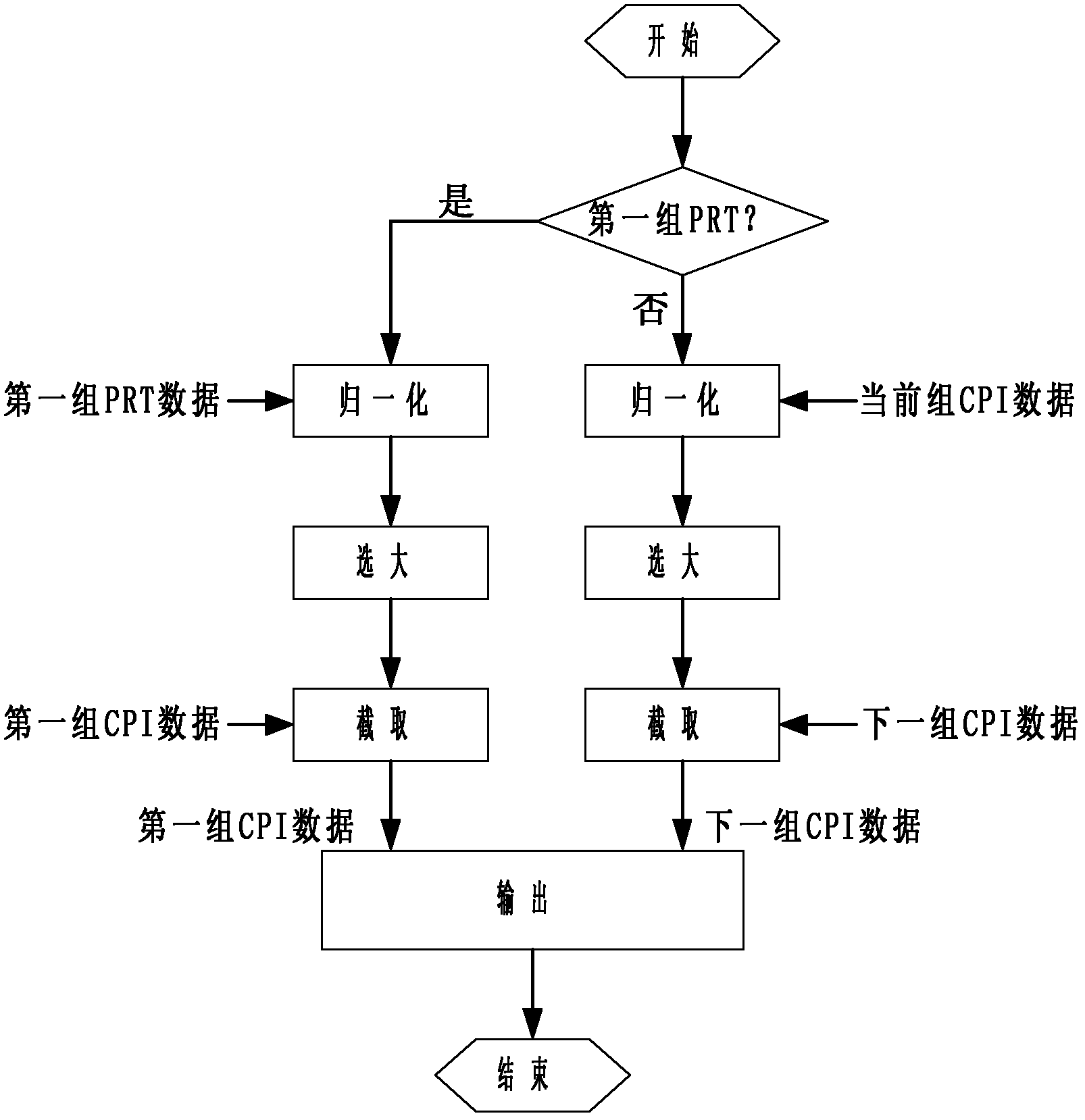
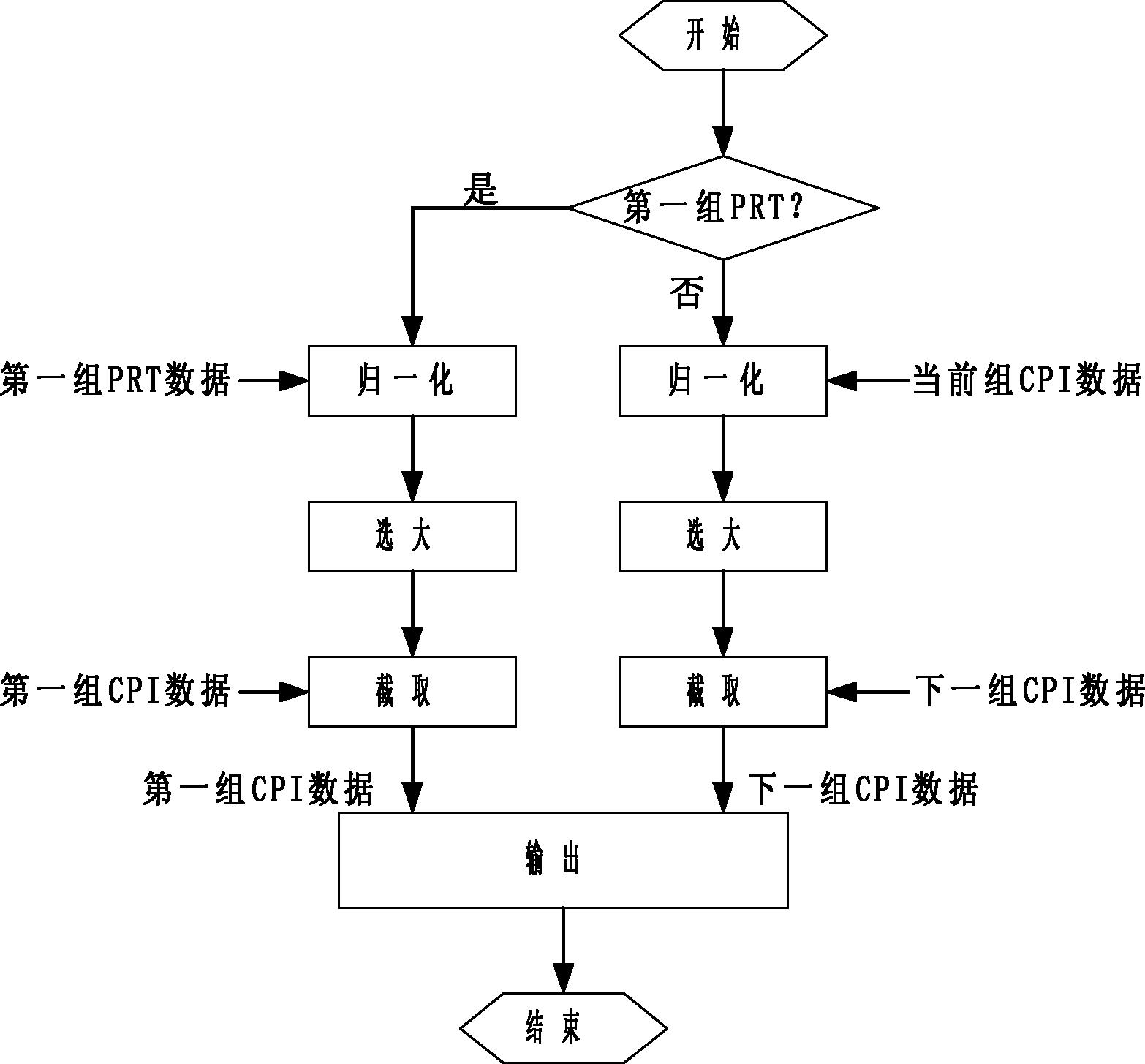
[0026] In Embodiment 1, the 42-bit input data D is truncated into 16-bit output data.
[0027] Step 1: Normalize the input data D. If the input data D is negative, the normalized data T is equal to the opposite of the input data D. If the input data D is positive or zero, then the normalized The data T is equal to the input data D itself, where the input data D is 42-bit data.
[0028] Step 2: Perform a logical OR operation on the normalized data T:
[0029] If the normalized data T belongs to the first group of pulse repetition period PRT, perform a logical OR operation on all the data in the pulse repetition period PRT to obtain the logical OR result B1 of all the data in the pulse repetition period PRT;
[0030] If the normalized data T belongs to the data in the coherent repetition interval CPI, that is, the data in the 64 sets of pulse repetition period PRT, the data in the coherent repetition interval CPI does not include the data in the first set of pulse repetition period PRT ...
Embodiment 2
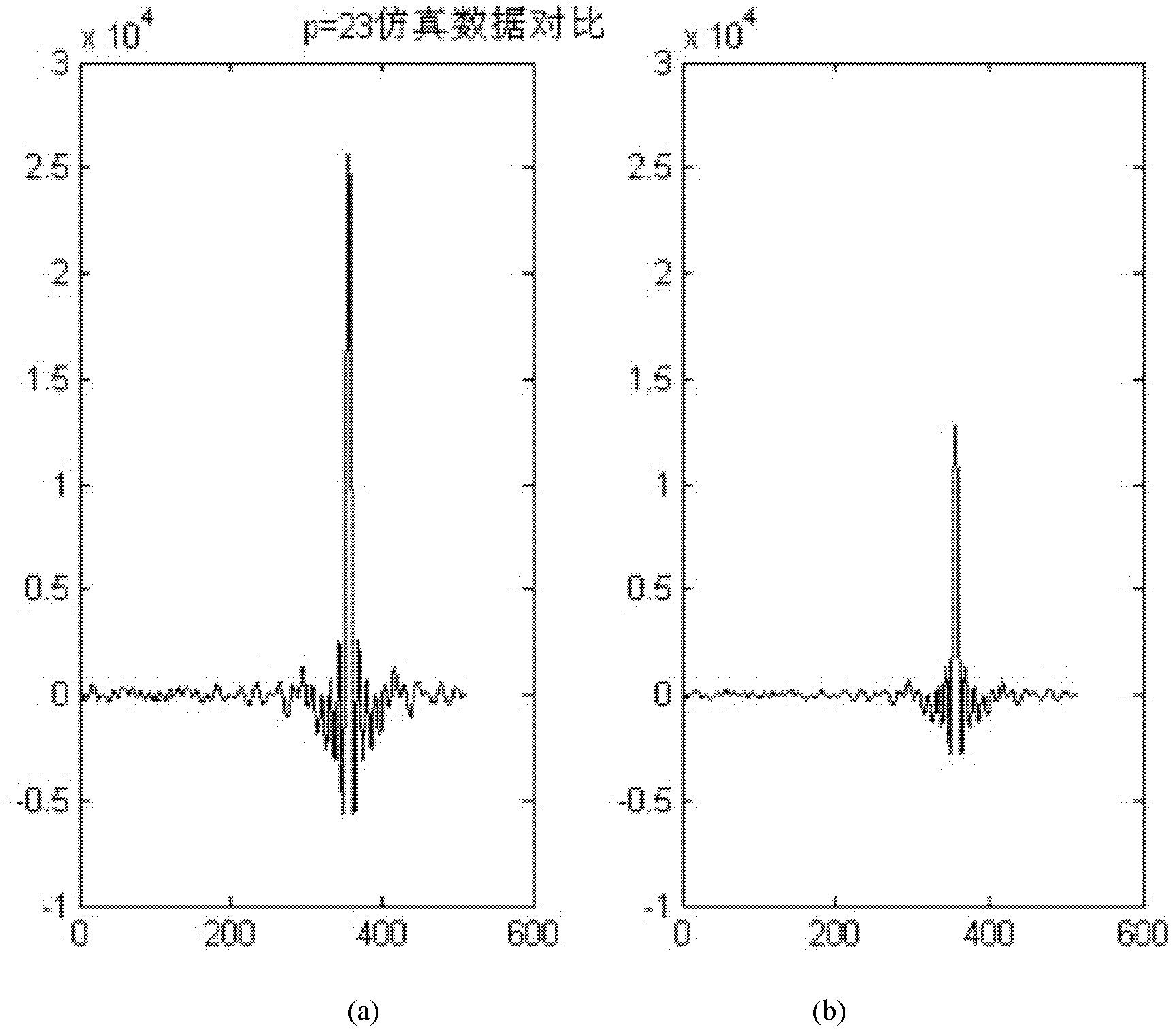
[0043] In Embodiment 2, the 26-bit input data D is truncated into 16-bit output data.
[0044] Step 1. Normalize the input data D. If the input data D is negative, the normalized data T is equal to the opposite of the input data D. If the input data D is positive or zero, then the normalized The data T is equal to the input data D itself, where the input data D is 26-bit data;
[0045] Step 2. Perform a logical OR operation on the normalized data T:
[0046] If the normalized data T belongs to the first group of pulse repetition period PRT, perform a logical OR operation on all the data in the pulse repetition period PRT to obtain the logical OR result B1 of all the data in the pulse repetition period PRT;
[0047] If the normalized data T belongs to the data in the coherent repetition interval CPI, that is, the data in the 64 sets of pulse repetition period PRT, the data in the coherent repetition interval CPI does not include the data in the first set of pulse repetition period PRT ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com