A mobility management method, gateway node and core network
A management method and gateway node technology, applied in the field of gateway nodes and core networks, and mobility management methods, can solve problems such as circuitous routes, inability to access external networks nearby, and long delays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
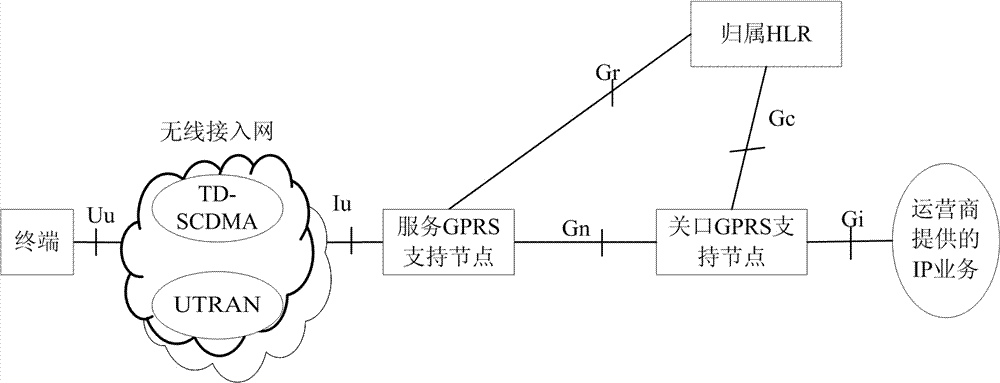
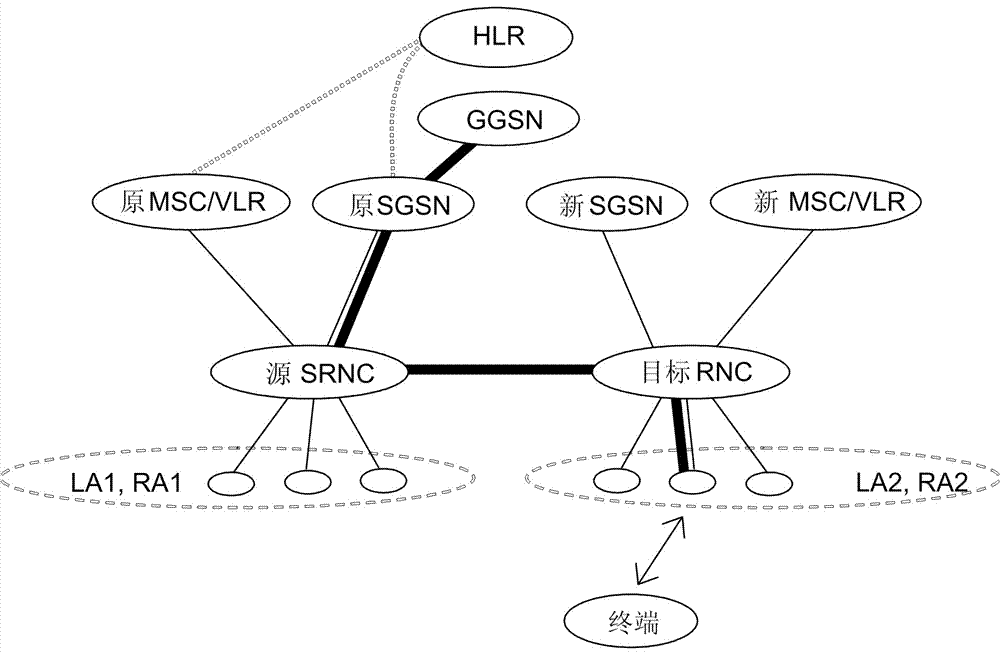
[0272] This embodiment is based on Figure 5 The described WCDMA core network architecture describes the relocation process of the serving SRNS without an anchor GGSN. There is no data loss during the handover process. After the handover is completed, the data packets of the MS are routed through the new GGSN to reduce routing detours.
[0273] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the flow of the service SRNS relocation process in this embodiment includes:
[0274] Steps 701-711: Same as steps 301-311 of the existing serving SRNS relocation process.
[0275] Step 712. The new SGSN signals the original SGSN that the SRNS relocation process has been completed by sending a Forward Relocation Complete message. Step 712 and step 713 can occur simultaneously. Step 712 is consistent with step 312 of the existing process.
[0276] Step 713a The new SGSN sends an update PDP context request message (new SGSN address, SGSN TEID (tunnel endpoint identifier), negotiated QoS, etc.) to the origin...
Embodiment 2
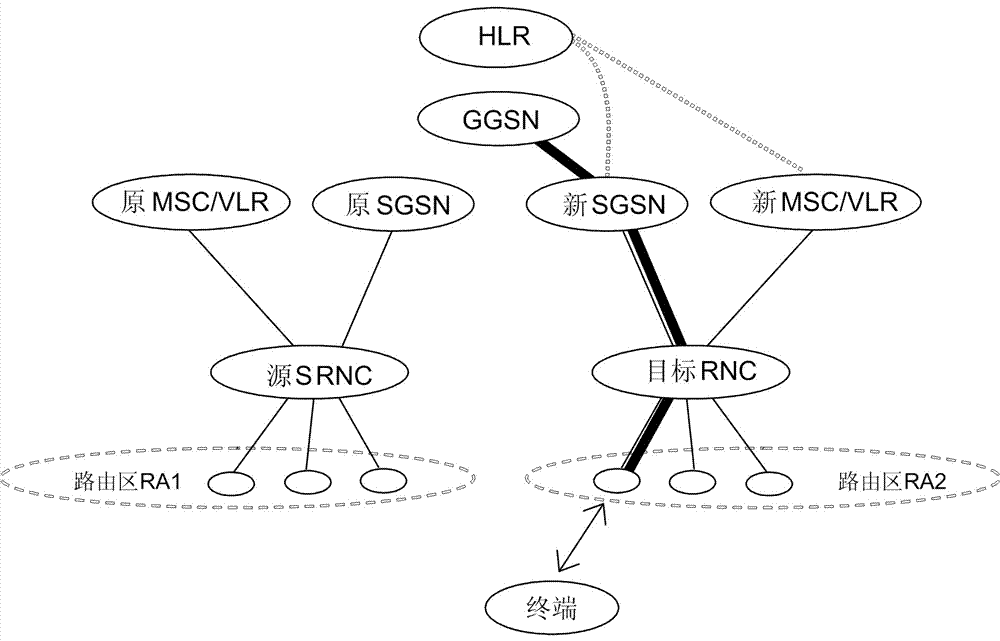
[0306] This embodiment is based on Figure 5 Describe the WCDMA core network architecture, and describe the joint hard handover and SRNS relocation process. After the joint hard handover and SRNS relocation process is completed, the MS associates to the new SGSN and new GGSN.
[0307] Step 801: The source RNC initiates joint hard handover and SRNS relocation of the PS domain. Same as the existing joint hard handover and SRNS relocation process.
[0308] Step 802: the source RNC initiates a relocation preparation process by sending a relocation request (Relocation Required) message to the original SGSN (OldSGSN); the relocation type, reason, source cell ID, target cell ID, source RNC to target RNC transparent container and other content. Different from step 702, here the relocation type is set to "involving UE". Same as the existing joint hard handover and SRNS relocation process.
[0309] Steps 803-807: similar to steps 703-707, same as the existing joint hard handover and...
Embodiment 3
[0328] This embodiment is based on Figure 5 The described WCDMA core network architecture describes the joint cell / URA and SRNS relocation process. After the joint cell / URA and SRNS relocation process is completed, the MS associates with the new SGSN and new GGSN.
[0329] Step 901: the terminal sends a cell update (Cell Update) message to the source RNC, or sends URA Update or Cell Update or GRA Update. Same as the existing joint cell / URA and SRNS relocation process.
[0330] Steps 902-909: similar to steps 702-709 in Embodiment 1. Same as the existing joint cell / URA and SRNS relocation process.
[0331] Step 910: The target RNC sends a cell update confirmation (Cell Update Confirm) message to the terminal, or sends a URA Update Confirm or Cell Update Confirm or GRA Update Confirm; the terminal sends a RAN Mobility Information Confirm message (RAN Mobility Information Confirm) to the target RNC . Same as the existing joint cell / URA and SRNS relocation process.
[0332] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com