Guide-sample-free GC-FID (Gas Chromatograph-Flame Ionization Detector) accurate quantifying method for organic impurities in an organic ester
A GC-FID and organic impurity technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large quantitative errors of organic impurities, and achieve the effect of simple method, improved detection sensitivity, and high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
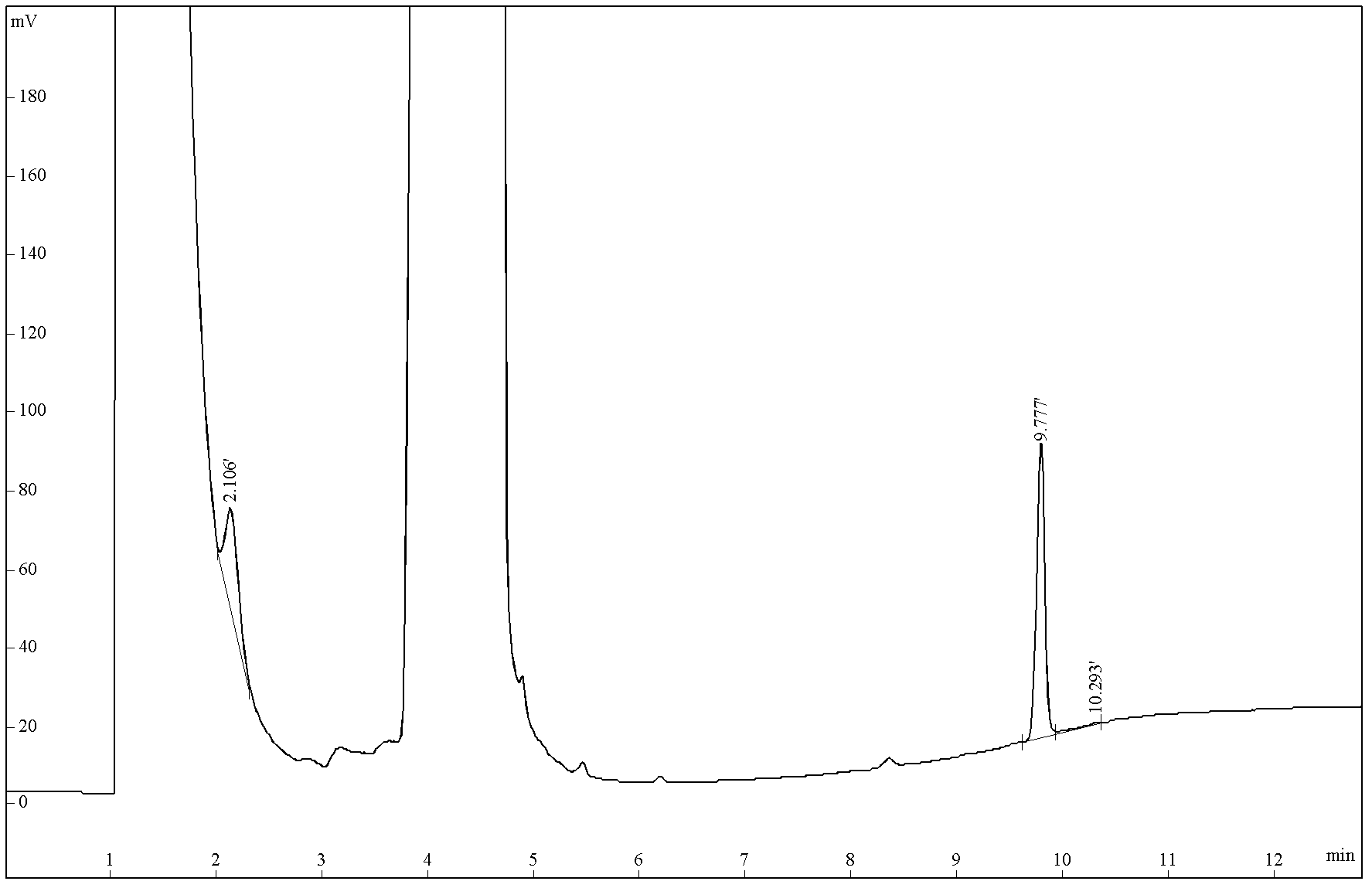
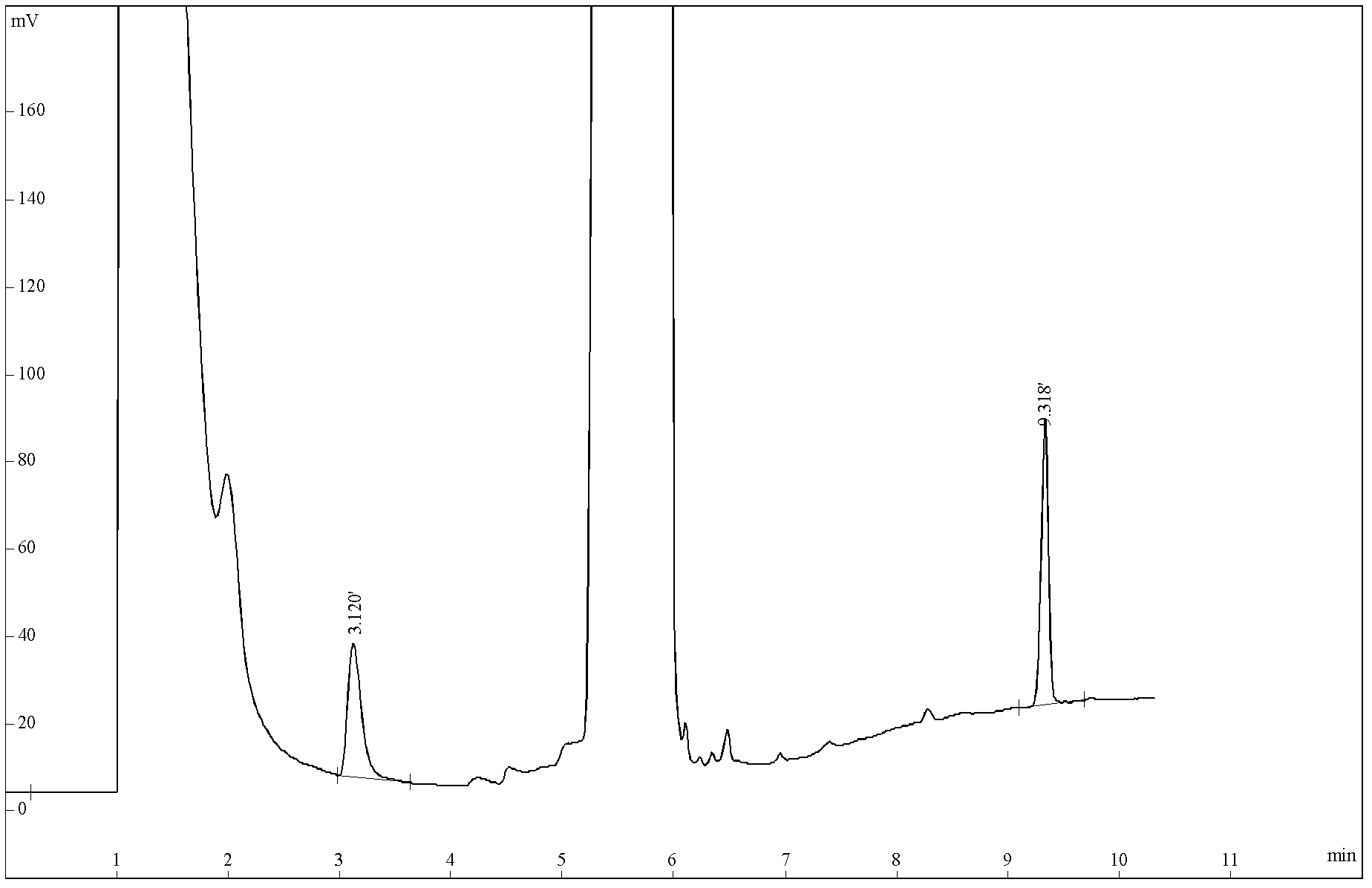
[0044] Embodiment 1: Impurity determination of organic ester analog sample DBP
[0045] In this embodiment, a simulated sample DBP (the impurities are 0.24% DEP and 0.27% DOP) is prepared with known impurity amount, and the impurity is determined by the method of the present invention. It is assumed that there is no corresponding standard sample for the impurity and cannot be valued by external standard method or internal standard method. At the same time, use the area percentage method to determine the value. The detection data of the present invention and the detection data of the area percentage method are compared with the real value.
[0046] 1. Preparation of simulated sample DBP
[0047] Accurately weigh 0.05096g of analytically pure diethyl phthalate (DEP), 0.05564g of dioctyl phthalate (DOP), and 20.72382g of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) and mix them together to prepare DBP The simulated sample, ie the DBP simulated sample contained "impurities" 0.24% DEP and 0.27% DOP....
Embodiment 2
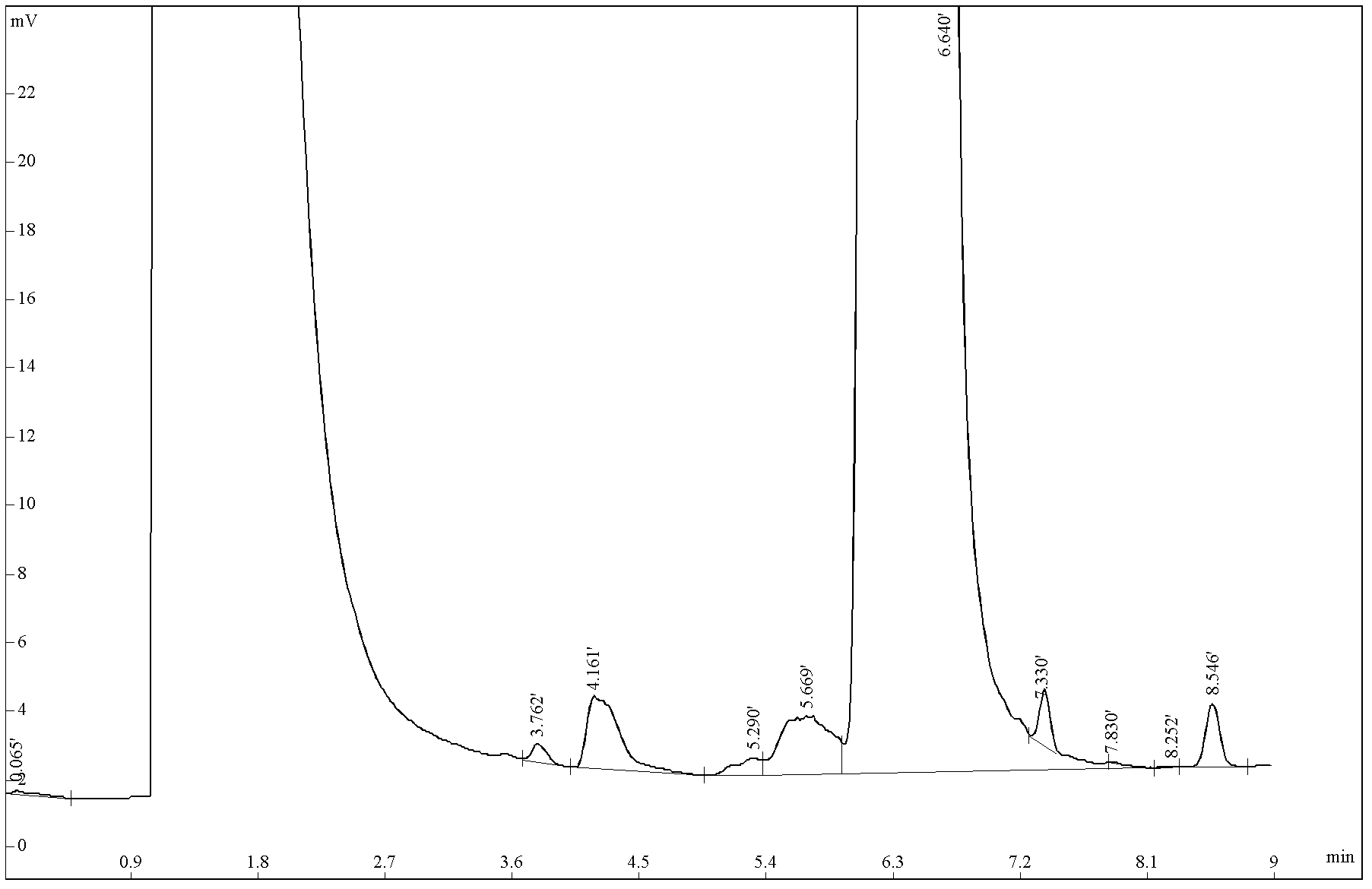
[0068] Embodiment 2: Determination of organic impurities in DBS standard substance candidate
[0069] A certain batch of DBS (dibutyl n-sebacate) samples was purified by vacuum distillation, and the DBS samples with high purity were obtained as standard substance candidates. The impurities in it are detected by GC-MS and combined with the process, they are characterized as butanol, ethyl butyl sebacate, dibutyl azelate, propyl sebacate butyl, stereoisomers of main substances, Butyl amyl sebacate, dibutyl C11 acid, dibutyl C12 acid, a total of 8 impurities. Among them, butanol can be found as a reference substance, which is detected by the conventional GC-FID external standard method. There are no corresponding commercially available reagents or standard samples for the remaining 7 impurities. If these 7 impurities are also valued by external standards, 7 products with a purity ≥ 95% must be specially synthesized, and the cost is too high to be adopted. Because the impurities...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap