Method and protection device for reducing object impulsion
A technology for protecting devices and objects, which is applied in the field of new devices, can solve the problems that water cushions cannot quickly impact and play a role, and achieve the effect of ensuring protection from damage and eliminating rebound
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
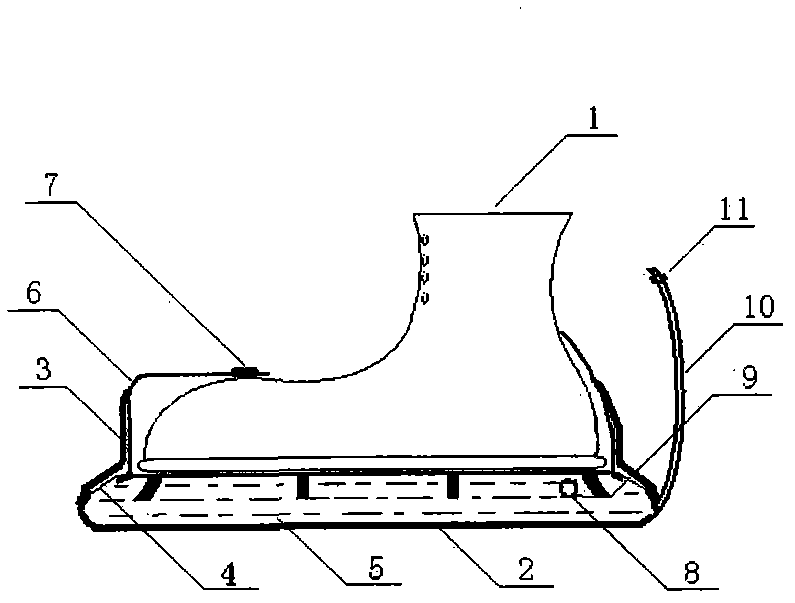
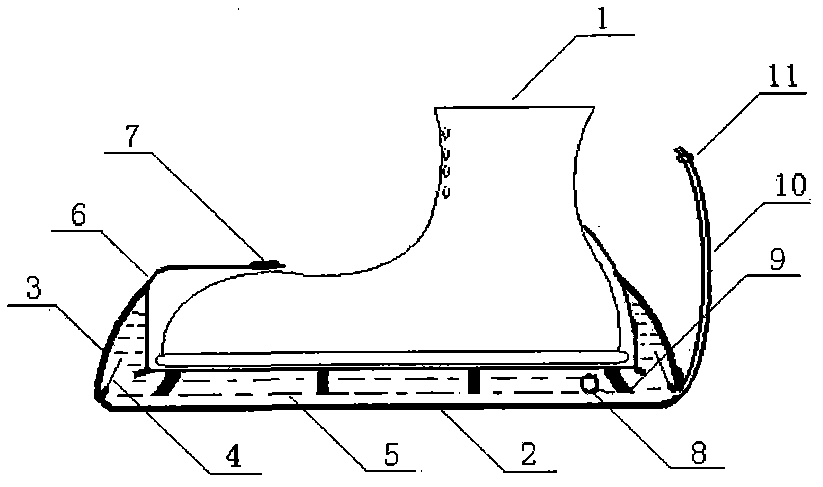
[0023] Such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, it is the multi-purpose airborne soldier shoe cover of the present invention, including shoe 1, main cavity body 2, water 5, fixing frame 6, lock buckle 7, fluid filling port 8, drinking water pipe 10, water valve 11, also includes vacuum Cavity 3, diaphragm 4 and support body 9, the main cavity 2 is set on the sole of the shoe through the fixing frame 6, and is firmly fixed on the shoe 1 by the slidable lock 7. The upper surface of the main cavity 2 is larger than the area of the sole , water 5 is injected into the main cavity 2 through the fluid filling port 8, the lower end of the drinking water pipe 10 communicates with the main cavity 2, and the upper end is equipped with a water valve 11 and is in a free state. The vacuum cavity 3 is located in the main cavity The surroundings and edges of the body 2 are attached to the side of the fixed frame 6 upwards, and 8 diaphragms 4 with a diameter of 1 cm are distributed on the separation ...
Embodiment 2
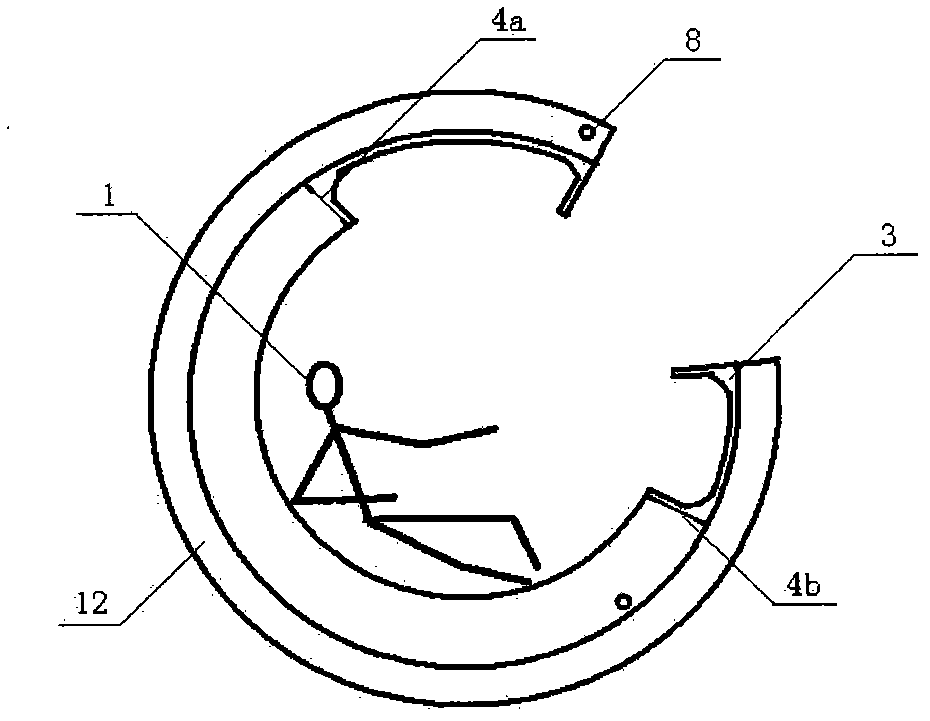
[0026] Such as image 3 , 4 Shown is the landing air cushion protection device for the spacecraft manned return module of the present invention. The fluid in the main cavity 2 of this embodiment is air, and a two-stage diaphragm structure is adopted. The rupture timing of the diaphragm 4 is designed to be when the landing momentum is close to the Protected object 1 (astronaut 1) normal bearing capacity is lower than main chamber 2 before the rebound starts, primary diaphragm 4a ruptures under 50 kg force, and the air in main chamber 3 will quickly enter vacuum chamber 3, and the chamber The increase of the body space and the reduction of the internal pressure of the cavity make the impulse force received by the astronaut 1 decrease with the pressure diffusion of the main cavity 2; and when the impulse force suffered by the astronaut 1 increases to 55 kg again, the secondary diaphragm 4b breaks, and at this moment, the impulse force suffered by astronaut 1 will be reduced agai...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Such as Figure 5 Shown is the combined fluid anti-overload protection device for spacecraft of the present invention, including an astronaut 1, a spherical main chamber 2, a base airbag 12, water 5 and a cover 14, and also includes the vacuum chamber 3, diaphragm 4 and Membrane breaker 13, the base airbag 12 is wrapped on the outside of the spherical main cavity 2, the astronaut 1 sits on the main cavity 2, the astronaut 1 seals the cover 14 from the inside of the main cavity 2, and the component One side of the series of vacuum chambers 3 is set on the inner wall of the main chamber 2, one end of the diaphragm 4 is connected to the inner wall of the main chamber 2, and one end of the membrane breaker 13 is fixed on the main chamber together with one end of the diaphragm 4 2, the other end is aligned with the central position of the diaphragm 4.
[0030] When the spacecraft is flying at high speed in the atmosphere, the astronaut 1 has to bear a large gravitational ac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com