Method of maskless manufacturing of OLED devices
A technology for devices and light-emitting devices, which is applied in the field of maskless manufacturing of OLED devices, can solve the problem of expensive mask processing, and achieve the effects of omitting requirements, small pattern size, and facilitating processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
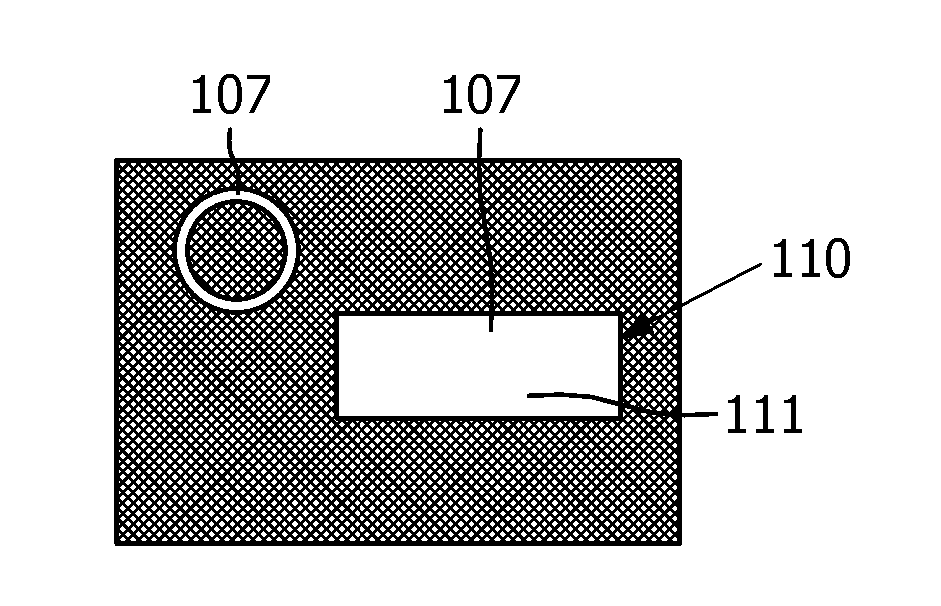
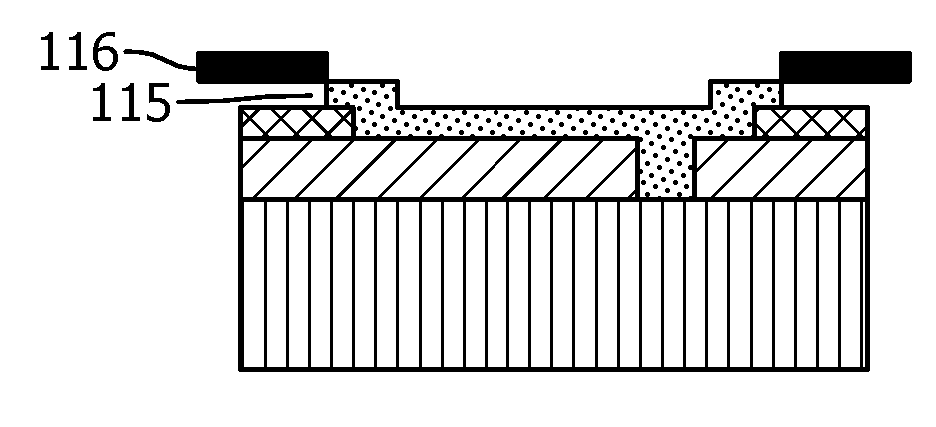
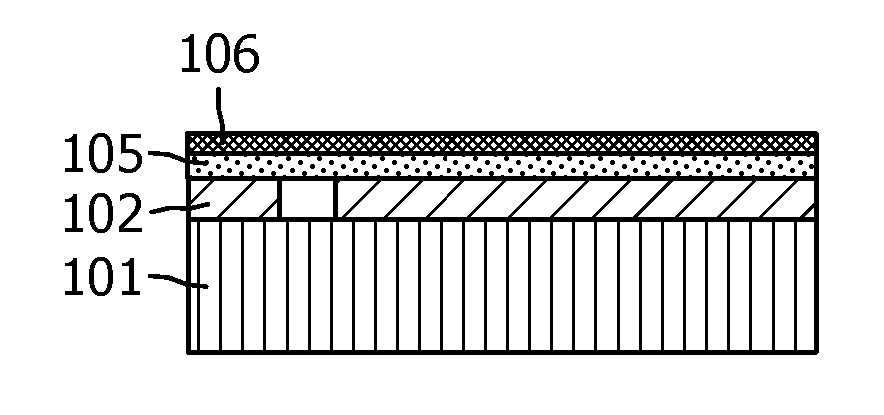
[0062] In FIG. 1 , a process scheme for producing an OLED according to the prior art is shown. In step 1A, a transparent conductor layer 102 is deposited on a carrier substrate 101 in a specific pattern defining the subsequent OLED device structure. Patterning can be done by masking areas not covered by deposition (eg, by sputtering by shadow masking or printing methods). The transparent conductor can be a ZnO, ITO and / or PEDOT / PSS layer. Optional metal lines 113 are deposited on the transparent conductor layer 102 . The patterned structure is filled with optoelectronically active material 105 in step 1B.
[0063] Small molecule optoelectronic active materials are generally deposited by thermal evaporation in vacuum. The deposition of organic material must be limited in such a way that at least the cathode contact 115 is not coated. Usually, the anode contact is also spared from coating, so that a good electrical contact can be obtained later. As can be seen in step 1C, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com