Load balancing method and device
A load balancing and average throughput technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problem of inability to effectively achieve HSDPA load load balancing, and achieve the effect of improving the utilization rate of HSDPA resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] refer to figure 1 , shows a flowchart of steps of a load balancing method according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0016] The load balancing method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0017] Step S102: Obtain the average throughput of a single HSDPA user in each cell among multiple cells that support HSDPA and are co-sited.
[0018] Among them, the average throughput of a single HSDPA user reflects the available resources of the cell. The higher the average throughput of a single HSDPA user, the more resources each user can provide in the cell, and the lower the HSDPA load is correspondingly.
[0019] Step S104: sort the multiple HSDPA-supporting and co-sited cells according to the acquired average throughput of a single HSDPA user in each cell.
[0020] In this step, each cell can be sorted according to the average throughput of the single HSDPA user in each cell and in the order of the average throughput of the single HSDPA user from larg...
Embodiment 2
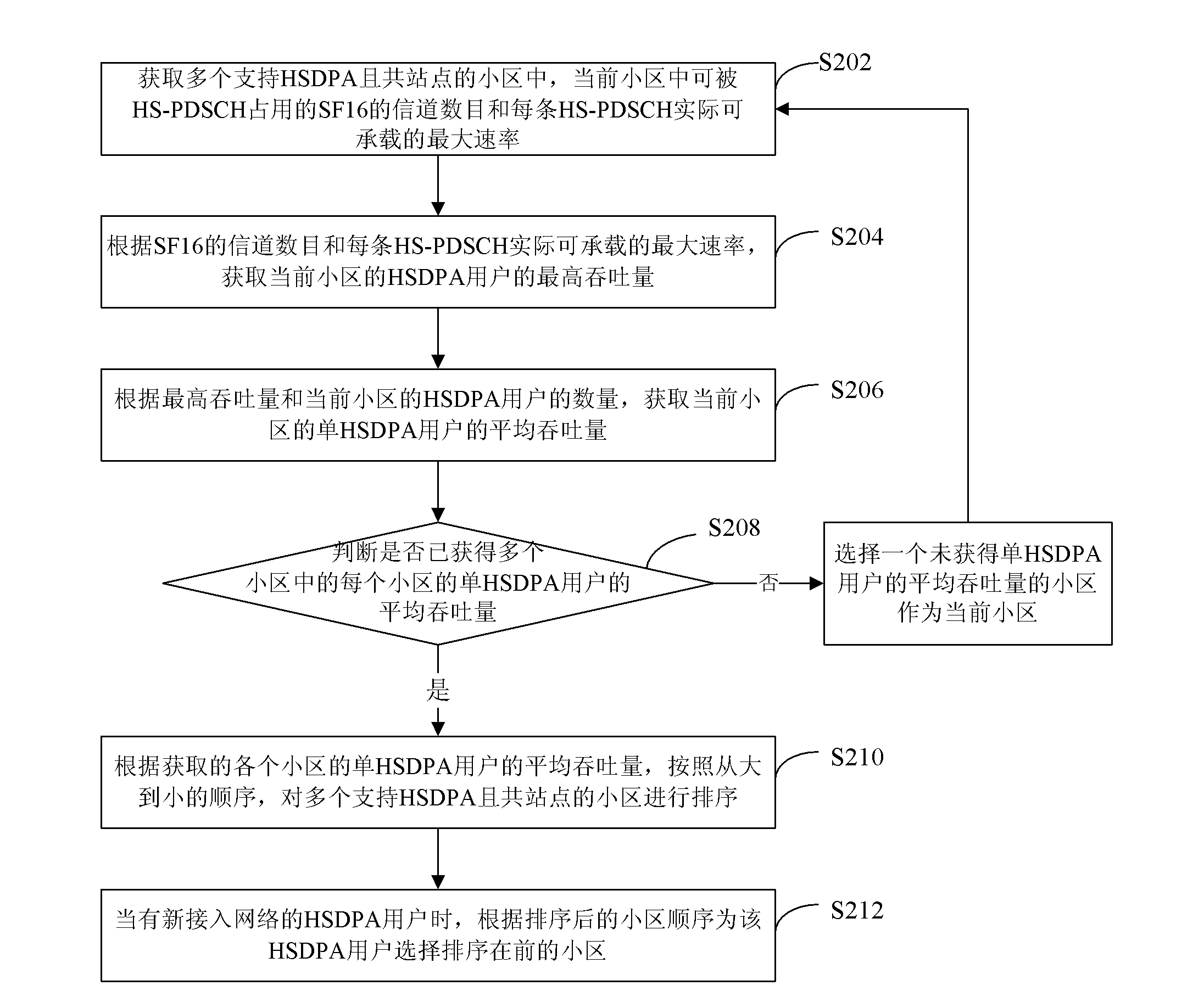
[0025] refer to figure 2 , shows a flowchart of steps of a load balancing method according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0026] The load balancing method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0027] Step S202: Obtain the number of SF16 channels that can be occupied by the HS-PDSCH in the current cell and the actual maximum rate that each HS-PDSCH can carry among multiple cells that support HSDPA and are co-sited.
[0028] Among them, the number of SF16 channels that can be occupied by HS-PDSCH in the current cell is counted as the non-HS-PDSCH occupied code channel, and the set spreading factor SF can be used as the statistical granularity, such as SF128 or SF256, etc. as the statistical granularity. Taking SF128 as the statistical granularity as an example, one SF16 channel is equivalent to occupying 8 SF128 channels. SF128 is the preferred statistical granularity, and the statistical granularity can effectively ensure the accuracy of statistics ...
Embodiment 3
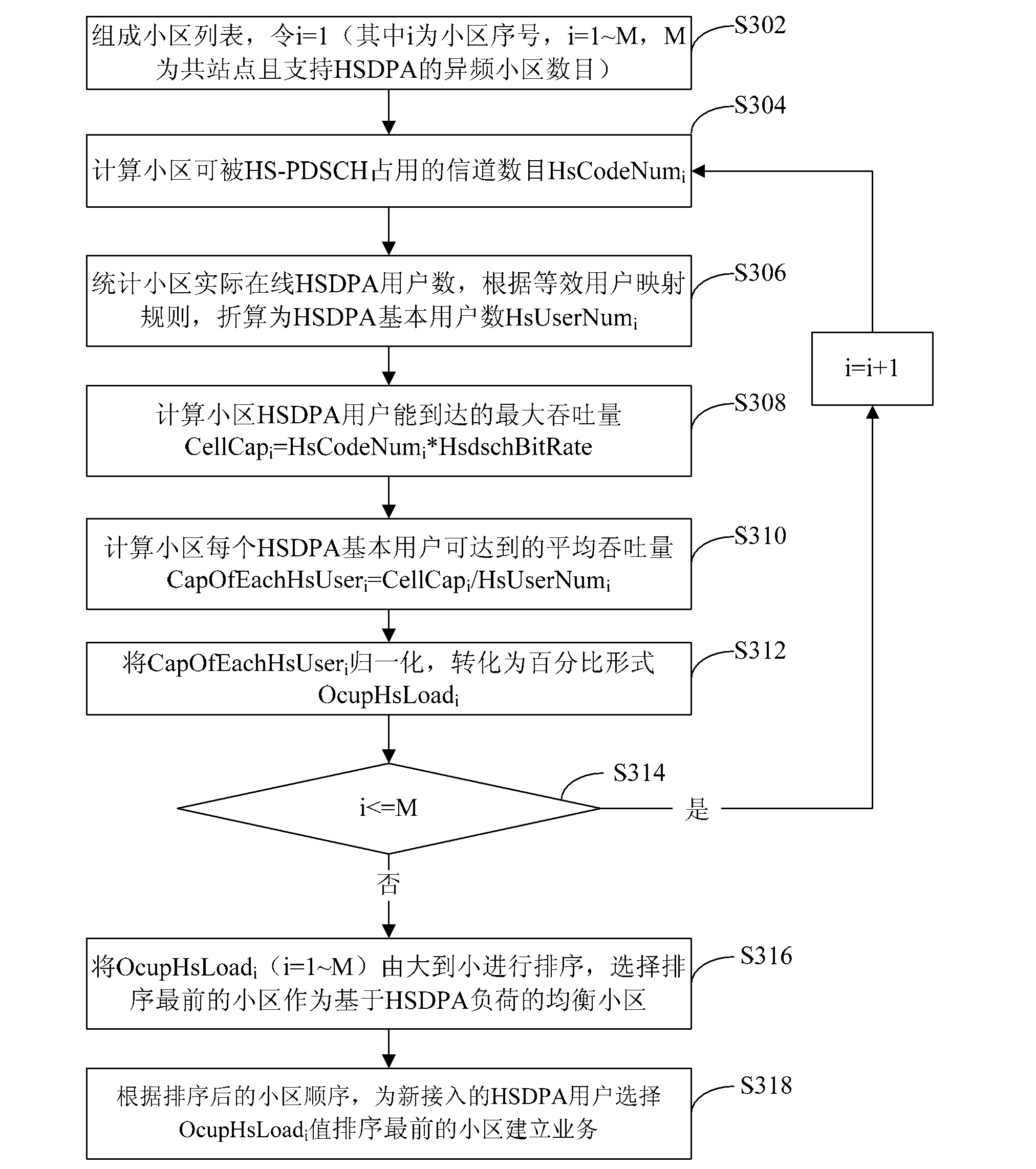
[0040] refer to image 3 , shows a flowchart of steps of a load balancing method according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. In this embodiment, multiple cells that support HSDPA and co-site are organized into a cell list.
[0041] The load balancing method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0042] Step S302: In the list of cells that support HSDPA and co-site, set i=1 (i is the serial number of the cell, i=1~M, and M is the number of inter-frequency cells that are co-sited)
[0043] That is, i represents the serial number of the current cell among multiple cells.
[0044] Step S304: Count the number of SF16 channels HsCodeNum that can be occupied by HS-PDSCH in the current cell i , where non-HS-PDSCH occupied code channels use SF128 as the statistical granularity (one SF16 channel is equivalent to occupying eight SF128 channels), then:
[0045]
[0046] in, Indicates rounding down.
[0047] Step S306: Count the number of HSDPA basic users onl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com