System and method for optimal load planning of electric vehicle charging
A technology for optimal planning and electric vehicles, applied in the direction of electric vehicle charging technology, electric vehicles, charging stations, etc., can solve the problems of huge peak power loads and transients in the transmission network of public utilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
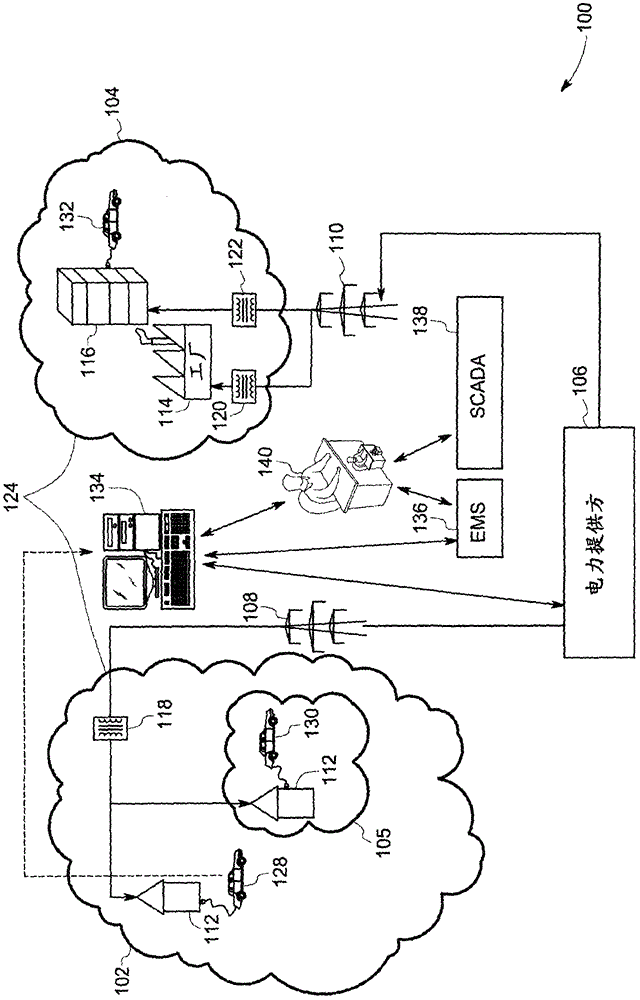
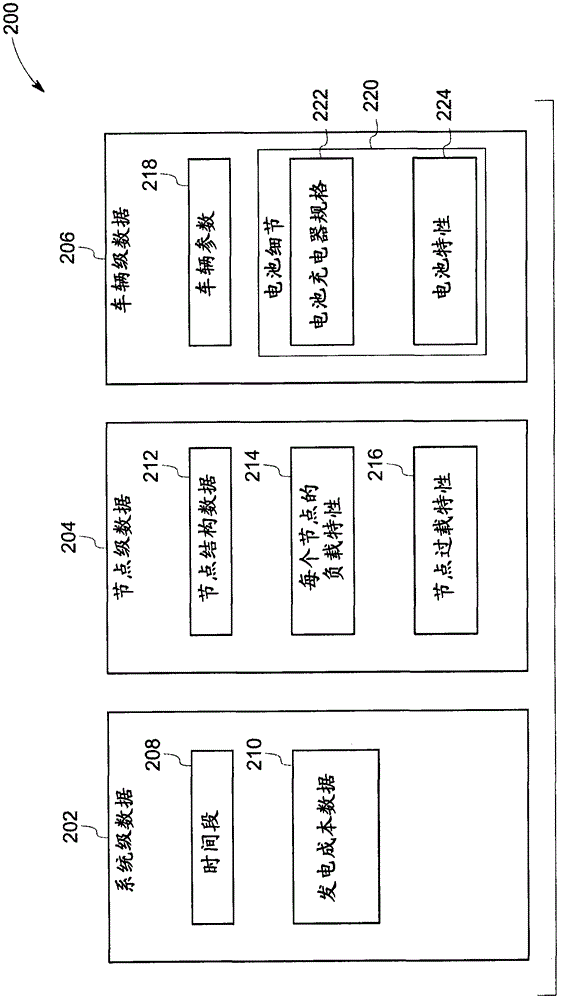
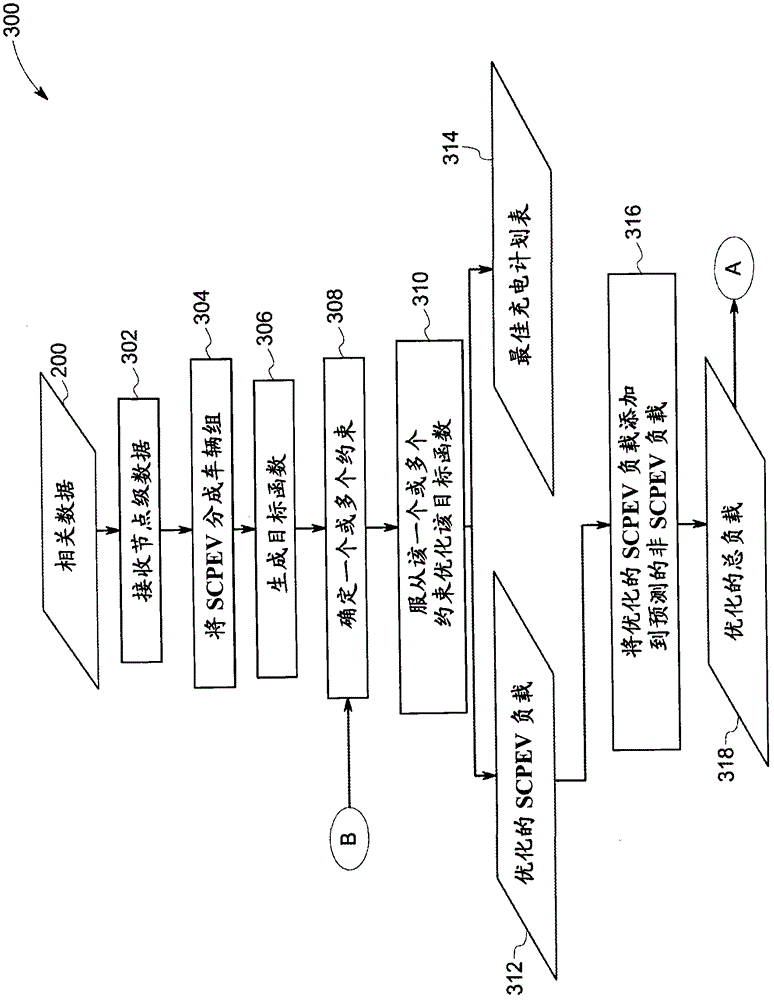
[0011] As discussed in detail below, embodiments of the present systems and techniques can plan optimized load and optimal charging schedules for smart charging plug-in electric vehicles (SCPEVs). Hereinafter, the terms "optimized load of a smart charging plug-in electric vehicle (SCPEV)" and "optimized SCPEV load" will be used interchangeably. The term "optimized SCPEV load" is used herein to refer to the predicted amount of electricity that can be provided to an SCPEV for a specified period of time to minimize costs associated with charging (or other goals determined by the utility) while adhering to one or more constraints. strength. For example, the one or more constraints may include constraints imposed by the owner of the SCPEV, constraints of the utility grid, constraints due to transformer ratings, constraints due to charger and battery specifications, and the like.
[0012] Additionally, the present systems and techniques can generate an optimal charging schedule for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com