Split leather base for car seats, method for manufacturing same, leather for car seats that uses same split leather base, and method for manufacturing same
A technology for car seats and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the field of leather for car seats and its manufacturing, can solve the problems of hard leather, difficult to stretch, heavy weight, insufficient surface properties such as surface smoothness of two-layer leather leather, etc., and achieve a solution heavier weight effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0240] preprocessing
[0241] The cowhide is pickled and preserved directly in the state of being peeled off from the animal.
[0242] Take it out and pass it through an antiseptic.
[0243] Subcutaneous tissue, pieces of meat, fat, etc. are attached to the inner surface of the raw hide, and the meat is shaved using a meat slicing machine to remove these.
[0244] The raw skin that has been softened by adding water is soaked in milk of lime to dissolve and remove the epidermal tissue.
[0245] Neutralize by deliming, add water to dissolve calcium hydroxide through shrinkage, and perform pickling treatment with acid after performing zymolytic softening treatment with enzyme treatment.
Embodiment 2
[0247] Tanning process
[0248] For 160kg of leather weight, add trivalent chromium complex of tanning agent, Cr in 156kg of water 2 (SO 4 ) 38.8kg and baking soda 0.6kg for tanning. The treatment temperature is 38° C., the pH is 3.5, and the treatment time is 12 hours.
Embodiment 3
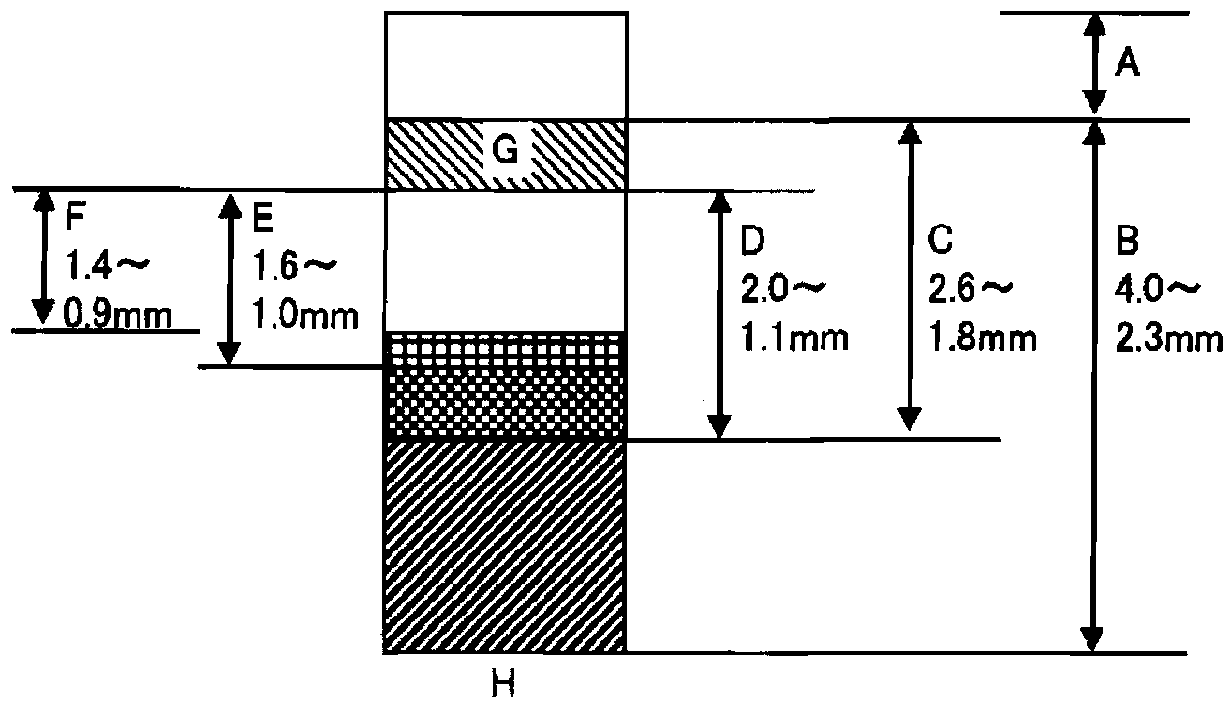
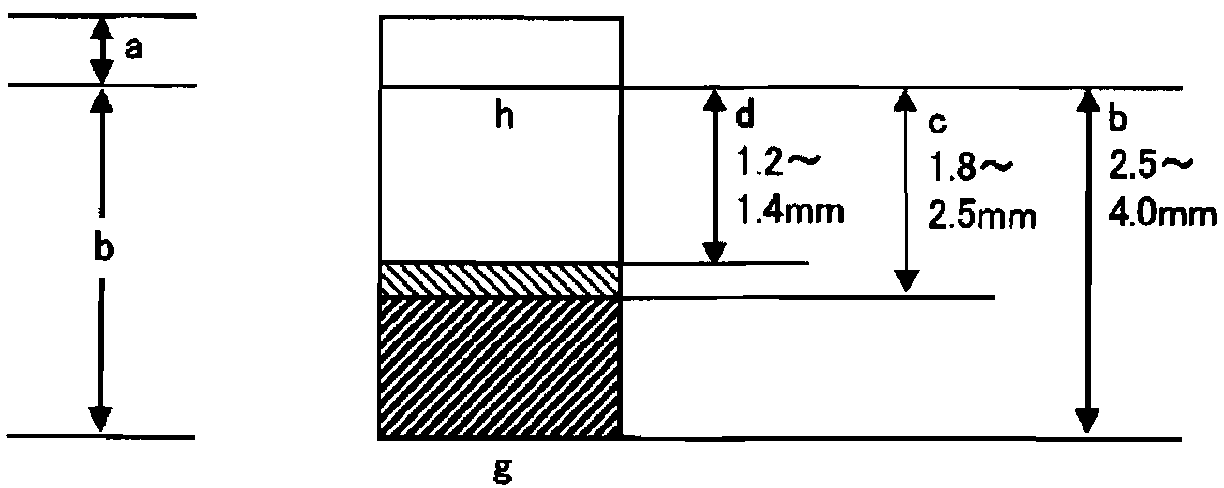
[0250] The obtained leather is divided into grain-containing leather and split leather with a thickness of 2.6 mm using a belt knife machine. , first cut the surface of the grain side with a belt knife, thereby obtaining a split layer of leather with a thickness of 2.5±0.3mm, and then use a shaving machine to cut the flesh side of the split layer to make the thickness 1.5±0.3mm, Further, the grain side is cut by a shaving machine to obtain a split leather of 1.3 ± 0.3 mm (± 0.3 mm is the tolerance range of the belt knife machine and the shaving machine).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com