Photoelectric conversion element and photoelectric conversion device
A technology of photoelectric conversion elements and photoelectric conversion devices, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, electric solid-state devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of image quality degradation, photodiodes are easily affected by optical noise, etc., and achieve the suppression of resolution reduction and reduction Influence and suppress the effect of false detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Deformed example
[0034] 6. Modification 4 (Example of deriving a signal from the lower side (n-type semiconductor layer))
Embodiment
[0036] structure
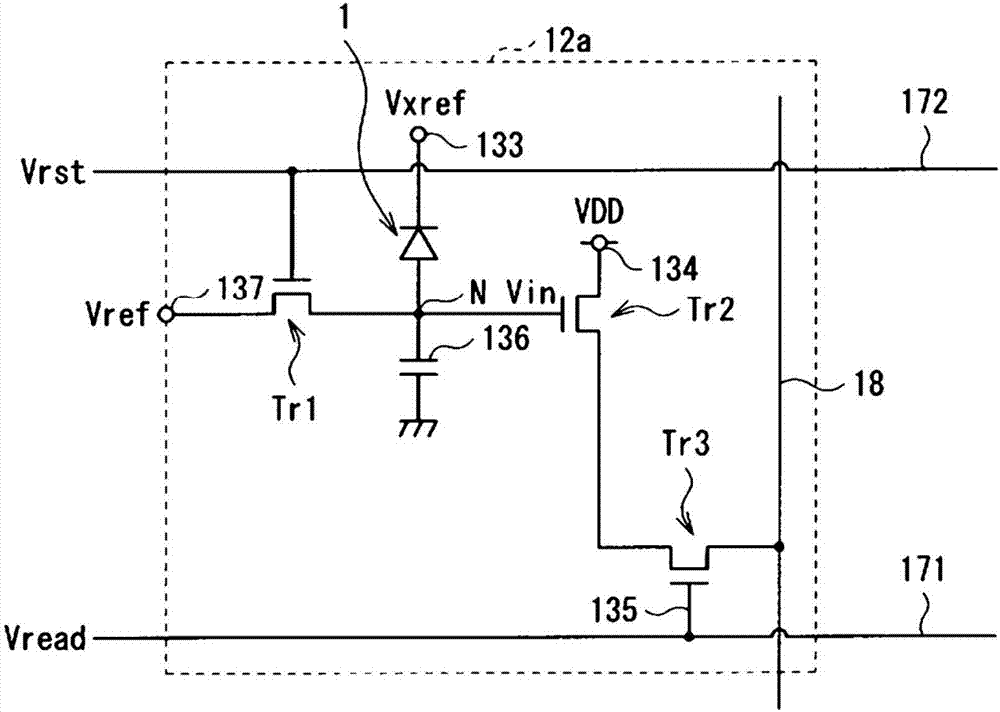
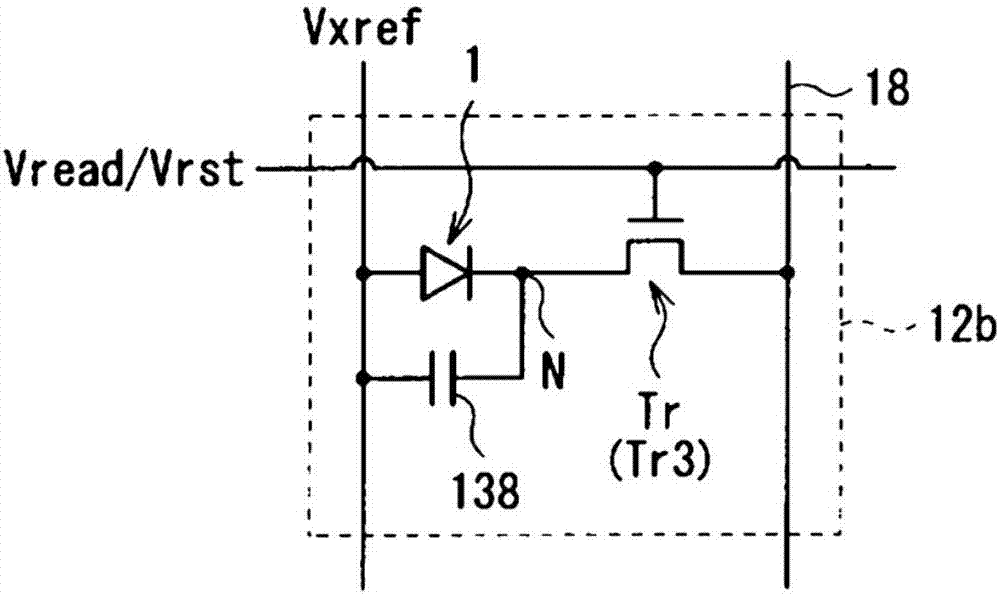
[0037] figure 1 A schematic structure of a photodiode (photodiode 1 ) according to an example of the present invention is shown. The photodiode 1 is a photoelectric conversion element for generating charges (photocharges) corresponding to the light amount of incident light (received light) and storing the generated charges inside it. The photodiode 1 is a PIN photodiode in which an i-type semiconductor layer (intrinsic semiconductor layer) is interposed between a p-type semiconductor layer and an n-type semiconductor layer.
[0038] The photodiode 1 has, for example, a p-type semiconductor layer 122 , an i-type semiconductor layer 123 , and an n-type semiconductor layer 124 stacked in this order from the side of a substrate 11 made of glass or other materials. More specifically, in the photodiode 1 , the p-type semiconductor layer 122 is provided in a selected region on the substrate 11 (more precisely, on an insulating film 121 described later). A first ...
Deformed example 1
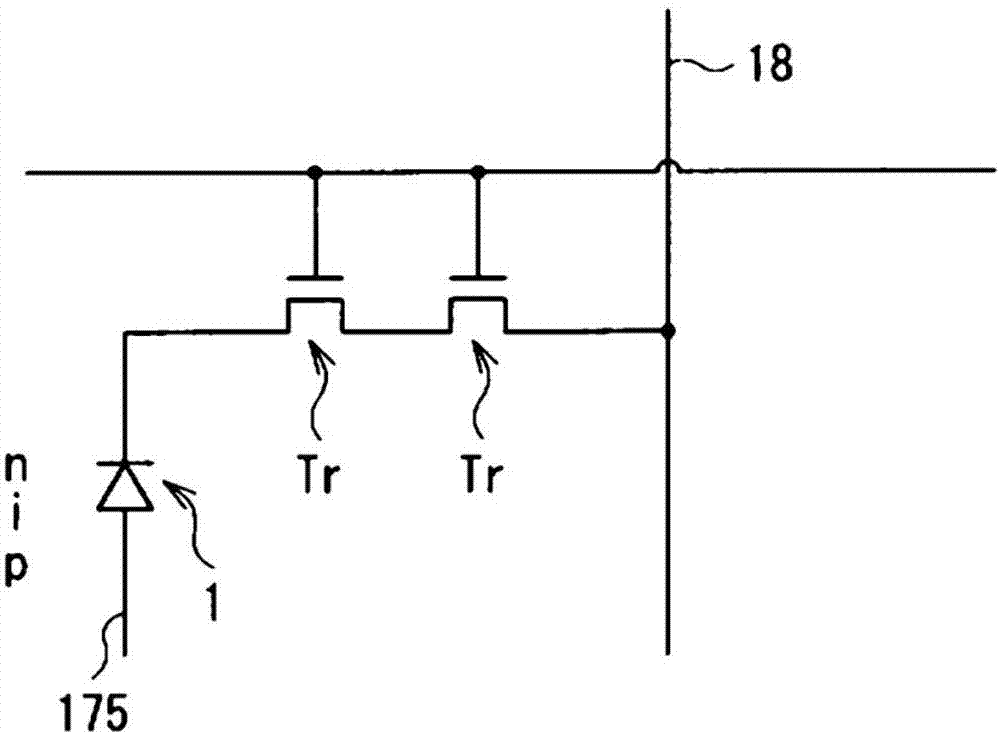
[0071] Figure 7 A cross-sectional structure of a photodiode (photodiode 1A) of this modified example is shown. Like the photodiode 1 in the above-described embodiment, the photodiode 1A is also a PIN type photodiode, and has a p-type semiconductor layer 122C, an i-type semiconductor layer 123 and an n-type semiconductor layer 124 stacked in this order from the substrate 11 side. More specifically, the p-type semiconductor layer 122C is provided in selected regions on the substrate 11 . The first interlayer insulating film 112A is provided to have a contact hole H1 opposite to the p-type semiconductor layer 122C. The second interlayer insulating film 112B having the contact hole H2 is provided on the n-type semiconductor layer 124 and the first interlayer insulating film 112A. The upper electrode 125 is connected to the n-type semiconductor layer 124 through the contact hole H2. Furthermore, a light shielding layer 120B is provided between the p-type semiconductor layer 122...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com