Resistance change memory device and method of operating resistance change memory device
A resistance-variable, storage device technology, applied in static memory, read-only memory, electric solid state devices, etc., can solve the problems of low repetition characteristics, difficulty in resistance, increase, etc., and achieve the effect of improving high-speed operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0045] 1. First Embodiment: A case in which a current is drawn from the bit line by starting the operation of reducing the resistance by lowering the potential of the bit line. A configuration is disclosed in which, at the start of the operation for reducing the resistance, the current flowing through the bit line is switched from the first current to the second current by using two transistors connected in parallel with each other.
no. 2 example
[0046] 2. Second Embodiment: When the bit line current is drawn out similarly to the case of the first embodiment, the switching of the current is performed by using one transistor.
no. 3 example
[0047] 3. Third Embodiment: The operation for reducing the resistance is started by raising the potential of the bit line, thereby applying a current to the bit line.
[0048] 4. Fourth Embodiment: A case where a P-channel transistor is used as an access transistor.
[0049] 5. Variations
[0050] 1. First Embodiment
[0051] The composition of the storage unit
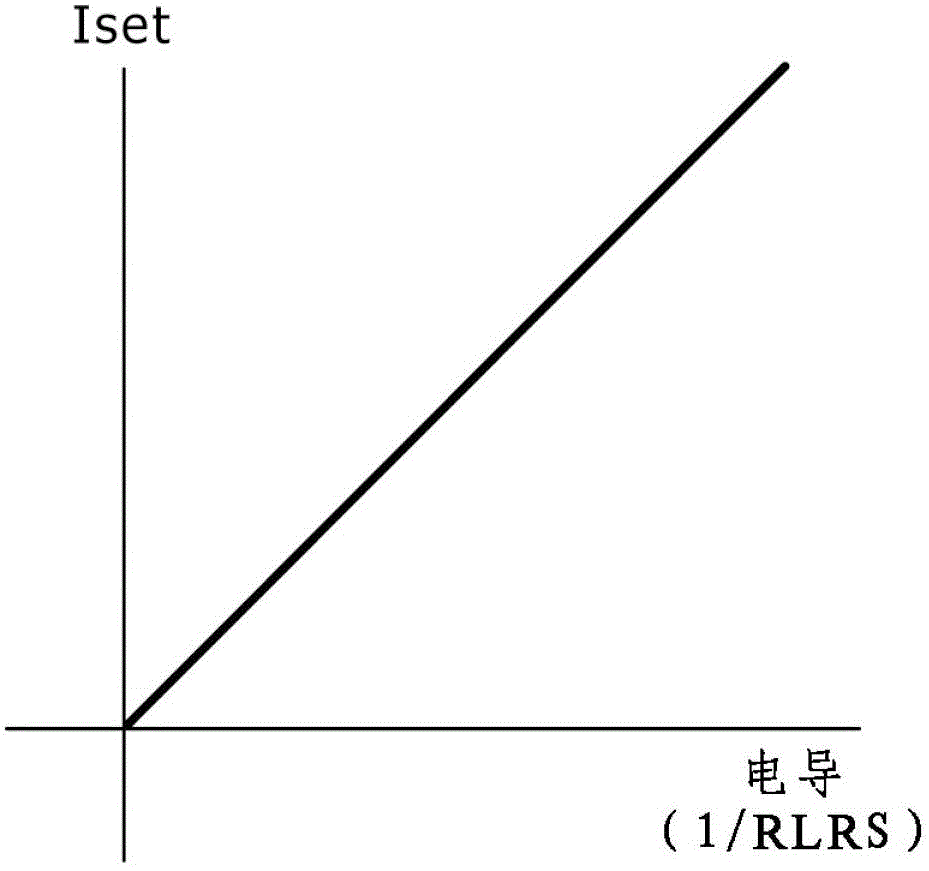
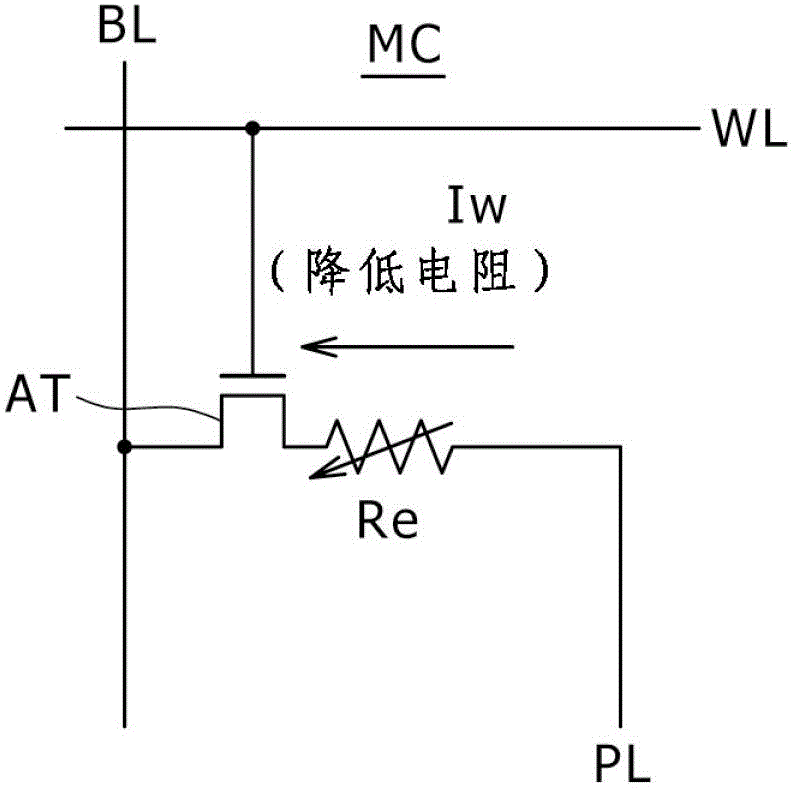
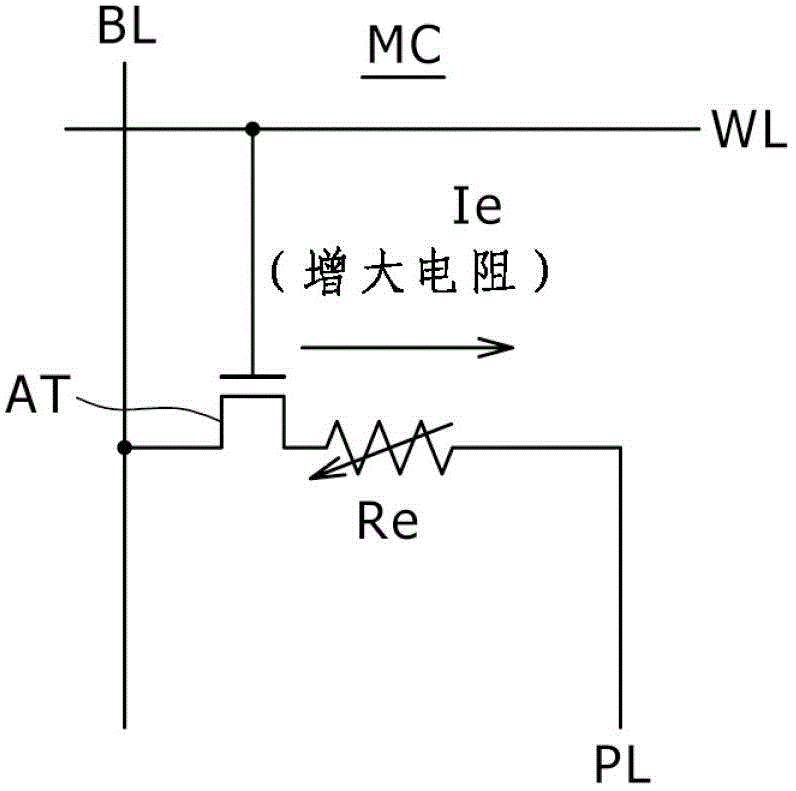
[0052] Figure 2A and Figure 2B Equivalent circuit diagrams of memory cells common to the embodiments of the present invention are respectively shown. It should be noted that although Figure 2A shows the direction of the write current, Figure 2B shows the direction of the erase current, but for Figure 2A and Figure 2B , the memory cell structure itself is the same.
[0053] Figure 2A and Figure 2B The memory cell MC shown in includes one variable resistance element Re and one access transistor AT as "memory elements".
[0054] One end of the variable resistance element Re is connected to the plate P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com