Method for estimating parameters of near-field broadband signal resources by utilizing less array elements
A broadband signal and parameter estimation technology, applied in the field of near-field broadband target positioning technology, can solve the problems of large amount of calculation, sensitive estimated value, and inability to form signal subspace, etc., and achieve the effect of small amount of calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
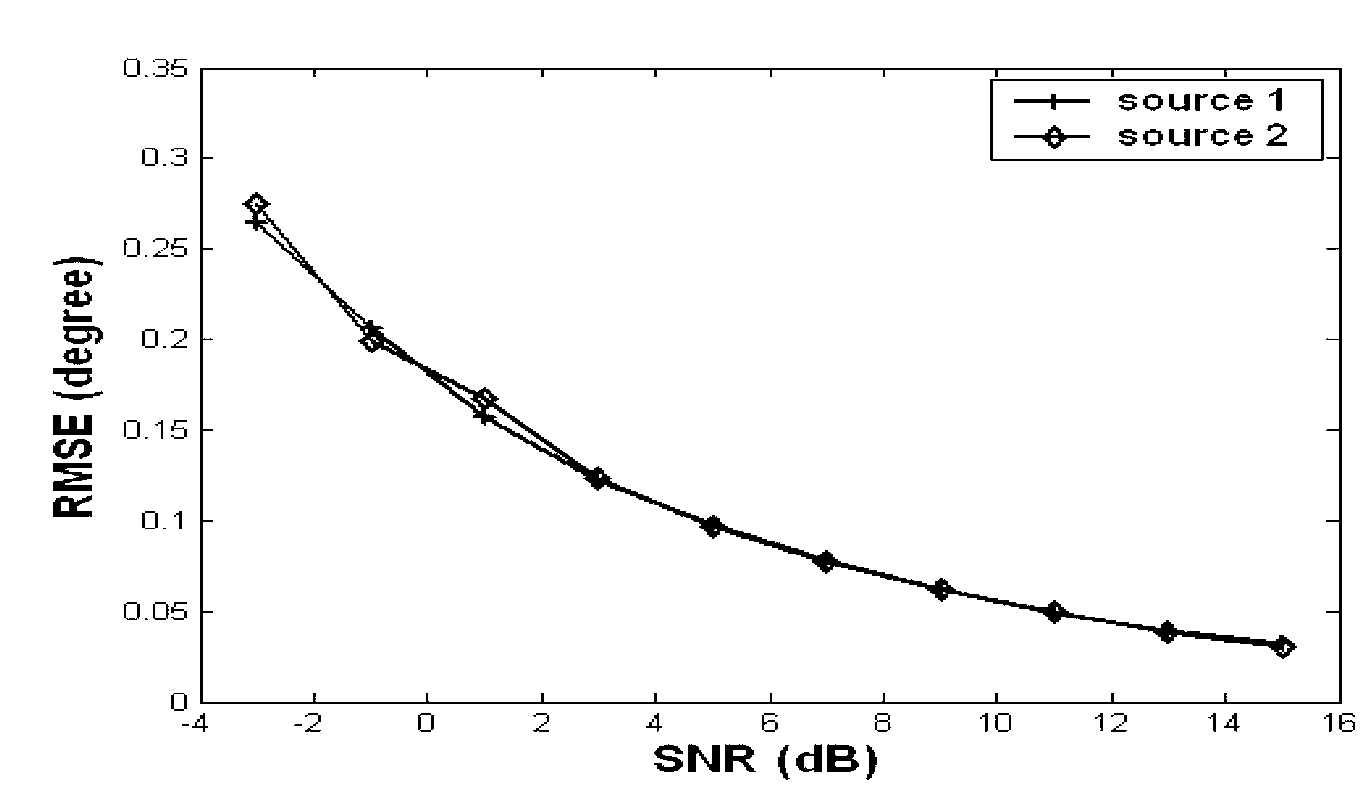
[0029] DOA and distance parameter estimation performance simulation of the present invention:
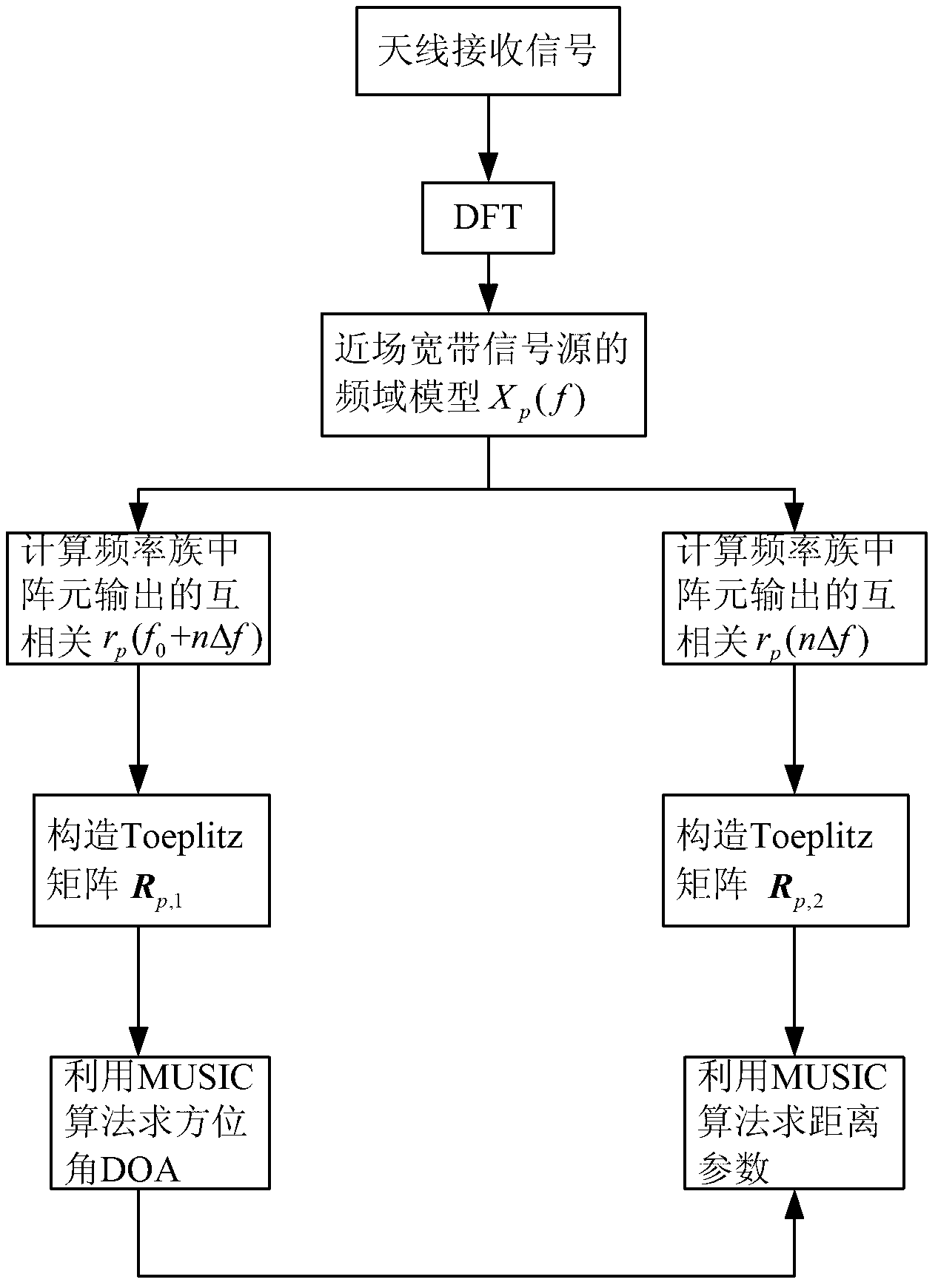
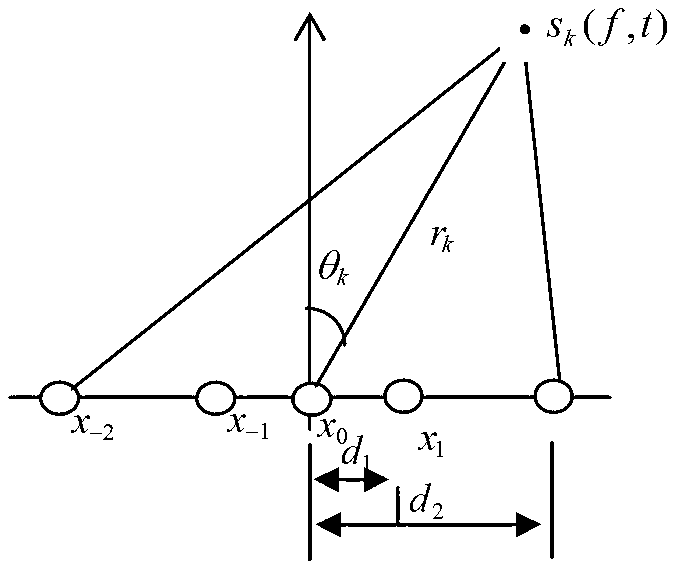
[0030] The method of embodiment 1 is attached figure 1 As shown, the receiving array is as attached figure 2 The non-uniform linear array composed of 5 array elements is shown, and the position of the array center is set as the phase reference point of the receiving array. The azimuth parameters and distance parameters of the two non-correlated near-field broadband signals are [θ 1 ,r 1 ], [θ 2 ,r 2 ], where [θ 1 ,r 1 ] = [-10°,4], [θ 2 ,r 2 ]=[5°,2], broadband signal [f min ,f max ] relative to the center frequency The normalized spectrum range of is [0.8,1.2], that is, its bandwidth is the center frequency f 0 40% of the broadband signal source is divided into 21 frequency groups (2N+1), that is, the maximum number of forward (or reverse) frequency segments is N=10, and the phase difference between adjacent frequency groups is The center array element is the referen...
Embodiment 2
[0076] The estimation ability of the present invention for multiple signal sources:
[0077] The method of embodiment 2 is attached figure 1 As shown, the incident angles of the 5 near-field non-correlated broadband signal sources are [-20°-10°0°10°20°], SNB=5dB, and the incident angles of the 6 near-field non-correlated broadband signal sources are [-30°-20°-10°0°10°20°], SNB=10dB, the rest of the simulation conditions are the same as in Example 1, after changing the simulation conditions, execute the steps of Example 1 again to get Figure 5 ,in Figure 5 (a) and (b) respectively give five and six near-field uncorrelated broadband signal sources whose incident angles are [-20°-10°0°10°20°] and [-30°-20° -10°0°10°20°] pseudospectrum. From Figure 5 It can be seen that the proposed algorithm can estimate near-field broadband signals exceeding the number of array elements, which cannot be achieved by traditional near-field broadband spatial spectrum algorithms.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com